Introduction to Boric Acid (H₃BO₃)
Boric acid (H₃BO₃) is a chemical compound that belongs to the boron family. It is an odorless and white crystalline solid that is soluble in water. Boric acid is a weak acid, meaning it partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions.
In chemistry, boric acid has various applications and uses. It is commonly used as an antiseptic, with its mild yet effective antimicrobial properties. Due to this, boric acid is often used in the manufacturing of eye washes, contact lens solutions, and antifungal creams.
Another significant use of boric acid is as an insecticide. It can be used to control pests such as cockroaches, ants, and termites. Boric acid acts as a stomach poison to these insects when ingested, leading to their elimination.
Furthermore, boric acid has a wide range of applications in the industrial sector. It is used as a precursor for the production of various boron compounds, including borate salts, borosilicate glass, and flame retardants. It is also utilized in the manufacturing of ceramics, enamel, and textile fiberglass.
Boric acid is also found in the field of chemistry research. It is often used as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions, enabling the formation of desired products. Additionally, it serves as a buffering agent and a pH regulator in various chemical processes.
However, it is important to note that boric acid should be used with caution. While it is relatively low in toxicity to humans and animals, prolonged exposure or ingestion can still lead to harmful effects. It is essential to follow safety guidelines and use protective measures when handling boric acid.
Overall, boric acid is a versatile compound in chemistry with numerous uses and applications. Its properties and effectiveness make it an important ingredient in various products used in medicine, pest control, industry, and research.
Chemical Structure and Properties of Boric Acid
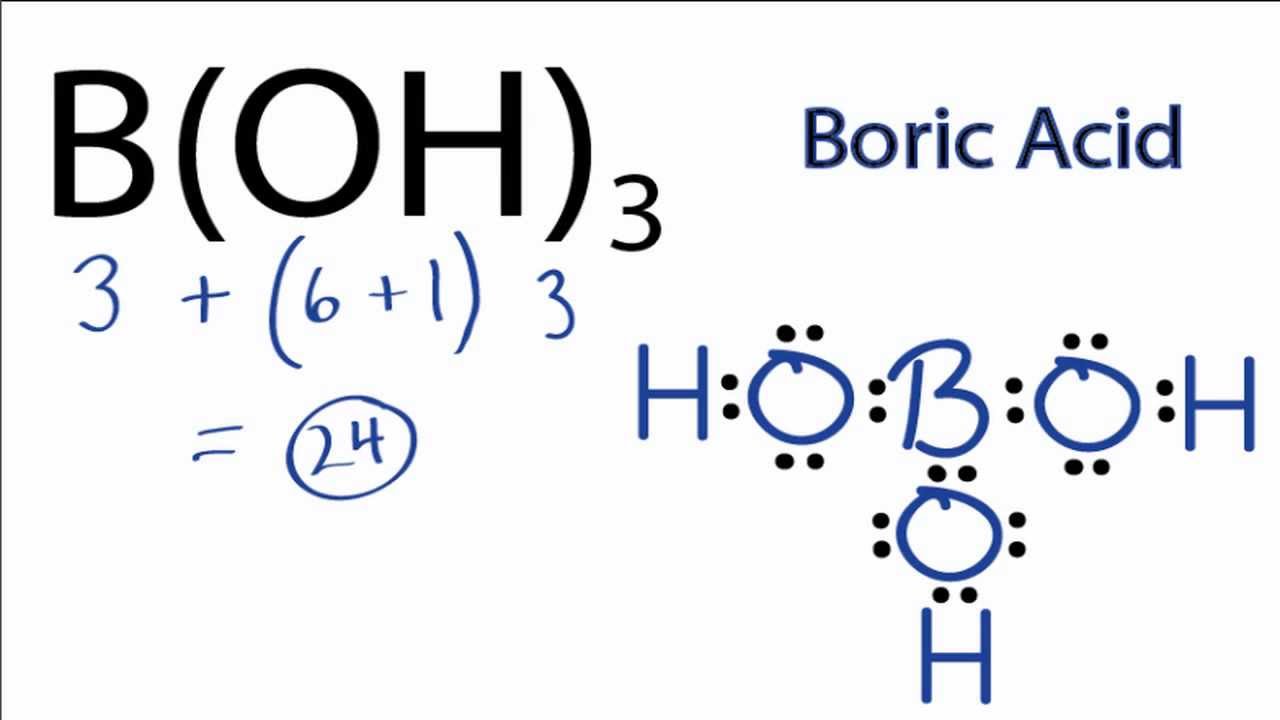
Boric acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H3BO3. It is a weak acid that exists in the form of white, crystalline powder or colorless, shiny plates. Boric acid is widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and pest control.
The chemical structure of boric acid consists of a central boron atom bonded to three hydroxyl groups (OH) and one oxygen atom. The boron atom is also surrounded by three pairs of electrons, making it a Lewis acid.
Boric acid is a weak acid, meaning it does not completely dissociate into ions in water. Instead, it forms equilibrium with the undissociated acid and its conjugate base (borate ion, B(OH)4-). The pKa value of boric acid is around 9, indicating its weak acidic nature.
One of the unique properties of boric acid is its ability to act as a buffer. It can stabilize the pH of a solution, preventing significant changes when acid or base is added. This property makes boric acid useful in various applications, such as eye drops and antiseptic solutions.
Another important property of boric acid is its ability to form complexes with various organic compounds and metal ions. These complexes have diverse applications, including as flame retardants, insecticides, and preservatives.
Boric acid has low toxicity to humans and animals, although it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled in large amounts. It is also a mild skin and eye irritant. Therefore, precautions should be taken when handling boric acid, and it should be kept out of reach of children.
Overall, boric acid is a versatile compound with various applications and unique chemical properties. Its structure and properties make it an essential component in many industries.
Common Uses of Boric Acid
Boric acid has a variety of common uses in chemistry, some of which include:
1. Buffer solution: Boric acid can be used as a buffer in various chemical reactions, as it can maintain a stable pH.
2. Antiseptic and disinfectant: Due to its antimicrobial properties, boric acid is used as an antiseptic and disinfectant in various products, such as eye drops, mouthwashes, and topical creams.
3. Flame retardant: Boric acid is often used as a flame retardant in materials such as textiles, plastics, and wood. It inhibits the spread of flames by releasing water upon exposure to heat.
4. Insecticide: Boric acid is a commonly used insecticide, particularly for controlling pests such as cockroaches, ants, and silverfish. It acts by affecting the insects’ nervous systems.
5. Fungicide: Boric acid is effective against various types of fungi, making it a useful ingredient in antifungal products like foot powders, creams, and other topical treatments.
6. Preservative: Due to its ability to inhibit the growth of certain microorganisms, boric acid is used as a preservative in some personal care products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
7. Flame colorant: When added to a flame, boric acid can produce a characteristic green color, which is often used in pyrotechnics and fireworks displays.
8. Welding flux: Boric acid is used as a component in some welding fluxes, as it helps to remove oxides from metal surfaces prior to welding, thus improving the quality of the weld.
9. Glass and ceramic production: Boric acid is a key ingredient in the production of some types of glass and ceramics, as it acts as a flux, helping to lower the melting point and improve the thermal stability of these materials.
10. Nuclear industry: Boric acid is employed in the nuclear industry as both a neutron absorber and a coolant. Its presence helps control the rate of nuclear reactions and helps regulate the temperature of reactor systems.
Safety Precautions and Handling of Boric Acid
Safety Precautions and Handling of Boric Acid in Chemistry
1. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety goggles, and a lab coat when handling boric acid. This will help to prevent direct contact with the skin, eyes, or clothing.
2. Work in a well-ventilated area or use a fume hood to minimize exposure to boric acid dust or vapors. Inhaling these particles or fumes can be harmful.
3. Avoid ingestion of boric acid. It should never be consumed or used near food preparation areas.
4. Keep boric acid away from open flames or sources of heat, as it can react with heat to release toxic fumes.
5. Do not mix boric acid with incompatible substances, such as strong acids or bases, as it may cause hazardous reactions or release toxic gases.
6. Store boric acid in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials.
7. Clean up spills immediately to prevent accidental ingestion or contact. Use proper cleaning procedures and equipment, and dispose of waste according to local regulations.
8. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling boric acid or any equipment that has come into contact with it.
9. Keep boric acid out of reach of children and pets, as it can be toxic if ingested.
10. Familiarize yourself with the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for boric acid, which contains detailed information about its physical properties, handling precautions, and emergency procedures.
Remember, these safety precautions are general guidelines, and it is always advisable to consult specific safety information provided by the manufacturer or chemical supplier for handling boric acid.
Importance and Applications of Boric Acid
Boric acid, also known as hydrogen borate, is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3BO3. It is a crystalline white powder that is soluble in water. Boric acid has numerous applications in the field of chemistry due to its unique properties.
One of the most important applications of boric acid is as a buffering agent. It can maintain a stable pH in a solution by resisting changes in acidity or alkalinity. This property makes it useful in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food and beverage production.
Boric acid is also used as an antiseptic and preservative due to its ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and yeast. It is commonly used in the manufacturing of personal care products, including eyewashes, antiseptic creams, and lotions.
In the field of metallurgy, boric acid is used as a fluxing agent to remove oxide impurities from metals during the welding, brazing, and soldering processes. It forms a protective layer on the metal surface, preventing oxidation and ensuring strong and clean joints.
Another important application of boric acid is as a fire retardant. It can inhibit the combustion of materials by releasing water when exposed to high temperatures. This property makes it valuable in the production of flame-resistant coatings, textiles, and polymers.
Boric acid also finds its use in the production of borosilicate glass, which has excellent thermal and chemical resistance. It is commonly used to make laboratory glassware, heat-resistant cookware, and optical fibers.
Additionally, boric acid is used in the manufacturing of fertilizers. It acts as a micronutrient for plants, promoting their growth and enhancing their resistance to diseases. It is particularly beneficial for crops such as legumes, beets, and fruit-bearing plants.
In conclusion, boric acid has various important applications in chemistry. Its buffering, antiseptic, fire-retardant, and fluxing properties make it versatile and useful in several industries. Its role in glass manufacturing and as a micronutrient in fertilizers further highlights its significance in the field of chemistry.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.