Introduction to Coefficients
Introduction to Coefficients:
In mathematics, coefficients play a fundamental role in various areas such as algebra, calculus, and statistics. A coefficient is a numerical value that is multiplied by a variable or a term in an equation or a function. It represents the relationship or proportionality between different quantities.
Coefficients can be found in different forms depending on the context in which they are used. In algebraic equations, coefficients are often represented by letters or symbols. For example, in the equation 2x + 3y = 10, the coefficients are 2 and 3, representing the multiplicative factors of the variables x and y respectively.
In calculus, coefficients are often associated with the terms in a polynomial function or a power series. For example, in the polynomial function f(x) = 3x^2 – 5x + 1, the coefficients are 3, -5, and 1, representing the multiplicative factors of the powers of x.
Coefficients are also used in statistics, particularly in regression analysis. In this context, a coefficient represents the change in the dependent variable associated with a one-unit change in the independent variable, while holding other variables constant.
The values of coefficients can have different meanings and interpretations depending on the specific problem or equation in which they appear. They can indicate rates of change, proportions, or the strength and direction of relationships between variables.
In summary, coefficients are numerical values that quantify the relationship between variables or terms in equations, functions, or statistical models. They are essential in various mathematical and analytical contexts and provide valuable information about the relationships between different quantities.
Definition of Coefficients in Mathematics
In mathematics, a coefficient is a numerical factor that is multiplied by a variable or a constant in an algebraic expression. It represents the magnitude or the amount of influence that a particular term has on the overall value of the expression.
For example, in the expression 3x^2 + 5x + 2, the coefficients are 3, 5, and 2. The coefficient 3 is multiplied by the variable x^2, the coefficient 5 is multiplied by the variable x, and the coefficient 2 is a constant term. The coefficients determine the relative importance or significance of each term in the expression.
Types of Coefficients
In mathematics, a coefficient refers to a numerical or constant term that appears in front of a variable or a term in an equation, polynomial, or algebraic expression. Coefficients can have different types based on their characteristics and usage in various mathematical scenarios. Some common types of coefficients include:
1. Linear coefficient: The linear coefficient is the coefficient of the first power of a variable in a linear equation or expression. For example, in the equation 2x + 3 = 7, the linear coefficient is 2.
2. Quadratic coefficient: The quadratic coefficient is the coefficient of the second power of a variable in a quadratic equation or expression. For example, in the equation 3x^2 + 5x + 2 = 0, the quadratic coefficient is 3.
3. Constant coefficient: The constant coefficient is a coefficient that does not involve any variable terms and remains constant regardless of the value of the variable. For example, in the equation 7x + 5 = 12, the constant coefficient is 5.
4. Leading coefficient: The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the highest power of the variable in a polynomial equation or expression. It is typically associated with the term with the highest degree. For example, in the equation 4x^3 – 2x^2 + 5x + 1 = 0, the leading coefficient is 4.
5. Binomial coefficient: In combinatorial mathematics, the binomial coefficient is a coefficient that appears in the expansion of a binomial raised to a power. It represents the number of ways to choose a certain number of elements from a set, without regard to order. Binomial coefficients are denoted by the notation “n choose k” or written as “(n)/(k)”. For example, in the expression (a + b)^3, the binomial coefficients are 1, 3, and 3, respectively.
These are just a few examples of the different types of coefficients commonly encountered in mathematics. The specific type of coefficient used depends on the context and problem at hand.
Applications of Coefficients in Mathematics
Coefficients have various applications in mathematics across different branches and areas of study. Here are some common applications of coefficients:
1. Algebra: Coefficients are fundamental in algebraic equations as they represent the numerical factors that multiply the variables. In linear equations, coefficients are used to determine the slope and intercept of a line. In polynomial equations, coefficients determine the degree, roots, and behavior of the polynomial.
2. Calculus: In calculus, coefficients play a crucial role in power series expansions. The coefficients in a power series represent the relative contributions of each term and are used to approximate functions. These expansions are used in numerous mathematical and scientific calculations.
3. Probability and Statistics: Coefficients find applications in probability and statistics, particularly in regression analysis. Coefficients such as correlation coefficients and regression coefficients help measure and quantify relationships between variables. They provide insights into the strength and direction of the relationship.
4. Number Theory: Coefficients play a significant role in number theory, especially in Diophantine equations. Coefficients are used to find solutions for equations with integer variables. For example, in Fermat’s Last Theorem, coefficients are used to study equations of the form a^n + b^n = c^n.
5. Geometry: Coefficients are used in analytic geometry to represent geometric figures and equations. For example, in the equation of a line in standard form (Ax + By = C), the coefficients A and B determine the slope and direction of the line. In quadratic equations, coefficients help determine the shape and position of conic sections.
6. Fourier Analysis: Coefficients play a crucial role in Fourier analysis, which decomposes complex functions into simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier series coefficients measure the contribution of each harmonic component in a periodic function and are used in signal processing, image analysis, and data compression.
7. Linear Algebra: Coefficients are extensively used in matrix operations and systems of linear equations. In matrix multiplication, coefficients determine the resulting entries. In solving systems of linear equations, coefficients form the matrix and are used to find solutions or determine properties such as linear independence or inconsistent systems.
These are just a few examples of how coefficients are used in mathematics. Coefficients provide important numerical information and are essential for understanding, analyzing, and solving mathematical problems in various domains.
Conclusion or Summary
In conclusion, a coefficient is a numerical value in a mathematical equation that indicates the strength or direction of the relationship between variables. It is used to quantify the extent of the relationship between the dependent variable and one or more independent variables. The coefficient can be positive, indicating a positive relationship, or negative, indicating a negative relationship. Additionally, the coefficient’s magnitude can indicate the strength of the relationship, with larger values indicating a stronger relationship. Coefficients are commonly used in statistics, econometrics, and other quantitative fields to interpret and analyze data.
Topics related to Coefficient
What is a coefficient – YouTube
What is a coefficient – YouTube
What’s a Coefficient? – YouTube
What’s a Coefficient? – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac2 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac2 – YouTube
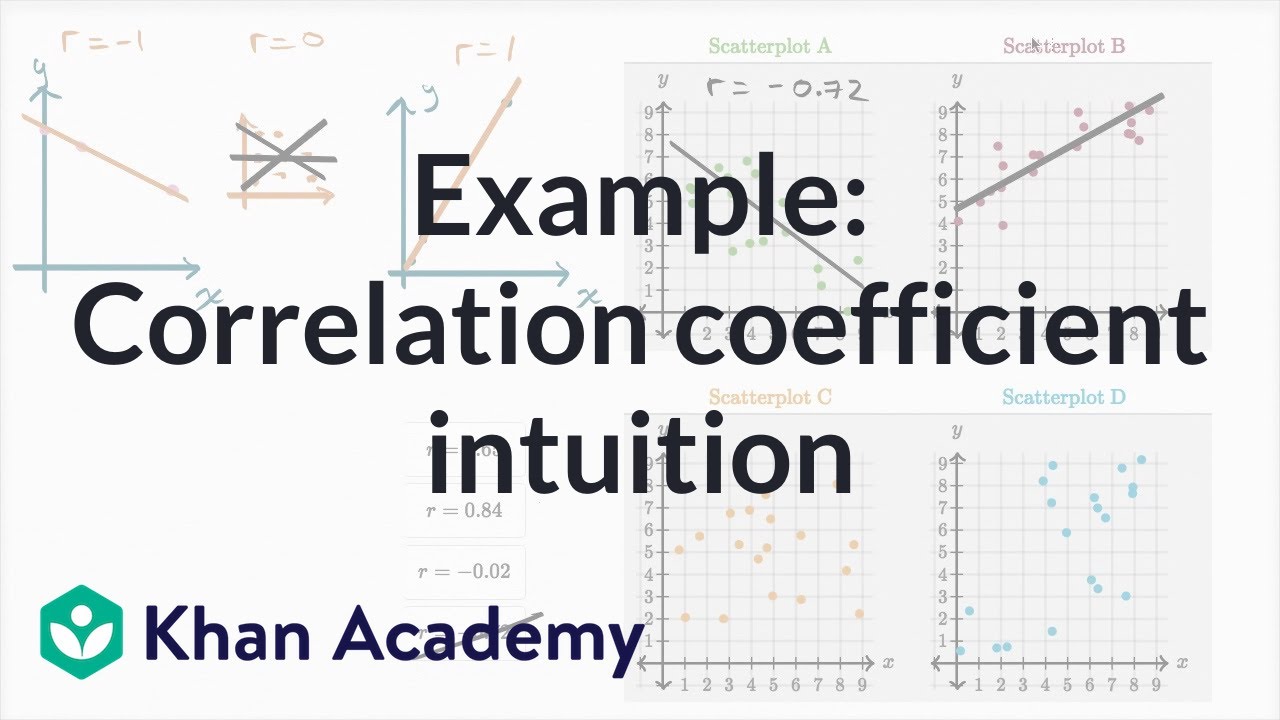
Example: Correlation coefficient intuition | Mathematics I | High School Math | Khan Academy – YouTube
Example: Correlation coefficient intuition | Mathematics I | High School Math | Khan Academy – YouTube
Coefficients, Constants, Terms, and Like Terms Vocab Review Video – YouTube
Coefficients, Constants, Terms, and Like Terms Vocab Review Video – YouTube
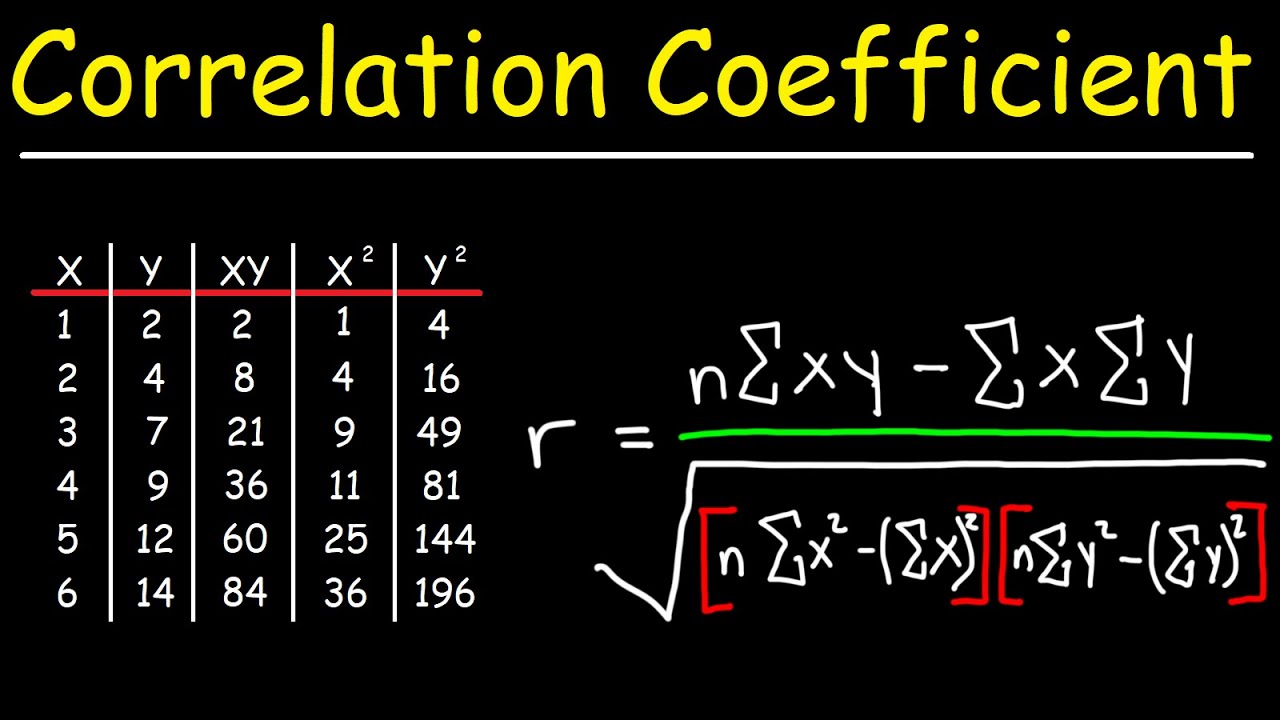
Correlation Coefficient – YouTube
Correlation Coefficient – YouTube
#variables #constants #coefficient #maths #viralshorts #viral #trending – YouTube
#variables #constants #coefficient #maths #viralshorts #viral #trending – YouTube
What is coefficient ? | Polynomial Basics #polynomials #coefficient #class10 #class9 #math #shorts – YouTube
What is coefficient ? | Polynomial Basics #polynomials #coefficient #class10 #class9 #math #shorts – YouTube
Binomial Coefficient in 5 sec| BINOMIAL THEOREM SHORTCUT-IIT/EAMCET/NDA – YouTube
Binomial Coefficient in 5 sec| BINOMIAL THEOREM SHORTCUT-IIT/EAMCET/NDA – YouTube
SHORTCUT (TRICK) TO FIND THE COEFFICIENT IN BINOMIAL EXPANSION | #Shorts – YouTube
SHORTCUT (TRICK) TO FIND THE COEFFICIENT IN BINOMIAL EXPANSION | #Shorts – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.