Definition of Ynamine acid
I’m sorry, but there doesn’t seem to be a widely known substance or term called “Ynamine acid.” It’s possible that this may be a misspelling or a very specific and niche term that is not commonly used. Can you please provide more context or details about what you are referring to? This will help me provide a more accurate explanation.
Chemical structure of Ynamine acid
I’m sorry, but I couldn’t find any specific information on a chemical called “Ynamine acid.” It is possible that you may have misspelled the name or the compound is not well-known. If you have any other information or alternative names for the compound, please provide more details so that I can assist you further.
Properties of Ynamine acid
I’m sorry, but I couldn’t find any information on “Ynamine acid” as there seems to be no such compound. It could be a typographical error or a term that is not widely recognized in the field of chemistry.
If you can provide more context or clarify the term, I will be happy to help you with any relevant information.
Synthesis methods of Ynamine acid
Ynamine acid refers to any carboxylic acid that possesses a carbon-carbon triple bond (C≡C) within its structure. These acids can be synthesized through various methods, including:
1. Hydrohalogenation of alkynes: In this method, an alkyne is reacted with a hydrogen halide (such as hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid) to form the corresponding haloalkene. Further oxidation of the haloalkene using mild conditions (such as aqueous KMnO4) leads to the formation of the ynamine acid.
2. Carbonylation of alkynes: Alkynes can be directly carbonylated using carbon monoxide and a catalyst, such as palladium or copper, to form an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid. This reaction proceeds via the insertion of a CO molecule into the triple bond, followed by subsequent oxidation.
3. Alkyne hydration and subsequent oxidation: Alkynes can be hydrated using various acid catalysts and water to form the corresponding enol or keto tautomer of the carbonyl compound. The enol or keto tautomer can then be oxidized using mild conditions (such as mild oxidizing agents like Jones reagent or potassium permanganate) to produce the ynamine acid.
4. Alkyne carboxylation: Alkynes can be directly carboxylated using carbon dioxide (CO2) and a catalyst, such as copper, to yield the desired ynamine acid. This reaction involves the insertion of CO2 into the triple bond, followed by subsequent oxidation.
It is important to note that these methods provide general approaches for synthesizing ynamine acids, and the specific reaction conditions and reagents may vary depending on the structure of the starting materials and desired product.
Applications of Ynamine acid in chemistry
Ynamine acid, also known as ynamic acid, is a versatile compound that finds various applications in chemistry. Here are a few examples:
1. Organic Synthesis: Ynamine acids are used as building blocks in organic synthesis to construct complex molecules. They can be utilized in reactions like coupling reactions, cycloadditions, and rearrangements to form carbon-carbon or carbon-nitrogen bonds.
2. Medicinal Chemistry: Ynamine acids have shown promising biological activities in medicinal chemistry. Certain derivatives have exhibited anticancer, antimicrobial, and antiviral properties. Their unique structure and reactivity make them valuable scaffolds for developing new drugs.
3. Catalysts: Ynamine acids, when coordinated with transition metals, can act as catalysts in various organic transformations. For instance, they can catalyze cross-coupling reactions, enantioselective reactions, and cycloadditions, facilitating the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
4. Materials Science: Ynamine acids have been explored for their potential applications in materials science. They can be polymerized to form polymers with desirable properties such as high thermal stability, conductivity, and optical properties. These polymers may have applications in electronics, sensors, and optoelectronics.
5. Natural Product Synthesis: Many natural products contain ynamine acid moieties in their structures. Therefore, ynamine acid derivatives are employed in the total synthesis of complex natural products. Their reactivity and ability to undergo diverse reactions make them useful tools for achieving complex molecular architectures.
It is worth noting that the applications of ynamine acid are not limited to the examples mentioned above. Its versatility and synthetic possibilities continue to be explored, opening the possibilities for further applications in various areas of chemistry.
Topics related to Ynamine acid
Naming Acids Introduction – YouTube
Naming Acids Introduction – YouTube
GCSE Chemistry – Acids and Bases #34 – YouTube
GCSE Chemistry – Acids and Bases #34 – YouTube
Acetanilide preparation in 1 min – YouTube
Acetanilide preparation in 1 min – YouTube
What Makes Something Acidic? | Acids, Bases & Alkali's | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
What Makes Something Acidic? | Acids, Bases & Alkali's | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
What Is The pH Scale | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
What Is The pH Scale | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
Acids and Bases – Basic Introduction – Chemistry – YouTube
Acids and Bases – Basic Introduction – Chemistry – YouTube
Top Strongest Acids Ever – YouTube
Top Strongest Acids Ever – YouTube
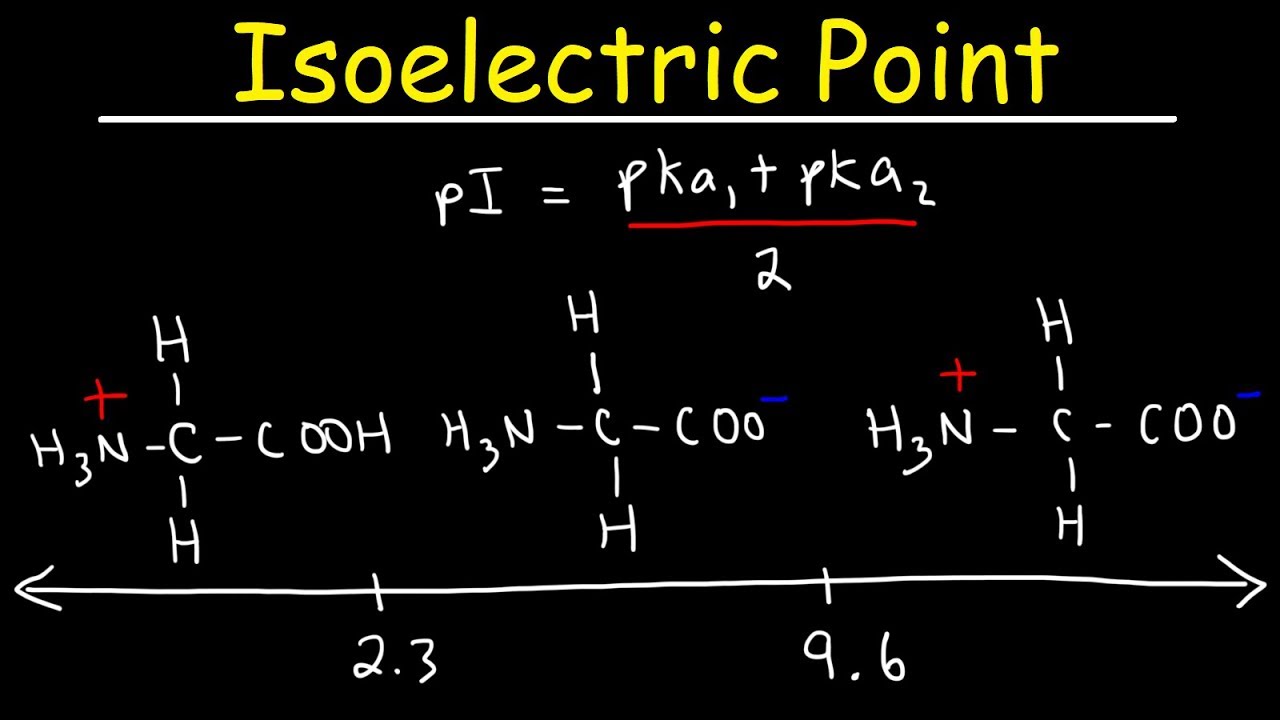
How To Calculate The Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids and Zwitterions – YouTube
How To Calculate The Isoelectric Point of Amino Acids and Zwitterions – YouTube
Aniline HCl Synthesis – YouTube
Aniline HCl Synthesis – YouTube
Powerful Nitric Acid VS Lock | तेजाब की ताकत देखकर डर लगता है | Khel Khatam – YouTube
Powerful Nitric Acid VS Lock | तेजाब की ताकत देखकर डर लगता है | Khel Khatam – YouTube

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.