Introduction
Chemistry is the scientific discipline that studies matter and the changes it undergoes. It is a branch of physical science that explores the properties, composition, structure, behavior, and transformations of different substances.
In the field of chemistry, scientists investigate the fundamental building blocks of matter, known as atoms, and how they combine and interact to form molecules and compounds. This knowledge allows us to understand and predict the behavior and properties of various substances in different conditions.
Chemistry plays a vital role in numerous aspects of our daily lives. It is integral to understanding the composition and reactions of natural and synthetic materials, such as medications, food, textiles, and plastics. Chemists also strive to develop new materials and technologies with desirable properties, ranging from advanced materials for electronics and energy storage to environmentally friendly solutions for waste management and pollution control.
Additionally, chemistry has significant implications in fields such as medicine, environmental science, forensic science, and materials science. Chemical research and innovation have led to breakthroughs in drug discovery, environmental monitoring and remediation, crime investigation, and the development of new materials for various industries.
Overall, chemistry is a diverse and dynamic discipline that encompasses a wide range of topics and applications. Through its study, chemists aim to deepen our understanding of the natural world and contribute to the betterment of society by addressing various challenges we face today.
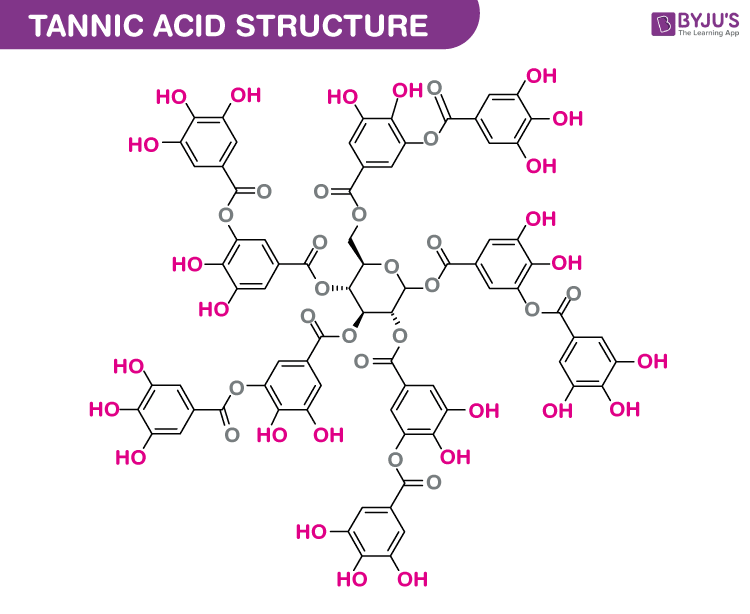
Properties of Tannic Acid
Tannic acid, also known as tannin, is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound found in various plants. It has several properties and uses, both in industrial applications and traditional medicine. Here are some of its key properties:
- Chemical Structure: Tannic acid is a type of polyphenol with a specific chemical structure. It is a large, complex molecule composed of glucose units that are esterified with gallic acid.
- Astringency: One of the most well-known properties of tannic acid is its astringent taste. It binds to and precipitates proteins in the saliva and mucous membranes, causing a dry and puckering sensation in the mouth.
- Antioxidant: Tannic acid exhibits antioxidant properties, which means it can neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Free radicals are associated with various diseases and the aging process.
- Metal Chelation: Tannic acid can chelate (bind to) metal ions, such as iron and copper. This property is often utilized in the preservation of certain foods and beverages.
- Preservative: Due to its ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, tannic acid is used as a natural preservative in food and beverages. It can also be found in some cosmetics and personal care products.
- Medicinal Uses: Tannic acid has been used in traditional medicine to treat minor burns, insect bites, and skin irritations due to its astringent and antiseptic properties. It is also sometimes used in the treatment of diarrhea.
- Leather Tanning: Historically, tannic acid has been widely used in the process of tanning leather. It forms a stable complex with the collagen proteins in animal hides, making the leather more durable and resistant to decomposition.
- Dyeing: Tannic acid is used as a mordant in natural dyeing processes. It helps natural dyes bind to the fabric fibers, making the color more stable and vibrant.
- Wine and Tea: Tannic acid is naturally present in grapes and tea leaves. It contributes to the astringency of red wines and certain types of teas.
- Safety: Tannic acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when consumed in moderate amounts through food and beverages. However, excessive consumption can lead to digestive issues and might interfere with the absorption of certain minerals like iron.
It’s important to note that while tannic acid has various applications, its usage should be appropriate and in accordance with safety guidelines and regulations.
Uses of Tannic Acid
Tannic acid is a naturally occurring polyphenol compound found in a variety of plants, such as oak bark, tea leaves, and fruits. In chemistry, tannic acid has several important uses:
1. Precipitation reactions: Tannic acid can form complexes with metal ions, leading to the precipitation of insoluble metal tannates. This property is utilized in analytical chemistry to separate and detect certain metal ions.
2. Reducing agent: Tannic acid can act as a reducing agent by donating electrons to other compounds. This property is utilized in organic chemistry to reduce certain functional groups, such as nitro groups (NO2), to corresponding amines (NH2).
3. Adhesive properties: Tannic acid has the ability to form strong bonds with proteins and other materials, making it useful in the formulation of adhesives. It is commonly employed in the production of leather, where it acts as a tanning agent to create a durable and flexible material.
4. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties: Tannic acid exhibits antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting oxidative damage. Additionally, it has antimicrobial properties and can be used as a preservative in various products, such as food, cosmetics, and beverages.
5. Dyeing and ink production: Tannic acid can be used as a mordant in the dyeing process to improve the colorfastness and adhesion of dyes to fabrics. It is also employed in ink production as a binder and tannin-enriched component.
6. Photographic development: Tannic acid can be used in developing solutions for photographic films and papers. It acts as a reducing agent, facilitating the conversion of exposed silver halide crystals into metallic silver.
7. Industrial applications: Tannic acid finds applications in various industries, such as the production of wood adhesives, corrosion inhibitors, and rust converters. It is also utilized in the synthesis of certain chemicals, including tannin-derived polyurethanes and pharmaceutical intermediates.
Overall, tannic acid has versatile uses in chemistry, ranging from analytical techniques to industrial processes, owing to its unique properties and reactivity.
Health Effects and Safety Considerations
Health effects and safety considerations are important in chemistry to ensure the well-being of individuals working with chemicals or in environments where chemical reactions occur. Chemicals can have various health effects, including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, irritation, sensitization, and carcinogenicity. Therefore, it is crucial to understand and mitigate the potential risks associated with chemical exposure.
Some common health effects of chemical exposure include respiratory issues, skin irritation, eye irritation, allergic reactions, and organ damage. The severity of these health effects depends on factors such as the type and concentration of the chemical, duration of exposure, and individual susceptibility. It is essential to follow proper safety protocols, wear personal protective equipment (PPE), and have adequate ventilation to minimize exposure and potential health risks.
Safety considerations in chemistry include proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals. Chemicals should be stored in appropriate containers and labeled correctly to prevent accidental exposures and mix-ups. Chemicals should also be handled with care, following recommended procedures and precautions outlined in safety data sheets (SDS).
Chemical laboratories should have effective safety measures in place, such as safety showers, eyewash stations, and fire extinguishers, to handle accidents and emergencies. Regular inspections and maintenance should be carried out on equipment to ensure their proper functioning.
Additionally, proper training and education on chemical safety and emergency procedures should be provided to individuals working with chemicals. This includes understanding the hazards associated with specific chemicals and knowing how to respond in case of accidents, spills, or exposures.
It is important to emphasize the importance of risk assessment and hazard evaluation. Risk assessments help identify potential hazards and implement measures to minimize risks. This can involve substituting hazardous chemicals with less toxic alternatives, improving ventilation systems, or implementing engineering controls to reduce exposure.
Overall, health effects and safety considerations in chemistry are essential to protect workers, researchers, and the environment from potential harm associated with chemical exposure. Implementing proper safety protocols, providing training, and maintaining a culture of safety in chemical workspaces are critical to ensuring the well-being of all individuals involved in chemical activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chemistry is a fundamental branch of science that explores the composition, structure, properties, and transformations of matter. It plays a crucial role in understanding the world around us, from the interactions of atoms and molecules to the chemical processes that occur in our bodies and the environment. Through various experiments and studies, chemistry has contributed to advancements in medicine, technology, and materials science. Furthermore, it has helped us better comprehend the behavior of substances, discover new compounds, and develop sustainable solutions for the challenges we face. Overall, chemistry is a dynamic and ever-evolving field that continues to expand our knowledge and improve our lives.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.