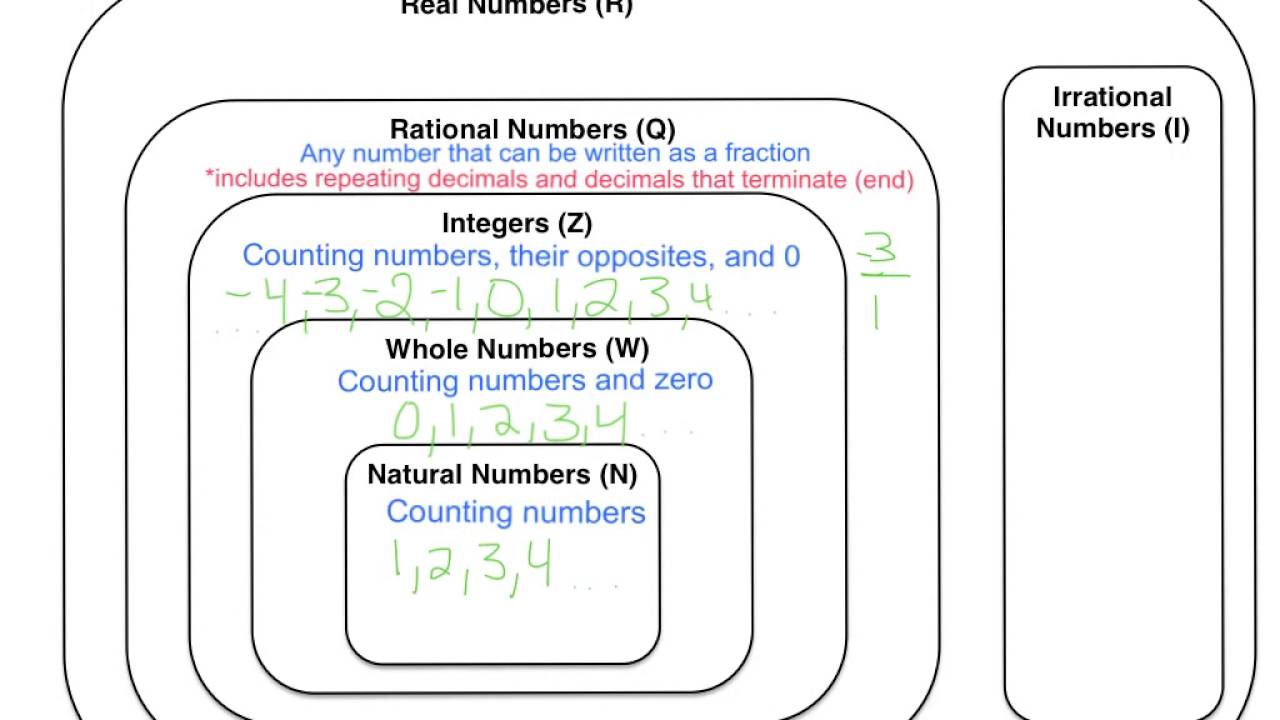
Definition of Real Numbers
Real numbers are the set of all numbers that can be represented on the number line, including integers, fractions, decimals, and irrational numbers. They are called “real” numbers because they are used to represent quantities in the real world. Real numbers can be positive, negative, or zero, and they can be expressed in various forms such as whole numbers, proper fractions, mixed numbers, or in decimal notation. Every real number has a unique position on the number line and can be compared using the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Properties of Real Numbers
Real numbers are a fundamental concept in mathematics that represents all possible values on the number line. Here are some properties of real numbers:
1. Closure property: The sum, difference, product, or quotient of any two real numbers is also a real number. For example, adding two real numbers will always result in a real number.
2. Commutative properties: The commutative property holds for addition and multiplication of real numbers. This means that changing the order of the numbers does not change the result. For example, a + b = b + a and a * b = b * a.
3. Associative properties: The associative property holds for addition and multiplication of real numbers. This means that changing the grouping of the numbers does not change the result. For example, (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a * b) * c = a * (b * c).
4. Identity properties: The identity element for addition of real numbers is 0, which means that adding 0 to any real number does not change the value. The identity element for multiplication is 1, which means that multiplying any real number by 1 does not change the value.
5. Inverse properties: Every real number has an additive inverse, which means that adding a number to its additive inverse will result in 0. Every non-zero real number has a multiplicative inverse, which means that multiplying a number by its multiplicative inverse will result in 1.
6. Distributive property: The distributive property holds for real numbers. It states that for any three real numbers a, b, and c, a * (b + c) = (a * b) + (a * c).
These properties of real numbers are fundamental and play a crucial role in various areas of mathematics and everyday life applications.
Operations with Real Numbers
Operations with real numbers involve various mathematical operations that can be performed on these numbers. Real numbers are a broad class of numbers that include rational numbers (fractions) and irrational numbers (numbers that cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers), such as square roots and decimal expansions. The four basic operations that can be performed on real numbers are:
1. Addition: This operation involves adding two or more real numbers together to obtain their sum. For example, adding 3 and 5 gives a sum of 8: 3 + 5 = 8.
2. Subtraction: This operation involves subtracting one real number from another to obtain the difference between them. For example, subtracting 5 from 9 gives a difference of 4: 9 – 5 = 4.
3. Multiplication: This operation involves multiplying two or more real numbers together to obtain their product. For example, multiplying 2 and 4 gives a product of 8: 2 * 4 = 8.
4. Division: This operation involves dividing one real number by another to obtain the quotient. For example, dividing 10 by 2 gives a quotient of 5: 10 / 2 = 5.
These operations can be combined and performed in various ways to solve more complex mathematical problems involving real numbers. Additionally, other operations, such as exponentiation and taking square roots, can also be performed on real numbers to further extend their use in mathematical calculations.
Real Numbers on the Number Line
Real numbers are a set of numbers that include both rational numbers (numbers that can be expressed as a fraction) and irrational numbers (numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction). Real numbers are represented on the number line, which is a line that extends in both positive and negative directions.
On the number line, real numbers are plotted at points that correspond to their values. For example, the number 0 is represented as a point at the center of the number line. Positive real numbers are plotted to the right of 0, while negative real numbers are plotted to the left of 0.
The number line is divided into intervals, with each interval representing a specific range of real numbers. The intervals can be further subdivided into smaller intervals to represent more precise values.
Real numbers can be ordered on the number line, meaning that they can be compared to each other based on their position. For example, a real number that is plotted to the right of another number is greater than that number.
In addition to rational and irrational numbers, real numbers also include integers (positive and negative whole numbers) and whole numbers (positive integers including 0). The set of real numbers is infinite, meaning there is an endless amount of them on the number line.
Applications of Real Numbers
Real numbers have a wide range of applications in various fields. Here are some notable applications:
1. Measurement and Engineering: Real numbers are used in measurements of length, weight, time, temperature, voltage, current, and more. They also play a crucial role in engineering disciplines such as civil engineering, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and aerospace engineering.
2. Finance and Economics: Real numbers are used extensively in finance and economics for accounting, financial analysis, investment decision-making, and risk management. They form the basis for financial calculations, interest rates, stock prices, and inflation rates.
3. Science: Real numbers are essential in scientific disciplines such as physics, chemistry, biology, and astronomy. They are used in measurements, calculations of physical properties, statistical analysis of data, modeling, and quantitative analysis.
4. Computer Science: Real numbers are widely used in computer science for algorithms, computer graphics, simulations, and numerical computations. They are necessary for solving mathematical problems, implementing machine learning algorithms, and performing calculations in computer programs.
5. Medicine and Healthcare: Real numbers play an important role in medical diagnostics, monitoring vital signs, drug dosages, patient charts, and medical research. They are used to measure various physiological parameters and interpret medical data.
6. Architecture and Design: Real numbers are vital in architecture and design for creating accurate blueprints, measurements, calculations, and spatial relationships. They enable precise design and construction of buildings, bridges, roads, and other structures.
7. Statistical Analysis: Real numbers are used extensively in statistical analysis for data collection, representation, and interpretation. Statistical models, probability distributions, regression analysis, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals are based on real numbers.
8. Communication and Information Technology: Real numbers are utilized in communication and information technology for encoding, signal processing, data storage, encryption, compression, and coding theory. They play a critical role in digital communication systems, data transmission, and encryption algorithms.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications of real numbers. In essence, real numbers provide a foundation for mathematical modeling and quantitative analysis in various fields, enabling precise measurements, calculations, and interpretations.
Topics related to Real numbers
What are the Types of Numbers? Real vs. Imaginary, Rational vs. Irrational – YouTube
What are the Types of Numbers? Real vs. Imaginary, Rational vs. Irrational – YouTube
What are Real Numbers? | Don't Memorise – YouTube
What are Real Numbers? | Don't Memorise – YouTube
WHAT IS A REAL NUMBER? WHOLE NUMBER? NATURAL NUMBER? – YouTube
WHAT IS A REAL NUMBER? WHOLE NUMBER? NATURAL NUMBER? – YouTube
The Real Number System – YouTube
The Real Number System – YouTube
What are Real Numbers ? Number System – YouTube
What are Real Numbers ? Number System – YouTube
Real Numbers – YouTube
Real Numbers – YouTube
Define Real Numbers #shorts – YouTube
Define Real Numbers #shorts – YouTube
Number System ( Natural Number, Whole Number, Integer, Rational Number, Irrational Number, Real) – YouTube
Number System ( Natural Number, Whole Number, Integer, Rational Number, Irrational Number, Real) – YouTube
Class9 Operation on Real Numbers – Addition – YouTube
Class9 Operation on Real Numbers – Addition – YouTube
Maths project on the topic " Real Numbers" – YouTube
Maths project on the topic " Real Numbers" – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.