Introduction to Stearic Acid
Stearic acid is a type of fatty acid that plays a significant role in chemistry. It is a saturated fatty acid, meaning it contains no double bonds in its carbon chain. As a result, stearic acid has a long, straight carbon chain that is hydrophobic (repels water).
Stearic acid is commonly found in various natural sources, including animal and vegetable fats. It is a solid substance at room temperature and has a waxy texture. Due to its stability, stearic acid has a wide range of applications in different industries.
In chemistry, stearic acid is widely used as a surfactant and emulsifying agent. Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension between two substances, enabling them to mix or spread evenly. Stearic acid can function in this capacity because its structure allows it to interact with both water and oil molecules. This property is particularly valuable in various cleaning and personal care products, such as soaps, detergents, and cosmetics.
Stearic acid also finds use as a lubricant in industrial processes. Its long carbon chain allows it to form a protective layer on surfaces, reducing friction and wear between moving parts. This property makes stearic acid an essential component in the production of various lubricants, greases, and coatings.
Furthermore, stearic acid is involved in the synthesis of other chemicals. It serves as a raw material for the production of esters, which are widely used in perfumes, flavors, and plasticizers. Stearic acid derivatives, such as stearates, are employed as additives in many industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
In summary, stearic acid is a versatile compound in chemistry. Its unique structure and properties make it useful as a surfactant, lubricant, and raw material for various processes. With its wide range of applications, stearic acid contributes significantly to the field of chemistry and numerous industries.
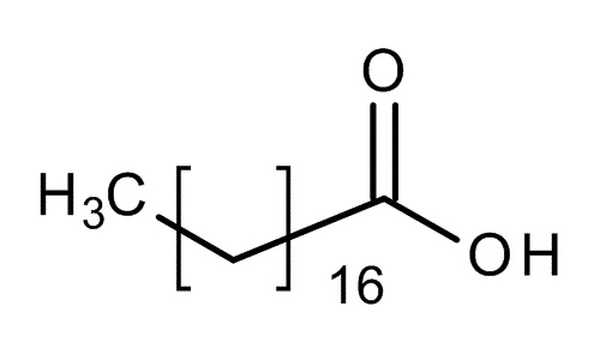
Chemical Formula and Structure of Stearic Acid
The chemical formula of stearic acid is C18H36O2.
Its structure consists of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain with 18 carbon atoms bonded together in a linear fashion. At one end of the chain, there is a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached which makes it an organic acid.
Each carbon atom in the chain is bonded to two hydrogen atoms, except for the terminal carbon atom bonded to the carboxyl group which is bonded to three oxygen atoms.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Stearic Acid
Physical properties of stearic acid:
– Stearic acid appears as a white, waxy solid.
– It has a melting point of around 69°C, which makes it a solid at room temperature.
– It has a molecular weight of 284.48 g/mol.
– Stearic acid is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether.
– It has a characteristic odor.
Chemical properties of stearic acid:
– Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2.
– It undergoes esterification reactions with alcohols to form stearates, which are used as emulsifiers and lubricants.
– It can undergo saponification reactions with bases to form soaps, which are used in various cleaning and cosmetic products.
– Stearic acid can react with strong oxidizing agents to form water and carbon dioxide.
– It can be hydrogenated to produce stearic acid derivatives such as stearates, which are commonly used in the production of candles, plastics, and rubber.
– Under certain conditions, stearic acid can undergo decarboxylation reactions to form fatty alcohols or alkanes.
– It is combustible and can undergo combustion reactions to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Uses of Stearic Acid
Stearic acid is a long-chain fatty acid that is commonly used in various chemical applications. Some of the uses of stearic acid in chemistry include:
1. Emulsifier: Stearic acid is frequently used as an emulsifier to create stable emulsions, where it helps to disperse oil droplets in water or vice versa. This property is useful in industries such as cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Surfactant: Stearic acid acts as a surfactant, reducing the surface tension of liquids and enabling them to spread more easily. This property is applied in products like detergents, soaps, and cleaning agents.
3. Lubricant: With its high melting point, stearic acid is used as a lubricant in various industries, including metalworking and plastic processing. It helps reduce friction and wear between moving parts.
4. Thickener: Stearic acid can thicken or increase the viscosity of liquid formulations, making it suitable for use in creams, lotions, and ointments in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries.
5. Mold release agent: Due to its hydrophobic nature, stearic acid is used as a mold release agent in various molding processes, including rubber and plastic manufacturing, where it helps parts detach easily from molds.
6. Candle production: Stearic acid is commonly used in candle making as it helps to increase the hardness and stability of the wax, allowing candles to burn slowly and evenly.
7. Coating and binding agent: Stearic acid is used as a coating agent in industries like rubber, textiles, and paper, where it provides a protective layer and improves durability. It is also utilized as a binding agent in the production of pressed powders and tablets.
8. Metal soap production: Stearic acid is a key ingredient in the production of metal soaps, which are used as catalysts, stabilizers, and flow agents in various chemical reactions and processes.
9. Esters production: Stearic acid is often used to produce esters, which are important compounds used in numerous industries, including cosmetics, flavors, fragrances, and plastics.
It is worth noting that stearic acid is a versatile compound, and its applications extend beyond chemistry into various other fields such as food, medicine, and personal care.
Safety and Health Effects of Stearic Acid
Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid that is commonly found in various foods, cosmetics, and industrial products. It is generally recognized as safe for consumption by regulatory agencies, such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and has been extensively studied for its safety and health effects. Here are some key points regarding the safety and health effects of stearic acid:
1. Safety for Consumption: Stearic acid is considered safe for consumption in food products. It is commonly used as a food additive and can be found in items such as chocolate, margarine, and baked goods. Regulatory agencies have approved its use as a food additive, and it is included on the FDA’s Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) list.
2. Digestibility: Stearic acid is easily digested by the human body and is metabolized like other dietary fats. It is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol, which can be absorbed and utilized by the body. It does not accumulate in the tissues or have any adverse effects on the digestive system.
3. Cardiovascular Health: Research suggests that stearic acid may have a neutral or even beneficial effect on cardiovascular health. Unlike most saturated fats, stearic acid does not raise levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. Instead, it is thought to have a more neutral effect on blood lipid levels.
4. Skin and Cosmetic Applications: In cosmetic products, stearic acid is commonly used as an emulsifier, thickening agent, or lubricant. It has a low irritation potential and is generally well-tolerated by the skin. However, sensitive individuals may experience mild irritations or allergies, so patch testing is recommended for new products.
5. Industrial Applications: Stearic acid is also used as a lubricant in various industrial processes, such as the production of rubber and plastics. It can help improve the processing and flowability of materials. In these applications, it poses minimal risks to human health when handled properly.
6. MSDS Precautions: When handling pure stearic acid in high concentrations, precautions should be taken as outlined in the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). These precautions may include wearing protective gloves, goggles, and avoiding direct contact with the eyes or prolonged skin exposure. Consult the specific MSDS provided by the manufacturer or supplier for detailed safety recommendations.
In conclusion, stearic acid is considered safe for consumption and has a low toxicity profile. It is widely used in various industries and food products without significant adverse health effects. However, as with any substance, it is important to use stearic acid in accordance with safety guidelines and follow appropriate precautions when handling concentrated forms.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.