Introduction to Volume
Volume is a basic concept in mathematics that measures the amount of space occupied by an object or substance. It is a fundamental property used to characterize and quantify three-dimensional objects.
Volume is typically measured in cubic units, such as cubic centimeters (cm³) or cubic meters (m³), depending on the scale of the object being measured. The volume of an object can be thought of as the sum of all the space it occupies in every direction.
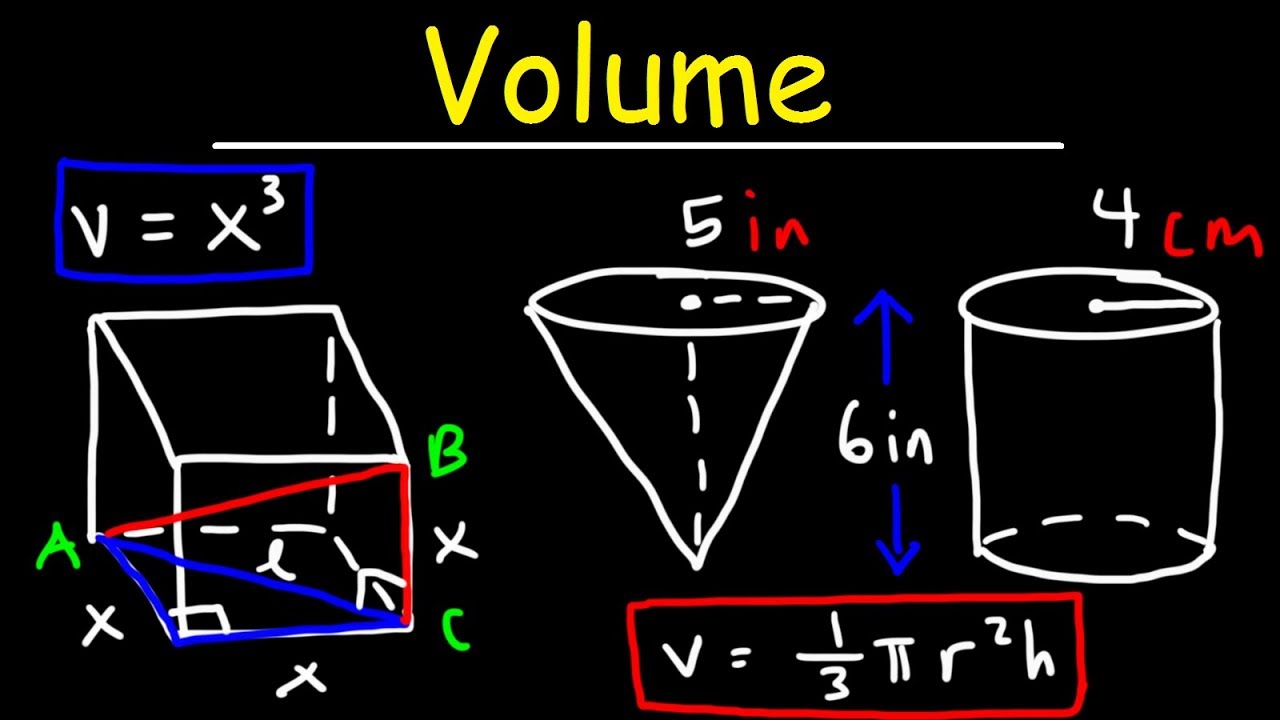
For regular geometric objects, such as cubes, spheres, or cylinders, formulas can be used to calculate the volume. These formulas are derived based on the specific shape and dimensions of the object. For example, the volume of a cube is found by multiplying the length of one side by itself twice (V= a³), while the volume of a sphere can be calculated using the formula V= (4/3)πr³, where r is the radius of the sphere.
For irregular objects, determining the volume can be more complex. In these cases, techniques like water displacement or integration can be used to estimate or calculate the volume.
Volume is an important concept not only in mathematics but also in various other fields, such as physics, chemistry, engineering, and architecture. It is used to measure and analyze the capacity of containers, the amount of liquid or gas that can be held by a vessel, the displacement of an object submerged in a fluid, and many other applications.
Understanding volume allows us to quantify and compare the size or capacity of objects, as well as to solve problems related to spatial dimensions and quantities.
Definition and Measurement of Volume
Volume refers to the three-dimensional space that an object or substance occupies. It is a fundamental property of matter and is typically measured in cubic units such as cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), or liters (L).
There are various ways to measure volume depending on the shape and state of the object or substance. For regular-shaped objects like a cube or rectangular prism, the volume can be calculated by multiplying the length, width, and height of the object. This formula is expressed as V = l × w × h.
For irregularly shaped objects, the volume can be determined using water displacement. This involves immersing the object in water and measuring the change in water level. The difference in water level is equal to the volume of the object.
In the case of liquids or gases, volume can be measured using specialized tools such as graduated cylinders, beakers, or volumetric flasks. These containers are calibrated with markings that indicate the volume of the substance they contain.
In scientific experiments, volume is often measured using a unit called the liter (L). One liter is equivalent to 1000 cubic centimeters (cm³) or 0.001 cubic meters (m³). This unit is commonly used for measuring the volume of liquids and gases.
Overall, volume is a crucial concept in various fields such as physics, chemistry, engineering, and medicine. It helps understand the physical properties and behavior of objects and substances, and it is an essential parameter in calculations and experiments.
Formulas and Calculations for Volume
To calculate the volume of various geometric shapes, you can use the following formulas:
1. Cube: V = s^3
– V represents the volume
– s represents the length of one side of the cube
2. Rectangular Prism: V = l × w × h
– V represents the volume
– l represents the length of the prism
– w represents the width of the prism
– h represents the height of the prism
3. Sphere: V = (4/3) × π × r^3
– V represents the volume
– π is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159
– r represents the radius of the sphere
4. Cylinder: V = π × r^2 × h
– V represents the volume
– π is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159
– r represents the radius of the cylinder
– h represents the height of the cylinder
5. Cone: V = (1/3) × π × r^2 × h
– V represents the volume
– π is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159
– r represents the radius of the cone
– h represents the height of the cone
6. Pyramid: V = (1/3) × b × h
– V represents the volume
– b represents the area of the base of the pyramid
– h represents the height of the pyramid
These are some common formulas for calculating the volume of different shapes. However, there are many other formulas available depending on the specific geometric shape you want to calculate the volume for.
Applications of Volume in Mathematics
Volume is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields. Here are some applications of volume:
1. Geometry: In geometry, volume is used to measure the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It is used to find the volume of various shapes such as cubes, spheres, cylinders, pyramids, and prisms. Knowledge of volume is vital for solving problems related to these shapes, including calculating surface areas and finding the capacity of containers.
2. Physics: Volume plays a significant role in physics. For example, in fluid dynamics, volume is used to measure the displacement of a fluid, determine the buoyant force, and calculate the flow rate. In thermodynamics, volume is an essential property used to describe the behavior of gases and the expansion of substances with changing temperature and pressure.
3. Engineering: Volume is crucial in engineering applications. It is used to determine the dimensions and capacities of various objects and structures, such as buildings, reservoirs, tanks, and pipelines. Engineers use volume calculations to design and plan their constructions effectively.
4. Chemistry: Volume is often used in chemistry for quantitative analysis and measuring the amount of a substance. It is essential for calculating concentrations, dilutions, and reactions in solutions. Gas volumes are particularly important in studying the behavior of gases, including the ideal gas law and gas stoichiometry.
5. Probability: Volume concepts are also applied in probability theory. For example, in the concept of probability density functions, volume can be used to determine the probability of an event occurring over a given area or region. This application is commonly seen in statistics, where probability distributions with continuous variables are used.
6. Optimization: Volume plays a role in optimization problems, where the objective is to find the maximum or minimum value of a function within a given region. By determining the volume of a bounded region, mathematicians can set constraints and solve optimization problems effectively.
These are just a few examples of how volume is applied in various mathematical disciplines. Volume is a crucial measure that helps us understand and quantify three-dimensional space, making it an integral part of many mathematical and real-world applications.
Conclusion and Importance of Volume
In conclusion, volume is an essential measurement in various fields and holds significant importance in different aspects of life. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and engineering.
Understanding volume helps in solving mathematical problems involving three-dimensional shapes, such as cubes, cylinders, and spheres. It is crucial in calculating the amount of space occupied by an object or substance.
In physics, volume is essential for determining the amount of space displaced by an object. This is significant in various areas, including fluid mechanics, where volume is used to calculate the flow rate of liquids or gases.
In chemistry, volume plays a crucial role in measuring the amount of a substance in a reaction. It is also essential in calculating concentrations and determining the amount of reactants and products involved.
Volume is also vital in engineering, where it is used to design structures and determine the capacity of containers. It helps engineers determine the amount of material required for construction projects and assess the suitability of certain spaces for specific purposes.
Moreover, understanding volume is important in everyday life situations as well. For example, knowing the volume of a container helps in determining how much liquid it can hold. It aids in cooking by measuring the volume of ingredients and ensures proper mixing and proportions.
Overall, volume is a fundamental measurement that holds great importance in various disciplines and practical applications. It helps in solving mathematical problems, understanding physical phenomena, conducting chemical experiments, designing structures, and everyday tasks.
Topics related to Volume
Math Antics – Volume – YouTube
Math Antics – Volume – YouTube
Volume of Rectangular Prisms | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
Volume of Rectangular Prisms | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac – YouTube
Volume – YouTube
Volume – YouTube
What is Volume in Math? Calculate Volume of Rectangular Prisms & Cubes w/ Units – [5-8-13] – YouTube
What is Volume in Math? Calculate Volume of Rectangular Prisms & Cubes w/ Units – [5-8-13] – YouTube
Focus Episode 1 + Addition Ad Desktop Arrow CTA – YouTube
Focus Episode 1 + Addition Ad Desktop Arrow CTA – YouTube
Volume Song | Measuring Volume For Kids | 4th Grade – 5th Grade – YouTube
Volume Song | Measuring Volume For Kids | 4th Grade – 5th Grade – YouTube
Finding Volume with Unit Cubes | How to Find Volume – YouTube
Finding Volume with Unit Cubes | How to Find Volume – YouTube
Grade 4 Math: Volume – YouTube
Grade 4 Math: Volume – YouTube
VOLUME OF SOLID FIGURES | GRADE 6 – YouTube
VOLUME OF SOLID FIGURES | GRADE 6 – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.