Introduction to Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable source of energy that is derived from the sun. It is harnessed using various technologies to convert sunlight into electricity or heat. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to environmental pollution, solar energy is clean, abundant, and sustainable.
The most common method of harnessing solar energy is through photovoltaic (PV) technology, which utilizes solar panels made up of multiple solar cells. These cells are made from semiconductor materials, such as silicon, and when sunlight hits them, the photons from the sun’s rays knock electrons loose from their atoms, generating a flow of electricity.
Another method of utilizing solar energy is through solar thermal technology. This involves using mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a fluid-filled pipe or tank, which captures the heat and transfers it to water or another fluid. The heated fluid is then used to generate steam, which can be used to power a turbine and produce electricity.
Solar energy can be used in a variety of applications, ranging from large-scale solar power plants that generate electricity for the grid, to smaller installations on residential or commercial buildings that provide onsite power. It can also be used for heating water, powering vehicles, and even for cooking.
One of the major advantages of solar energy is its environmental friendliness. It does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, or noise while generating electricity. Additionally, solar energy is infinitely renewable, as the sun’s rays will be available for billions of years to come.
However, solar energy does have some limitations. It is intermittent, meaning it is only available during daylight hours and is dependent on weather conditions. This necessitates the use of energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess solar energy for use when the sun is not shining. Solar energy also requires a significant upfront investment for the installation of solar panels and associated equipment.
Despite these limitations, solar energy is rapidly gaining popularity as a viable and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. It offers numerous benefits, including reduced reliance on fossil fuels, lower energy costs, and a reduced carbon footprint. As technology advances and costs continue to decrease, solar energy has the potential to play a major role in our transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Understanding the Physics of Solar Energy
Solar energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity. Understanding the physics behind solar energy involves knowing how sunlight is converted into usable energy.
The basic principle behind solar energy is the photovoltaic effect. This effect occurs when sunlight, which is composed of photons, interacts with certain materials such as crystalline silicon. When photons strike the surface of solar cells, they transfer their energy to the atoms within the material.
This transfer of energy causes electrons within the atoms to become excited and break free from their atoms. These free electrons then flow through the material, creating an electric current. This current can be captured and directed through electrical conductors to power various devices.
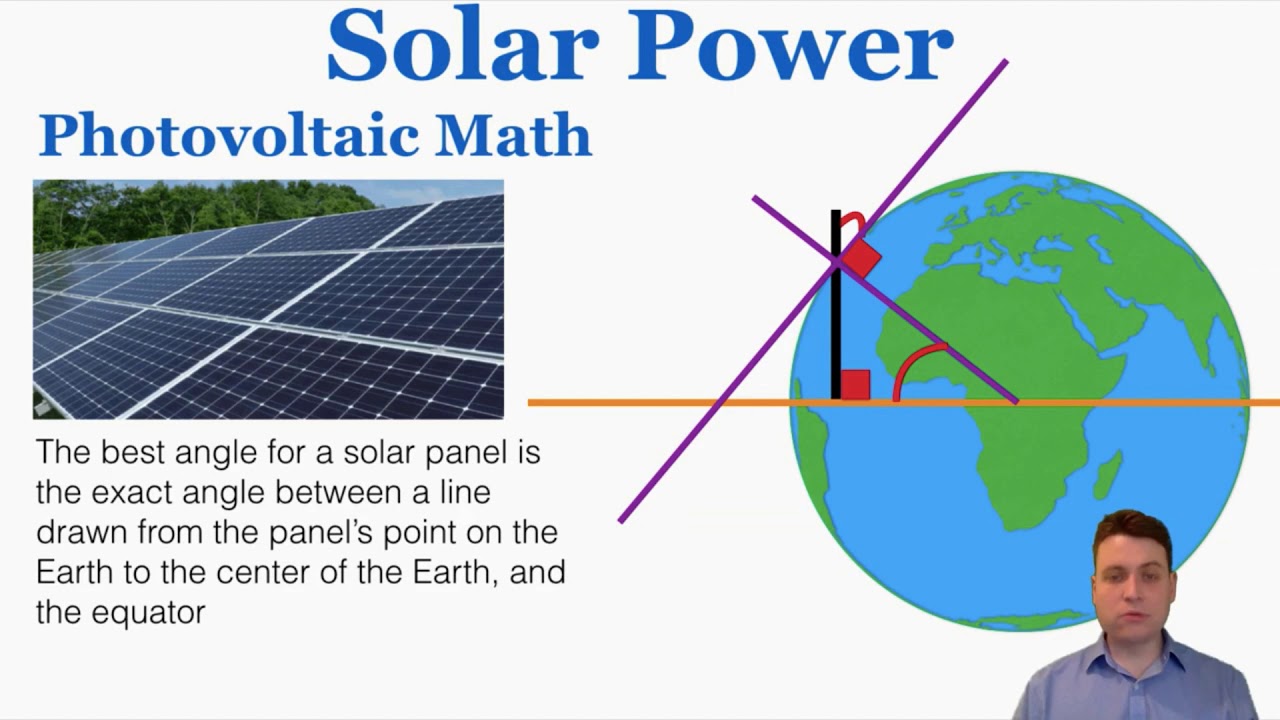
The efficiency of solar panels, or the percentage of sunlight that can be converted into usable energy, is influenced by several factors. One critical factor is the intensity of sunlight. Solar panels work best when they receive direct sunlight, so their angle and positioning are crucial for maximizing efficiency.
Additionally, the quality and composition of the solar cells themselves impact their efficiency. Different types of solar cells, such as monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, have varying characteristics that affect their ability to convert sunlight into electricity.
Temperature also plays a role in the efficiency of solar panels. High temperatures can decrease the efficiency of solar cells, so proper ventilation and cooling mechanisms are utilized to mitigate this effect.
Understanding how solar energy works also involves knowledge of other related concepts, such as the solar spectrum and the electromagnetic spectrum. The solar spectrum describes the distribution of different wavelengths of sunlight and their corresponding energy levels. The electromagnetic spectrum, on the other hand, encompasses all forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light.
Solar energy has several advantages over other forms of energy production. It is a clean and renewable source of energy, meaning it does not produce harmful emissions or deplete finite resources. Furthermore, solar energy systems can be installed at various scales, from individual homes to large power plants, providing flexibility in meeting energy demands.
Overall, grasping the physics behind solar energy involves understanding the conversion of sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect and considering factors such as sunlight intensity, the quality of solar cells, and temperature. With this knowledge, scientists and engineers can continue to improve and innovate solar energy technologies, driving the transition towards a more sustainable energy future.
Photovoltaic Effect and Solar Cells
The photovoltaic effect is a phenomenon in which certain materials generate an electric current when exposed to light. It is the basis of solar cells, which are devices that convert sunlight into usable electrical energy.
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are typically made of silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight hits the silicon surface, photons (particles of light) are absorbed, causing electrons in the silicon atoms to be excited and break free from their atomic orbit. These free electrons can then move through the silicon and create an electric current.
Solar cells are arranged in modules to form solar panels, which can be installed on rooftops or in large-scale solar farms. When sunlight falls on the solar panel, the photovoltaic effect occurs, generating an electrical current. This current can be used immediately to power electronic devices or stored in batteries for later use.
Solar energy is a renewable and abundant source of clean electricity. It is a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. Solar cells can generate electricity without producing harmful emissions or depleting finite resources, making them environmentally friendly.
With advancements in technology, solar cells have become increasingly efficient and affordable. The cost of solar panels has significantly reduced over the years, making solar energy more accessible to individuals and businesses. Additionally, solar power systems can be integrated into existing power grids or used as standalone systems in remote areas with limited access to electricity.
Solar energy offers numerous benefits, including reducing electricity bills, promoting energy independence, and mitigating climate change by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. It is a key player in the transition towards a clean and sustainable energy future.
Applications and Benefits
Solar energy refers to the energy that is derived from the sun. It is a renewable source of energy and has a wide range of applications and benefits. Here are some of the applications and benefits of solar energy:
1. Electricity generation: Solar energy can be used to generate electricity through the use of photovoltaic cells or solar panels. These panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, which can be used to power homes, buildings, and even entire communities.
2. Water heating: Solar energy can be used to heat water for domestic and commercial purposes. Solar water heating systems are cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional water heaters that rely on fossil fuels.
3. Heating and cooling: Solar energy can be used for space heating and cooling in buildings. Solar heating systems use solar thermal collectors to absorb sunlight and convert it into heat, which can then be used to warm up indoor spaces. Solar-powered air conditioning systems can also be used to cool buildings.
4. Transportation: Solar energy can be used to power electric vehicles (EVs) and boats. Solar-powered charging stations can be installed to recharge EVs with clean and renewable energy.
5. Remote power systems: Solar energy can be used in remote areas, where access to the conventional power grid is limited or non-existent. Solar power systems can provide electricity for lighting, communication devices, and other basic needs in these areas.
6. Agricultural applications: Solar energy can be used in agriculture for various purposes. It can power irrigation systems, crop drying, and lighting in greenhouses. Solar-powered fencing can also be used to protect crops from animals.
Benefits of solar energy:
1. Renewable and sustainable: Solar energy is a renewable source of energy, as sunlight is available abundantly and indefinitely. It reduces reliance on finite fossil fuels and helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Environmental-friendly: Solar energy is clean and produces no pollution or harmful emissions during its operation. It helps in reducing air pollution, water pollution, and carbon footprint.
3. Cost-effective: Although the initial investment in solar panels and equipment may be high, solar energy is a cost-effective solution in the long run. Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance and the operational costs are significantly lower than conventional energy sources.
4. Energy independence: Solar energy provides the opportunity for individuals and communities to generate their own electricity and be less dependent on the traditional power grid. It provides energy security and reduces the impact of power outages and fluctuations in energy prices.
5. Job creation: The solar industry has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, ranging from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. This helps in boosting the economy and creating employment opportunities.
In conclusion, solar energy has diverse applications and numerous benefits. Its use can help in reducing reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating climate change, and fostering sustainable development.
The Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy looks bright and promising. As technology advances, solar power is becoming more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible.
One of the key reasons for the future success of solar energy is its sustainability. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power is a renewable energy source that does not deplete natural resources. As concerns about climate change and the environmental impact of fossil fuels grow, there is an increasing global demand for clean energy alternatives like solar power.
Advancements in solar panel technology are improving the efficiency of converting sunlight into usable electricity. The development of new materials, such as perovskite solar cells, is increasing the efficiency and reducing the cost of solar panels. Additionally, innovations in energy storage systems are addressing the intermittent nature of solar power, allowing excess energy to be stored for use during cloudy periods or at night.
Governments around the world are also playing a crucial role in supporting the growth of solar energy. Many countries have set renewable energy targets and introduced incentives, such as feed-in tariffs or tax credits, to encourage the adoption of solar power. These policies are driving investment and creating jobs in the solar energy industry.
The future of solar energy also extends beyond traditional solar panels. Emerging technologies, such as solar windows, solar-powered vehicles, and solar shingles, are expanding the applications of solar power. These advancements have the potential to integrate solar energy into various aspects of our daily lives, making it more ubiquitous and convenient.
Furthermore, the falling cost of solar energy is making it more economically viable. The past decade has seen a significant reduction in the cost of solar panels, making solar power competitive with traditional forms of energy in many parts of the world. As economies of scale and technological advancements continue, the cost of solar energy is expected to decrease further, leading to even broader adoption.
Overall, the future of solar energy is promising. With ongoing advancements in technology, supportive government policies, and increasing affordability, solar power has the potential to become a major player in the global energy landscape, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Topics related to Solar energy
How do Solar cells work? – YouTube
How do Solar cells work? – YouTube
Solar Power – IB Physics – YouTube
Solar Power – IB Physics – YouTube
GCSE Physics – Wind and Solar #10 – YouTube
GCSE Physics – Wind and Solar #10 – YouTube
Solar Energy – GCSE Physics – YouTube
Solar Energy – GCSE Physics – YouTube
How Do Solar Panels Work? (Physics of Solar Cells) – YouTube
How Do Solar Panels Work? (Physics of Solar Cells) – YouTube
How do solar cells work? – YouTube
How do solar cells work? – YouTube
POWERING the US ENTIRELY with SOLAR explained by Elon Musk❗️⚡️ – YouTube
POWERING the US ENTIRELY with SOLAR explained by Elon Musk❗️⚡️ – YouTube
Concept of Solar Cell | warm-up match with physics | class12 physics semiconductor | ssp sir – YouTube
Concept of Solar Cell | warm-up match with physics | class12 physics semiconductor | ssp sir – YouTube
Essay On Solar Energy – YouTube
Essay On Solar Energy – YouTube
How to make solar power car || Solar energy science project #scienceproject #solar #shorts – YouTube
How to make solar power car || Solar energy science project #scienceproject #solar #shorts – YouTube

Konstantin Sergeevich Novoselov is a Russian-British physicist born on August 23, 1974. Novoselov is best known for his groundbreaking work in the field of condensed matter physics and, in particular, for his co-discovery of graphene. Novoselov awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Konstantin Novoselov has continued his research in physics and materials science, contributing to the exploration of graphene’s properties and potential applications.