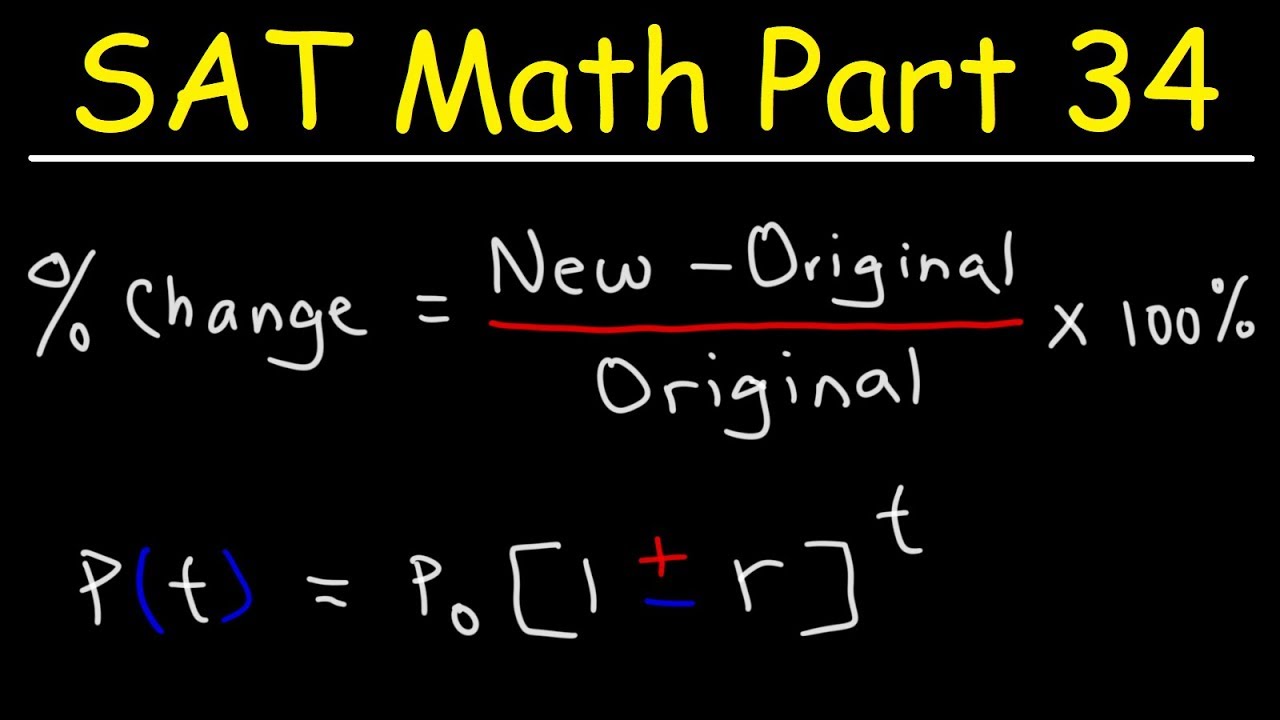Introduction
Introduction: Population
Population refers to the total number of individuals living in a particular area, whether it be a country, city, or region. It provides a measure of the size and density of the human inhabitants within a defined geographical boundary.
Understanding population dynamics is crucial for various reasons, including planning social services, infrastructure development, resource allocation, and policy formulation. The study of population covers a range of aspects, such as birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, age structure, and demographic trends.
Population growth is a key concern for many countries, as it affects economic development, environmental sustainability, and social cohesion. Rapid population growth can strain resources, lead to overcrowding, and create challenges in meeting the needs of the population. Conversely, declining populations may face issues related to an aging workforce, reduced economic productivity, and an increased burden on social support systems.
Demographic factors such as fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration play significant roles in population changes. Governments and organizations often employ measures to track and manage population dynamics, aiming to achieve sustainable development and improve the quality of life for their citizens.
In this article, we will explore various aspects of population, including its definition, factors affecting population growth, population distribution, and the impact of population changes on society and the environment.
Definition of Population in Mathematics
In mathematics, a population refers to a set or collection of individuals, objects, or elements that are being studied or analyzed. The population can be finite, meaning it has a definite number of members, or infinite, indicating that the number of members is uncountable. In statistical studies, the population is the entire group from which a sample is obtained for analysis and inference. It represents the larger group to which the findings from the sample are generalized.
Examples and Applications of Population in Mathematics
Population is a concept in mathematics that refers to a set of individuals or objects of interest. It can be applied in various areas of mathematics and has several examples and applications.
1. Statistics: In statistics, a population represents the entire group of individuals or objects that a researcher wants to study. For example, if a researcher is interested in studying the average height of all adults in a particular city, the population would consist of all adults in that city. By collecting data from a sample of the population, statisticians can make valid inferences and draw conclusions about the entire population.
2. Probability: In probability theory, a population can refer to the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment or random variable. For instance, if you are flipping a fair coin, the population would consist of the two possible outcomes: heads or tails. Understanding the population is essential for calculating probabilities and determining the likelihood of certain events occurring.
3. Number theory: In number theory, a population can refer to a set of numbers with specific properties or characteristics. For example, the population of prime numbers consists of all positive integers greater than 1 that are divisible only by 1 and themselves. Analyzing the properties and behavior of populations of numbers is a fundamental aspect of number theory.
4. Graph theory: In graph theory, a population can represent a set of vertices or nodes in a graph. For instance, considering a social network, the population could be the users of the network, and the connections between them would be the edges. Studying populations in graph theory involves analyzing the structure and properties of networks, such as finding the most connected individual or identifying clusters of closely connected nodes.
5. Mathematical modeling: In mathematical modeling, populations are often used to represent quantities that change over time. Examples include population growth models, where the population represents a group of individuals that increase or decrease in size. These models are used in various fields, such as biology (population dynamics), physics (particle populations), and economics (consumer populations), to understand and predict the behavior of complex systems.
In all these examples and applications, understanding and analyzing populations in mathematics allow researchers and practitioners to gain insights, make predictions, and solve problems in a wide range of disciplines.
Key Properties and Concepts Related to Population
Some key properties and concepts related to population are:
1. Population size: This refers to the total number of individuals in a population at a given time. It provides an estimate of the total population present in a particular area.
2. Population density: This is the number of individuals per unit area or volume. It gives an idea of how crowded or dispersed a population is within a given space.
3. Population distribution: This refers to the spatial pattern or arrangement of individuals within a population. It can be clumped, random, or evenly spaced.
4. Birth rate: This is the number of live births per thousand individuals in a population over a given period of time. It provides an indication of the population’s potential for growth.
5. Death rate: This is the number of deaths per thousand individuals in a population over a given period of time. It reflects the population’s mortality rate and can influence population change.
6. Immigration: This is the movement of individuals into a population from another population or geographic area. It can contribute to population growth and diversity.
7. Emigration: This is the movement of individuals out of a population to another population or geographic area. It can lead to population decline and impact the characteristics of the population remaining.
8. Population growth rate: This is the rate at which the population size of a given area or population changes over time. It is influenced by birth rate, death rate, immigration, and emigration.
9. Age structure: This refers to the distribution of individuals in a population across different age groups. It can provide insights into population dynamics, such as the potential for future growth or decline.
10. Population pyramid: This is a graphical representation of the age and sex structure of a population. It can show the percentage or proportion of males and females in different age groups, providing information about the population’s demographic composition.
Understanding these properties and concepts related to population is crucial for studying and managing population dynamics, predicting future population trends, and making informed decisions regarding resource allocation, public policies, and social development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the population refers to the total number of individuals living in a specific area or region. It is an essential factor in various aspects of society, including government planning, resource allocation, and socio-economic development. Understanding population dynamics, such as growth rates, age distribution, and migration patterns, is crucial in addressing challenges related to healthcare, education, employment, and infrastructure. The accurate assessment and projection of population trends contribute to informed decision-making and the creation of effective policies to ensure the well-being and sustainable development of a population.
Topics related to Population
Identifying a sample and population | Study design | AP Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
Identifying a sample and population | Study design | AP Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH – YouTube
Population growth rate based on birth and death rates | Ecology | AP Biology | Khan Academy – YouTube
Population growth rate based on birth and death rates | Ecology | AP Biology | Khan Academy – YouTube
Modeling population with simple differential equation | Khan Academy – YouTube
Modeling population with simple differential equation | Khan Academy – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH || FINDING THE RATE – YouTube
POPULATION GROWTH || FINDING THE RATE – YouTube
Percent Increase & Decrease, Population Growth Problems – SAT Math Part 34 – YouTube
Percent Increase & Decrease, Population Growth Problems – SAT Math Part 34 – YouTube
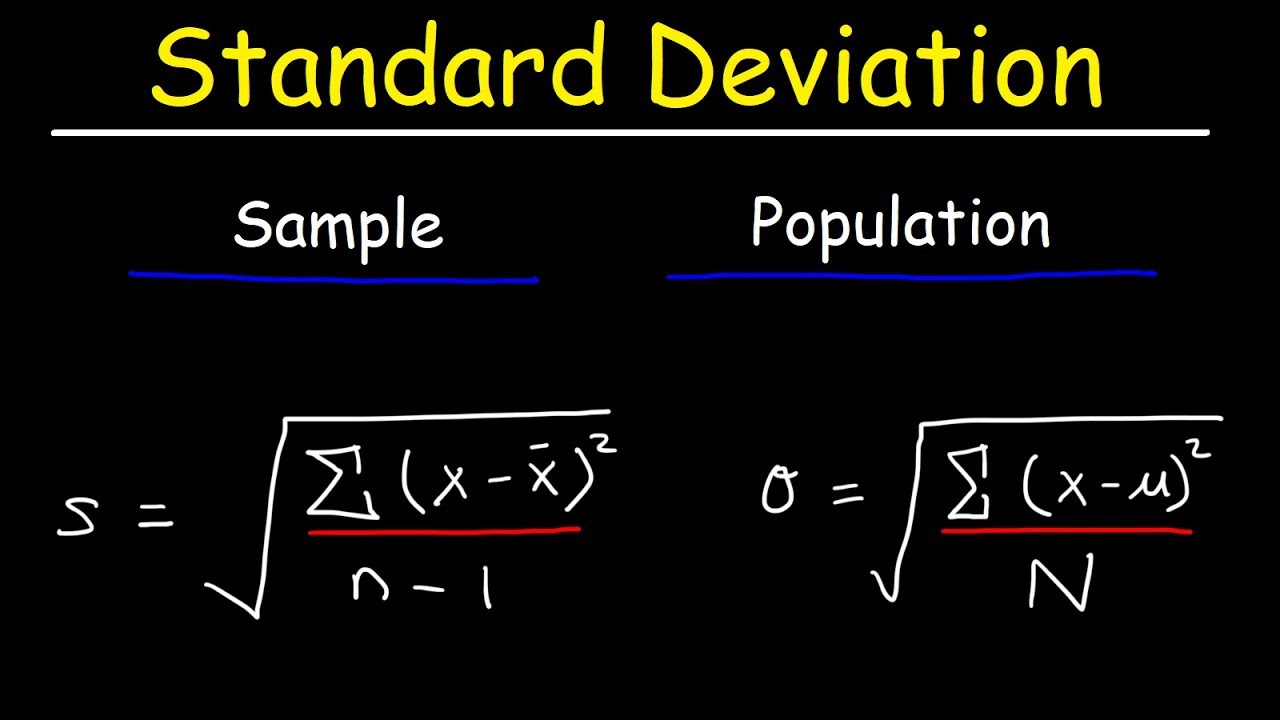
Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean – YouTube
Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean – YouTube
Exponential and logistic growth in populations | Ecology | Khan Academy – YouTube
Exponential and logistic growth in populations | Ecology | Khan Academy – YouTube
Human Population Through Time (Updated for 2023) – YouTube
Human Population Through Time (Updated for 2023) – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.