Definition of the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, denoted as |x|, is a mathematical function that returns the non-negative value of a number. In other words, it measures the distance between a number and zero on a number line, regardless of the direction.
The absolute value function takes a real number as input and returns its magnitude without considering its sign. This means that if the input number is positive or zero, the output will be the same as the input. However, if the input number is negative, the output will be the opposite of the input, as it is the same distance from zero but in the opposite direction.
For example, the absolute value of 4 is 4 because it is already a non-negative number. The absolute value of -4 is also 4 because it is the same distance from zero, but in the opposite direction. Therefore, the absolute value function removes the negative sign and always returns a positive or zero value.
Properties of the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, denoted as |x|, is a mathematical function that returns the non-negative magnitude or distance of a real number from zero. It can be represented graphically as a V-shaped graph.
Here are some key properties of the absolute value function:
1. Non-negativity: The output of the absolute value function is always non-negative. This means that |x| ≥ 0 for any real number x.
2. Symmetry: The graph of the absolute value function is symmetric about the y-axis. This means that |x| = |(-x)| for any real number x.
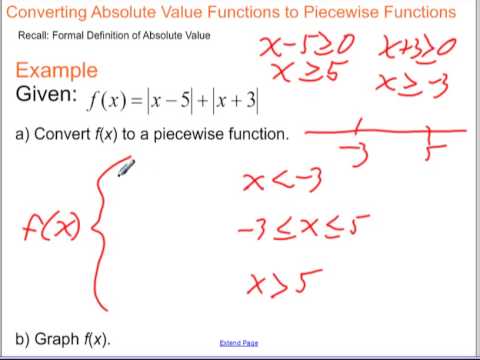
3. Piecewise definition: To define the absolute value function algebraically, it can be written as a piecewise function:
– For x ≥ 0, |x| = x.
– For x < 0, |x| = -x.
4. Absolute value property: The absolute value function satisfies the property |ab| = |a| |b| for any real numbers a and b.
5. Triangle inequality: The absolute value function satisfies the triangle inequality property, which states that for any real numbers a and b, |a + b| ≤ |a| + |b|. This means that the absolute value of the sum of two numbers is less than or equal to the sum of their absolute values.
These properties make the absolute value function useful in various areas of mathematics and real-world applications. It is commonly used to represent distances, find the solutions to equations, and define the concept of absolute difference.
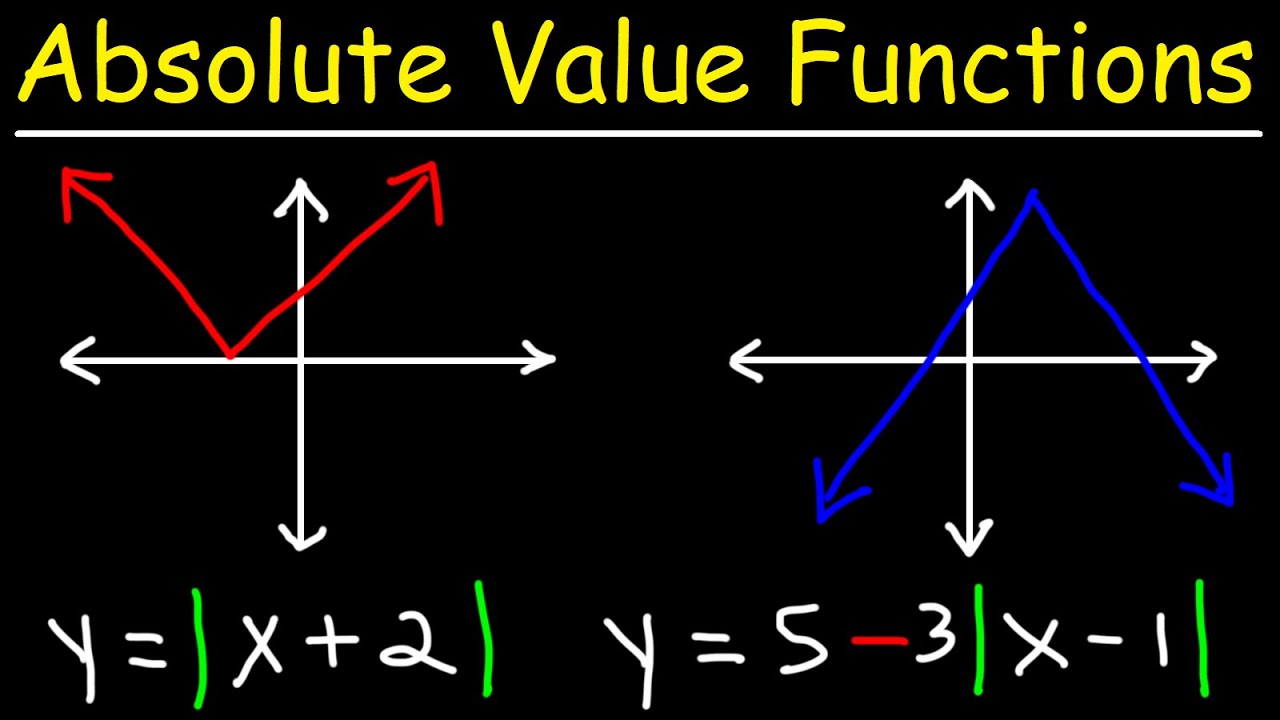
Graphical Representation of the Absolute Value Function
The graphical representation of the absolute value function is a V-shaped graph. It consists of two line segments, one opening upwards and the other opening downwards, intersecting at a point called the vertex. The vertex is located at the origin (0,0).
The line segment opening upwards represents all the positive values of the function, while the line segment opening downwards represents all the negative values of the function. The x-intercept, where the graph intersects the x-axis, is always at the vertex (0,0).
The absolute value function can be expressed as f(x) = |x|. It takes any real number x as input and returns the absolute value of x as the output. The absolute value of a number is its distance from zero on a number line and is always positive.
For example, f(2) = |2| = 2, since 2 is a positive number. Similarly, f(-2) = |-2| = 2, since the absolute value of -2 is also 2.
In summary, the graphical representation of the absolute value function is a V-shaped graph that opens upwards and downwards, with the vertex at the origin (0,0). The absolute value function returns the positive value of any input and is represented by the equation f(x) = |x|.
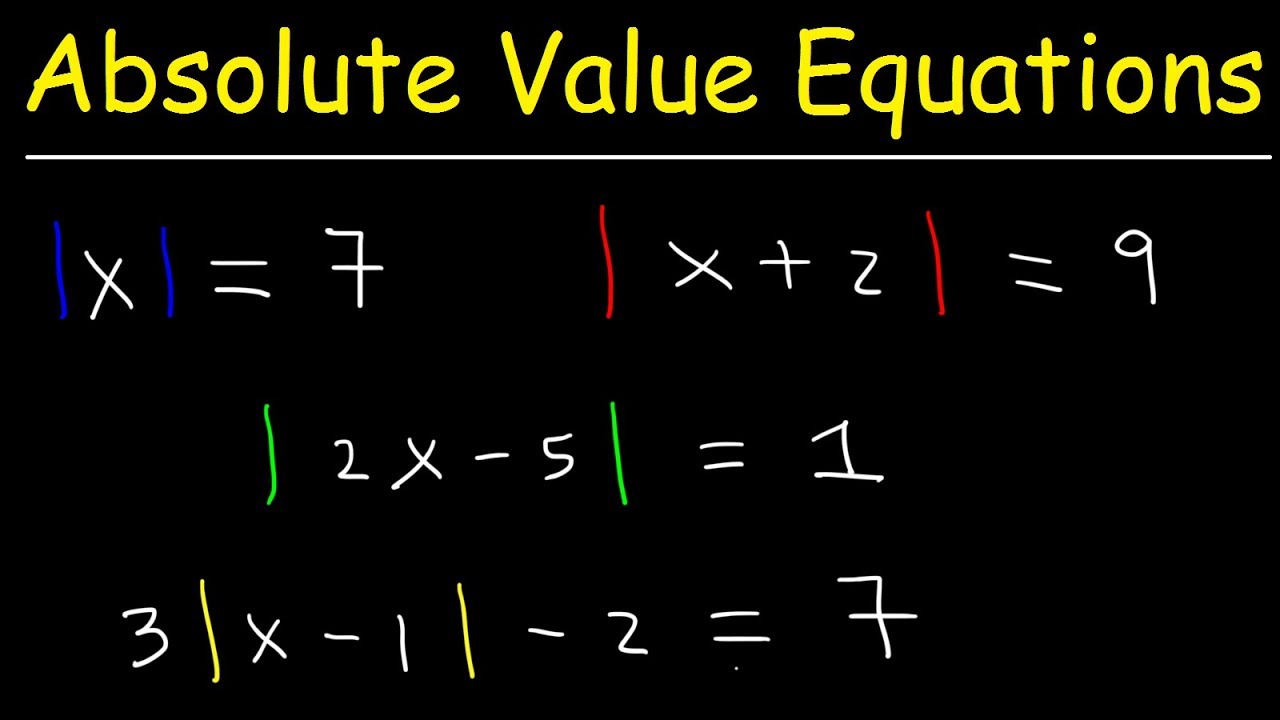
Solving Equations Involving the Absolute Value Function
To solve equations involving the absolute value function, you need to isolate the absolute value term and consider two cases: when the expression inside the absolute value is positive and when it is negative.
Here are the general steps to solve an equation involving the absolute value function:
1. Write the equation in the form |expression| = constant.
2. Consider two cases:
a. When the expression inside the absolute value is positive:
Solve the equation without the absolute value symbols, treating the expression inside the absolute value as if it were positive.
b. When the expression inside the absolute value is negative:
Change the sign of the expression inside the absolute value, remove the absolute value symbols, and solve the resulting equation.
3. Check your solutions by substituting them back into the original equation to ensure they satisfy the equation.
Here’s an example to illustrate the process:
Problem: Solve the equation |2x + 3| = 9.
Solution:
1. The equation is already in the form |expression| = constant, with the expression being 2x + 3 and the constant being 9.
2. Consider two cases:
a. When 2x + 3 is positive:
Solve the equation without the absolute value symbols: 2x + 3 = 9.
Simplify and solve for x: 2x = 6, x = 3.
b. When 2x + 3 is negative:
Change the sign of 2x + 3: -(2x + 3) = 9.
Simplify and solve for x: -2x – 3 = 9, -2x = 12, x = -6.
3. Check the solutions:
Substitute x = 3: |2(3) + 3| = 9, |6 + 3| = 9, |9| = 9 (True).
Substitute x = -6: |2(-6) + 3| = 9, |-12 + 3| = 9, |-9| = 9 (True).
The solutions to the equation |2x + 3| = 9 are x = 3 and x = -6.
Applications of the Absolute Value Function
The absolute value function, denoted by |x|, is a mathematical function that returns the positive magnitude of a number. It essentially measures the distance of a number from zero on the number line. Here are some applications of the absolute value function:
1. Distance: The absolute value function can be used to find the distance between two points on a number line. For example, if you have two points a and b, the distance between them would be |b – a|.
2. Magnitude: In physics, the absolute value function is often used to calculate the magnitude of a physical quantity. For example, the magnitude of a vector can be found using the absolute value function.
3. Inequality: The absolute value function is commonly used to solve inequalities. When solving absolute value inequalities, you typically set up two separate cases – one where the expression inside the absolute value is positive and one where it is negative.
4. Modulus function: The absolute value function is also referred to as the modulus function. It is used in complex number theory to find the modulus or absolute value of a complex number, which represents its distance from the origin in the complex plane.
5. Statistical analysis: The absolute value function can be used in statistical analysis to calculate differences or deviations from a mean or average value. For example, the absolute deviation measures how far each data point is from the mean without considering the direction.
6. Optimization problems: The absolute value function appears in various optimization problems where the objective is to maximize or minimize a quantity. In such cases, the absolute value expression may represent a constraint or objective function.
These are just a few examples of how the absolute value function is used in various fields, including mathematics, physics, statistics, and optimization. Its versatility makes it an essential tool in mathematical modeling and solving real-world problems.
Topics related to Absolute value function
How To Solve Absolute Value Equations, Basic Introduction, Algebra – YouTube
How To Solve Absolute Value Equations, Basic Introduction, Algebra – YouTube
The Absolute Value Function – YouTube
The Absolute Value Function – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Antics – Absolute Value – YouTube
Math Antics – Absolute Value – YouTube
How To Graph Absolute Value Functions – Domain & Range – YouTube
How To Graph Absolute Value Functions – Domain & Range – YouTube
What is Absolute Value? | Absolute Value Examples | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
What is Absolute Value? | Absolute Value Examples | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
Graphs of absolute value functions | Functions and their graphs | Algebra II | Khan Academy – YouTube
Graphs of absolute value functions | Functions and their graphs | Algebra II | Khan Academy – YouTube
Writing an Absolute Value as a Piecewise-Defined Function – YouTube
Writing an Absolute Value as a Piecewise-Defined Function – YouTube
Converting absolute value functions into piecewise functions – YouTube
Converting absolute value functions into piecewise functions – YouTube
القيمة المطلقة Absolute Value بالتفصيل وكيف نحل معادلة بيانياً وجبرياً – YouTube
القيمة المطلقة Absolute Value بالتفصيل وكيف نحل معادلة بيانياً وجبرياً – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.