Introduction to Dimethyl Sulfoxide (C₂H₆OS)
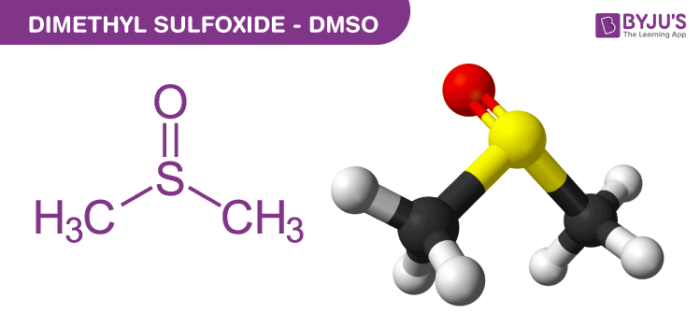
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a highly versatile organic solvent commonly used in the field of chemistry. Its chemical formula is C₂H₆OS, indicating that it consists of two methyl groups (CH₃) attached to a sulfur atom (S), which is in turn bonded to an oxygen atom (O).
DMSO is a colorless and odorless liquid, making it desirable for various applications in the laboratory. It is known for its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds, including many polar and nonpolar substances. This unique property has led to its extensive use as a solvent in organic synthesis, pharmaceutical research, and biochemical studies.
The high solubility of DMSO makes it particularly useful in sample preparation for spectroscopic techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS). It can serve as a universal solvent, allowing for the dissolution of both hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds, thus aiding in the analysis of complex mixtures.
Another notable characteristic of DMSO is its significant ability to penetrate biological membranes. This property has contributed to its use as a carrier or vehicle in drug delivery systems. DMSO has been employed to enhance the skin permeability of therapeutic drugs, enabling their efficient absorption and distribution within the body.
Moreover, DMSO exhibits some unique physical and chemical properties that differentiate it from other common solvents. It has a high boiling point (189°C) and a low freezing point (18°C), allowing for its application in reactions carried out at both high and low temperatures. Furthermore, DMSO has a relatively high dielectric constant, making it a solvent of choice in certain electrolyte solutions and electrochemical processes.
It is important to note that although DMSO is a highly effective solvent, it can also act as a reactant or a catalyst in some chemical reactions. Its reactivity with certain compounds can result in the formation of new products or intermediates, adding another dimension to its versatility in chemical processes.
In summary, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a widely used solvent in chemistry due to its excellent solvating properties, high permeability, and unique physical characteristics. Its applications range from organic synthesis to drug delivery systems, making it an invaluable tool in many scientific fields.
Chemical Properties of Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a versatile solvent with various chemical properties that make it useful in many fields of chemistry. Some of these chemical properties include:
1. Solvent Properties: DMSO has the ability to dissolve a wide range of polar and nonpolar compounds. This property makes it a popular choice as a solvent in organic synthesis and analytical chemistry.
2. High Boiling Point: DMSO has a boiling point of 189°C, which makes it useful for high-temperature reactions and as a solvent for compounds with high boiling points.
3. Hygroscopic Nature: DMSO is highly hygroscopic, meaning it has a strong tendency to absorb water from the surrounding environment. This property can affect the stability and solubility of certain compounds in DMSO.
4. Good Dissolving Power: DMSO has a high dielectric constant, which results in its ability to solvate ions effectively. This property makes it useful in a variety of chemical reactions and as a solvent for electrolytes.
5. Reaction Medium: DMSO can serve as a reaction medium or co-solvent in many chemical reactions. Its high boiling point and excellent solvating power allow for the dissolution of reactants and intermediates, facilitating various organic reactions.
6. Stability: DMSO is a stable compound under normal storage and handling conditions. It is non-reactive towards most common reagents, which makes it a reliable solvent in chemical processes.
7. Toxicity: Although DMSO is generally considered a low-toxicity compound, it can cause skin irritation and has a distinctive odor that can be bothersome. Proper safety precautions should be taken when handling DMSO to avoid exposure.
These are some of the important chemical properties of dimethyl sulfoxide that contribute to its widespread use in various fields of chemistry.
Synthesis and Production of Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a highly versatile solvent and reagent used in various chemical synthesis and production processes. It is produced through the oxidation of dimethyl sulfide using an oxidizing agent such as oxygen or hydrogen peroxide.
The synthesis of DMSO involves three major steps: oxidation, purification, and distillation.
1. Oxidation: Dimethyl sulfide (DMS) is reacted with an oxidizing agent in the presence of a catalyst to form dimethyl sulfoxide. Oxygen gas or hydrogen peroxide is commonly used as the oxidizing agent, and various catalysts such as transition metal complexes or sulfur compounds can be employed. The oxidation reaction can occur under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to optimize the yield and selectivity of DMSO formation.
2. Purification: The reaction mixture obtained from the oxidation step contains DMSO along with impurities such as water, unreacted reactants, and side products. These impurities need to be removed for obtaining a pure DMSO product. Purification techniques such as distillation, extraction, and crystallization can be used to separate and remove these impurities.
3. Distillation: After purification, the crude DMSO is further processed using distillation. Distillation involves heating the DMSO mixture to separate it from other volatile compounds. DMSO has a relatively high boiling point (189°C), meaning it can be easily separated from lower boiling point impurities. Vacuum distillation is often employed to lower the boiling point of DMSO and reduce thermal degradation.
Overall, the synthesis and production of DMSO involve careful control of reaction conditions, purification techniques, and distillation to obtain a high-purity DMSO product. DMSO is widely used in various chemical industries, including pharmaceuticals, polymers, and organic synthesis, due to its unique solvent properties and reactivity.
Applications of Dimethyl Sulfoxide in Chemistry
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a widely used solvent in chemistry due to its unique properties. It is a powerful polar aprotic solvent, meaning it can dissolve both polar and nonpolar compounds. Here are some applications of DMSO in various areas of chemistry:
1. Solvent for organic synthesis: DMSO is commonly used as a solvent for a wide range of organic reactions. Its high polarity allows for the dissolution of various organic compounds, including polar and nonpolar substances. It is particularly useful for reactions involving metal ions, organometallic compounds, and transition metal catalysts.
2. Solubilizing agent: DMSO has the ability to solubilize a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds that are insoluble or poorly soluble in other solvents. It is often used to dissolve compounds like polymers, peptides, proteins, and pharmaceutical drugs for analytical and experimental purposes.
3. Reaction medium: DMSO can act as a reaction medium, especially in processes involving reagents that are not soluble in water or other common solvents. It is commonly used in reactions such as oxidation, reduction, condensation, and isomerization.
4. Cryoprotectant: DMSO has the ability to protect living cells and tissues during freezing and thawing processes. It has been extensively used as a cryoprotectant in the preservation of cells, tissues, and organs for medical and research purposes.
5. Analytical techniques: DMSO is also used in various analytical techniques in chemistry. It can be employed as a solvent or co-solvent in spectroscopic methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and infrared (IR) spectroscopy. DMSO is also used as a matrix for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS).
6. Solvent for peptide and protein studies: DMSO is commonly used as a solvent for peptide and protein studies. It helps to maintain the solubility and stability of peptides and proteins during experiments, such as protein folding studies and peptide synthesis.
7. Reaction accelerator and catalyst: DMSO can enhance the rate of certain reactions and act as a catalyst in various chemical transformations. It has been used in reactions like the Swern oxidation, Mitsunobu reaction, and other organic synthetic transformations.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of dimethyl sulfoxide in chemistry. Its unique solvent properties and compatibility with a wide range of compounds make it a valuable tool in many areas of chemical research and industry.
Safety and Precautions when Handling Dimethyl Sulfoxide
When handling dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in a chemistry laboratory, it is important to follow appropriate safety measures and precautions. Here are some key safety guidelines:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE when handling DMSO. This may include safety goggles, lab coat or chemical-resistant apron, gloves, and closed-toe shoes.
2. Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhaling DMSO vapors. Use local exhaust ventilation if possible.
3. Storage: Store DMSO in a tightly sealed container away from heat, sources of ignition, and incompatible materials. Keep the container in a cool, dry place.
4. Handling: Handle DMSO with care to prevent spills. Use appropriate tools, such as a pipette or a syringe, to dispense the liquid.
5. Fire safety: DMSO is highly flammable. Keep it away from open flames, sparks, or other sources of ignition. Use non-sparking tools when working with DMSO.
6. Chemical compatibility: Avoid contact of DMSO with reactive or incompatible substances. Consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and chemical compatibility charts for specific information.
7. Skin and eye contact: Avoid direct contact with DMSO on the skin or eyes. In case of contact, immediately wash affected areas with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
8. Ingestion and inhalation: Do not consume or inhale DMSO. In case of accidental ingestion or inhalation, seek medical help immediately or contact a local poison control center.
9. First aid: Ensure that appropriate first aid measures and emergency equipment, such as eyewash stations and safety showers, are readily available in case of accidents or spills.
10. Waste disposal: Dispose of DMSO waste according to local regulations and available guidelines. Do not pour DMSO down the drain.
Remember to consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and follow the specific safety instructions provided by the manufacturer when working with DMSO.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.