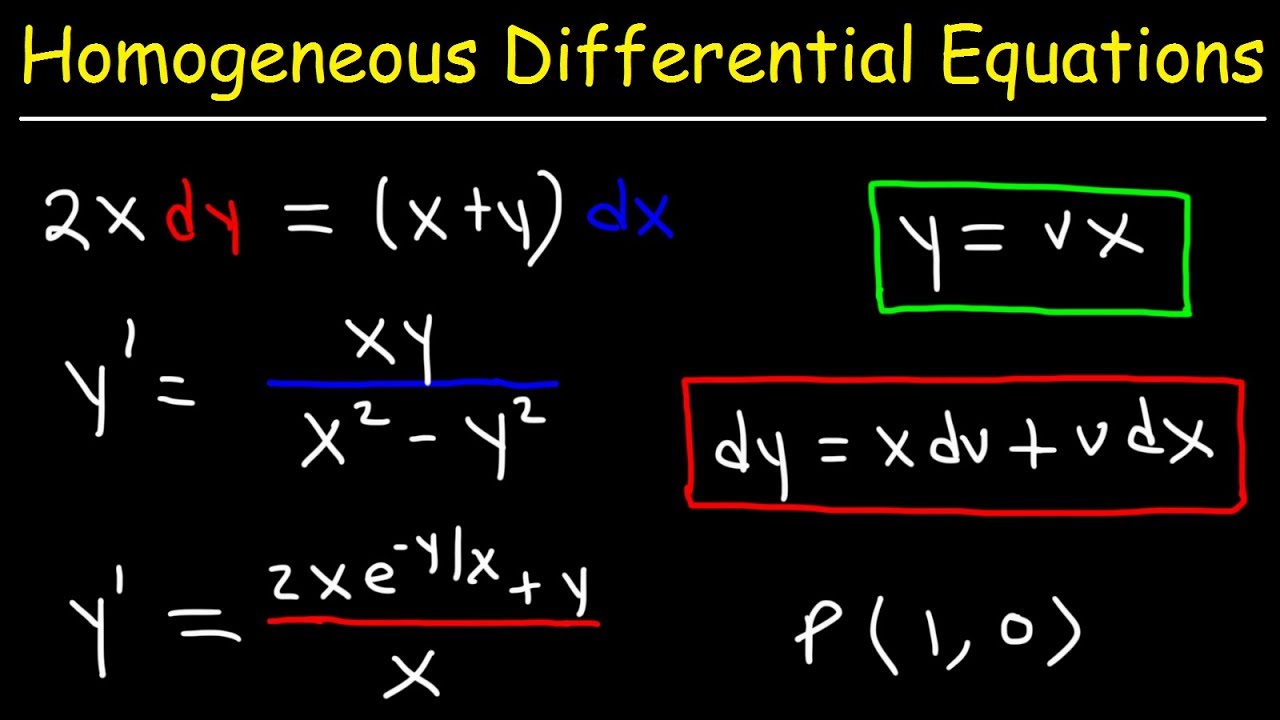
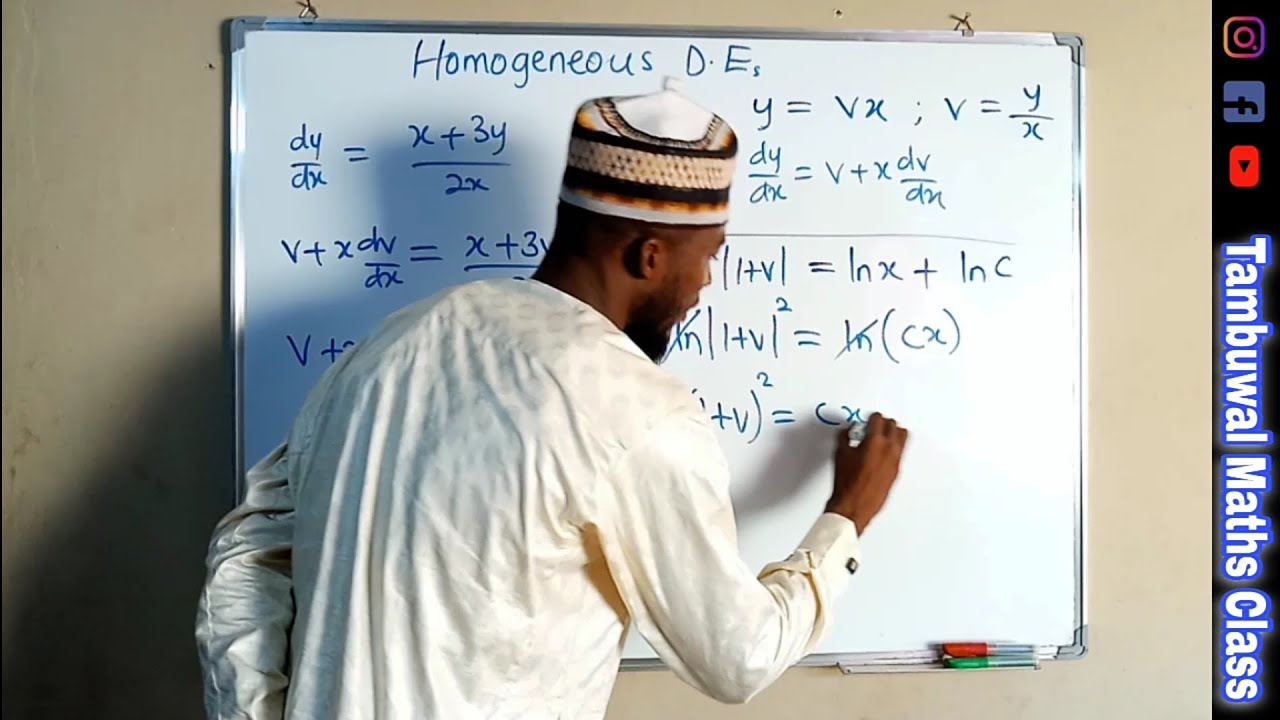A homogeneous equation is a type of equation in mathematics where all terms have the same degree or homogeneous degree. In other words, all the terms in the equation have the same power of variables.
For example, the equation 3x + 2y = 0 is a homogeneous equation because both terms, 3x and 2y, have a degree of 1 (constant terms have a degree of 0). Similarly, the equation x^2 + 2xy – 3y^2 = 0 is also a homogeneous equation because all the terms have a degree of 2.
Solving a homogeneous equation involves finding solutions that satisfy the equation. One way to solve it is by using substitution or variable substitution to simplify the equation. Another method is by using linear algebra techniques such as eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
Homogeneous equations are used in various fields of mathematics, including linear algebra, differential equations, and optimization problems. They have many applications in physics, chemistry, engineering, and other scientific disciplines.
Introduction
Introduction:
In mathematics, an equation is a statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. Equations are used to model and solve a wide range of mathematical and real-world problems. One type of equation that frequently arises is a homogeneous equation.
Homogeneous Equation:
A homogeneous equation is a type of equation in which all terms have the same degree. In other words, if the degree of each term in the equation is the same, the equation is said to be homogeneous.
For example, the equation 2x + 3y = 0 is a homogeneous equation because all terms have degree 1. On the other hand, the equation 2x + 3y = 4 is not homogeneous because the constant term, 4, has degree 0.
Solving homogeneous equations often involves finding a solution in the form of a non-zero vector. This is because homogeneous equations have the property that if a particular vector is a solution, then any scalar multiple of that vector is also a solution.
Homogeneous equations are important in various areas of mathematics and science, including linear algebra, differential equations, and physics. They often arise when studying systems that exhibit proportionality or symmetry.
In conclusion, a homogeneous equation is a type of equation in which all terms have the same degree. Solving these equations involves finding solutions in the form of non-zero vectors, where any scalar multiple of a solution is also a solution. Homogeneous equations have applications in various mathematical and scientific fields.
Definition of Homogeneous Equation
A homogeneous equation is a mathematical equation in which all the terms have the same degree. In other words, each term in a homogeneous equation has the same power of the variables that appear in the equation.
In linear algebra, a homogeneous equation is a system of linear equations in which the constant term in each equation is zero. This means that the right side of each equation is equal to zero. A homogeneous system of equations always has at least one solution, which is the trivial solution where all variables are equal to zero.
Properties and Characteristics
In mathematics, a homogeneous equation is a mathematical equation in which all terms have the same degree, or power. It is called “homogeneous” because the equation is invariant under scaling or homothety, meaning that if (x,y) is a solution of the equation, then so is (ax,ay) for any non-zero constant a.
In terms of properties and characteristics, a homogeneous equation has the following properties:
1. It always has a trivial solution. This means that there will always be a solution where all variables are set to zero. For example, in the equation 2x + 3y = 0, the solution (x, y) = (0, 0) is trivial.
2. It can have non-trivial solutions. Non-trivial solutions are solutions in which at least one variable is non-zero. For example, in the equation x^2 + y^2 = 0, the solution (x, y) = (1, i) is non-trivial.
3. It forms a vector space. The set of all solutions to a homogeneous equation forms a vector space, because it satisfies the properties of vector addition and scalar multiplication. This vector space is called the null space or kernel of the equation.
4. It can be solved using linear algebra techniques. Homogeneous equations can often be written in matrix form, and their solutions can be found using techniques such as Gaussian elimination or finding the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the associated matrix.
5. It can have infinitely many solutions. If a homogeneous equation has one non-trivial solution, then it will have infinitely many solutions, because any scalar multiple of a solution is also a solution.
Overall, homogeneous equations are a fundamental concept in mathematics and have many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
Examples and Applications
The homogeneous equation is a type of linear equation that is frequently encountered in various fields of mathematics and science. Here are some examples of the homogeneous equation and its applications:
1. Physics: The wave equation, which describes the behavior of waves in various physical systems, is a homogeneous partial differential equation. It is commonly used to study phenomena such as sound waves, electromagnetic waves, and seismic waves.
2. Engineering: In structural analysis, the equations governing the behavior of a system in equilibrium, such as the equations for trusses or beams, are often homogeneous. These equations provide insights into the stability and load-bearing capacity of structures.
3. Economics: The Cobb-Douglas production function is a homogeneous function that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs in the production process. This equation is widely used in economics to study production and productivity growth.
4. Differential equations: Many types of ordinary differential equations can be transformed into homogeneous equations by introducing appropriate substitutions. Solving these equations helps to understand various phenomena, such as population growth, radioactive decay, and chemical reactions.
5. Geometry: In linear algebra, the homogeneous equation arises when studying systems of linear equations with unknowns that are homogeneous coordinates in projective geometry. It provides a geometric perspective on linear transformations and their matrices.
6. Probability theory: The homogeneous equation also appears in applications related to probability. For example, the homogeneous Poisson process is a stochastic process that models the occurrences of events in time, where the rate of events remains constant over time.
Overall, the homogeneous equation is a versatile tool that finds applications in diverse areas, including physics, engineering, economics, differential equations, geometry, and probability theory. Its solutions can provide valuable insights into the behavior of systems and help solve various practical problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a homogeneous equation is a type of mathematical equation in which all the terms have the same degree and there are no constant terms. It can be solved by finding the roots of the corresponding characteristic equation. Homogeneous equations are commonly used in various fields of mathematics and physics to model systems that exhibit symmetry or proportionality.
Topics related to Homogeneous equation
Homogeneous Differential Equations – YouTube
Homogeneous Differential Equations – YouTube
How To Solve First Order Homogeneous Differential Equation – YouTube
How To Solve First Order Homogeneous Differential Equation – YouTube
First order homogenous equations | First order differential equations | Khan Academy – YouTube
First order homogenous equations | First order differential equations | Khan Academy – YouTube
Homogeneous Equation | Short Tricks | JEE Bytes by Unacademy | Shantanu Sir | Raunak Sir – YouTube
Homogeneous Equation | Short Tricks | JEE Bytes by Unacademy | Shantanu Sir | Raunak Sir – YouTube
homogeneous differential equations – YouTube
homogeneous differential equations – YouTube
How To Solve Homogeneous Equations? (12th Maths) – 1 Video 1 Mark पक्का in Board Exam #shorts – YouTube
How To Solve Homogeneous Equations? (12th Maths) – 1 Video 1 Mark पक्का in Board Exam #shorts – YouTube
the differential equations terms you need to know. – YouTube
the differential equations terms you need to know. – YouTube
DEGREE OF HOMOGENEOUS FUNCTION 🥸|| 12TH MATH'S #shorts – YouTube
DEGREE OF HOMOGENEOUS FUNCTION 🥸|| 12TH MATH'S #shorts – YouTube
Hey, if you are taking differential equations, then I just want to wish you the best luck! – YouTube
Hey, if you are taking differential equations, then I just want to wish you the best luck! – YouTube
How to find degree of Homogeneous Function #Shorts – YouTube
How to find degree of Homogeneous Function #Shorts – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.