Introduction to Silver Nitrate (AgNO₃)
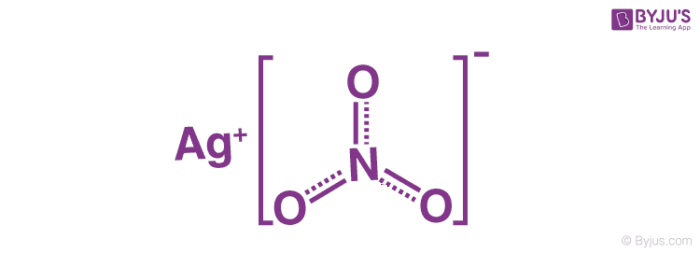
Silver nitrate (AgNO₃) is a chemical compound that is commonly used in chemistry due to its versatile properties. It is an inorganic salt composed of a silver cation (Ag⁺) and a nitrate anion (NO₃⁻).
Silver nitrate is a crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water, making it easy to dissolve and work with in laboratory settings. It is also known for its characteristic white color and is often used as a reagent in various chemical reactions.
One of the notable features of silver nitrate is its ability to react with halogens, specifically with chloride ions (Cl⁻), resulting in the formation of a white, insoluble precipitate called silver chloride (AgCl). This reaction is often used in analytical chemistry for the detection and quantification of chloride ions in a solution.
Silver nitrate is also known for its antimicrobial properties. It has been used as a disinfectant or antiseptic agent for ages, particularly in the treatment of wounds. The silver ions released from the silver nitrate solution have a toxic effect on pathogens, preventing their growth and replication.
In addition to its applications in medical and analytical fields, silver nitrate is widely used in photography as a light-sensitive material. It reacts with light to form metallic silver, which creates the desired image on photographic films and papers. This was one of the earliest uses of silver nitrate and contributed significantly to the development of photography as we know it today.
Despite its many uses, silver nitrate is a toxic substance and should be handled with care. It can cause skin and eye irritations upon contact and can be harmful if ingested or inhaled. Proper safety precautions should always be taken when working with silver nitrate in the laboratory.
In conclusion, silver nitrate is a versatile compound that finds applications in various fields of chemistry. Its ability to form insoluble precipitates, antimicrobial properties, and light-sensitive nature make it a valuable reagent in different chemical processes. Nonetheless, safety should always be a top priority when handling silver nitrate.
Chemical Composition of Silver Nitrate
The chemical composition of silver nitrate is AgNO3. It consists of one silver atom (Ag), one nitrogen atom (N), and three oxygen atoms (O).
Properties and Characteristics of Silver Nitrate
Silver nitrate (AgNO3) is a chemical compound composed of silver, nitrogen, and oxygen. It is a versatile and important chemical with several properties and characteristics:
1. Appearance: Silver nitrate is a white, crystalline solid at room temperature.
2. Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, producing a clear solution. It is also soluble in ethanol and acetone.
3. Reactivity: Silver nitrate is a strong oxidizing agent and is sensitive to light. It decomposes upon exposure to light or organic matter, turning grey or black due to the formation of elemental silver.
4. Toxicity: Silver nitrate is toxic and can cause burns upon skin contact. It can cause eye and respiratory irritation and is harmful if ingested.
5. Precipitation Reactions: When silver nitrate is added to a solution containing chloride ions (Cl-), bromide ions (Br-), or iodide ions (I-), it forms insoluble silver chloride (AgCl), silver bromide (AgBr), or silver iodide (AgI), respectively. These reactions are often used in qualitative analysis to detect the presence of these ions in a solution.
6. Uses:
- Photography: Silver nitrate is used in black and white photography to sensitize emulsions to light.
- Medical Applications: It has antiseptic properties and has been historically used in the treatment of wounds and burns.
- Chemical Reagent: Silver nitrate is used as a reagent in various chemical reactions, including the preparation of other silver compounds.
- Laboratory Testing: It is used in laboratories for various tests, such as the detection of halide ions.
- Mirrors: Silver nitrate is involved in the production of mirrors through a process called silvering, where a thin layer of silver is deposited on glass.
7. Light Sensitivity: As mentioned earlier, silver nitrate is sensitive to light and decomposes upon exposure. This property is utilized in various chemical and photographic processes.
8. Stability: While silver nitrate is stable under normal conditions, it should be stored in a dark, cool, and dry place to prevent decomposition due to light exposure.
It’s important to handle silver nitrate with care due to its reactivity and toxicity. Proper safety precautions, including the use of gloves and protective eyewear, should be taken when working with this compound.
Applications and Uses of Silver Nitrate in Chemistry
Silver nitrate (AgNO3) is a versatile compound that is widely used in chemistry for various applications. Here are some of the common uses of silver nitrate:
1. Laboratory Reagent: Silver nitrate is commonly used as a reagent in laboratory experiments, such as in titrations and precipitation reactions.
2. Detection of Chloride Ions: Silver nitrate is used to detect the presence of chloride ions (Cl-) in a solution. When silver nitrate is added to a solution containing chloride ions, a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) is formed.
3. Photography: Silver nitrate is used in traditional black and white photography as a component of the light-sensitive emulsion on photographic film. It reacts with light to form silver metal, which creates the image.
4. Silver Mirror Reaction: Silver nitrate can be used to perform the silver mirror reaction, which involves the reduction of silver ions to form a reflective silver coating on the inside of a glass container.
5. Silver Plating: Silver nitrate is used for electroplating to produce a layer of silver on various metals objects. This is commonly used to improve the appearance, corrosion resistance, and conductivity of objects like jewelry, cutlery, and electrical connectors.
6. Medicinal Uses: Silver nitrate has antimicrobial properties and is used in some medical applications, such as in wound dressings and eye drops to prevent bacterial infections.
7. Organic Chemistry Reactions: Silver nitrate is utilized in various organic chemistry reactions. It can be used as an oxidizing agent, for example, in the preparation of aldehydes and ketones. It is also used in the Tollens’ test to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones based on the formation of a silver mirror.
8. Dye and Ink Production: Silver nitrate is used in the production of dyes and inks, particularly for staining glass and porcelain.
These are just a few examples of the many applications and uses of silver nitrate in chemistry.
Safety and Precautions When Handling Silver Nitrate
Handling silver nitrate requires careful attention to safety precautions due to its reactivity, toxicity, and potential hazards. Here are some important safety guidelines to follow when working with silver nitrate:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Wear gloves made of nitrile or latex when handling silver nitrate to prevent skin contact.
- Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from splashes.
- Wear a lab coat or appropriate protective clothing to prevent contact with skin and clothes.
2. Ventilation:
- Work in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to prevent inhalation of fumes or vapors.
- Avoid working in confined spaces without adequate ventilation.
3. Avoid Contamination:
- Use clean and dry utensils and equipment to handle silver nitrate.
- Do not touch your face, especially your eyes and mouth, while working with silver nitrate.
- Avoid contamination of solutions; use clean and dry containers and utensils.
4. Storage:
- Store silver nitrate in a tightly sealed, light-resistant container in a cool, dry place away from organic materials and reducing agents.
- Keep silver nitrate away from direct sunlight or sources of intense light, as it is sensitive to light and can decompose.
5. Handling and Spills:
- Handle silver nitrate solutions with care to prevent spills.
- In case of a spill, neutralize the spilled solution with sodium bicarbonate or another appropriate neutralizing agent.
- Clean up spills immediately, wearing appropriate protective equipment.
6. First Aid:
- In case of skin contact, wash the affected area thoroughly with plenty of water and soap. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
- In case of eye contact, rinse the eyes immediately with gently flowing water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention promptly.
- If silver nitrate is ingested, seek medical attention immediately. Do not induce vomiting unless instructed by medical personnel.
7. Disposal:
- Dispose of silver nitrate and its solutions as hazardous waste according to local regulations. Do not pour them down the drain.
8. Training:
- Ensure that personnel handling silver nitrate are trained in proper handling techniques and are aware of the potential hazards associated with the compound.
Always refer to the safety data sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer for specific information about the safe handling, storage, and disposal of silver nitrate.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.