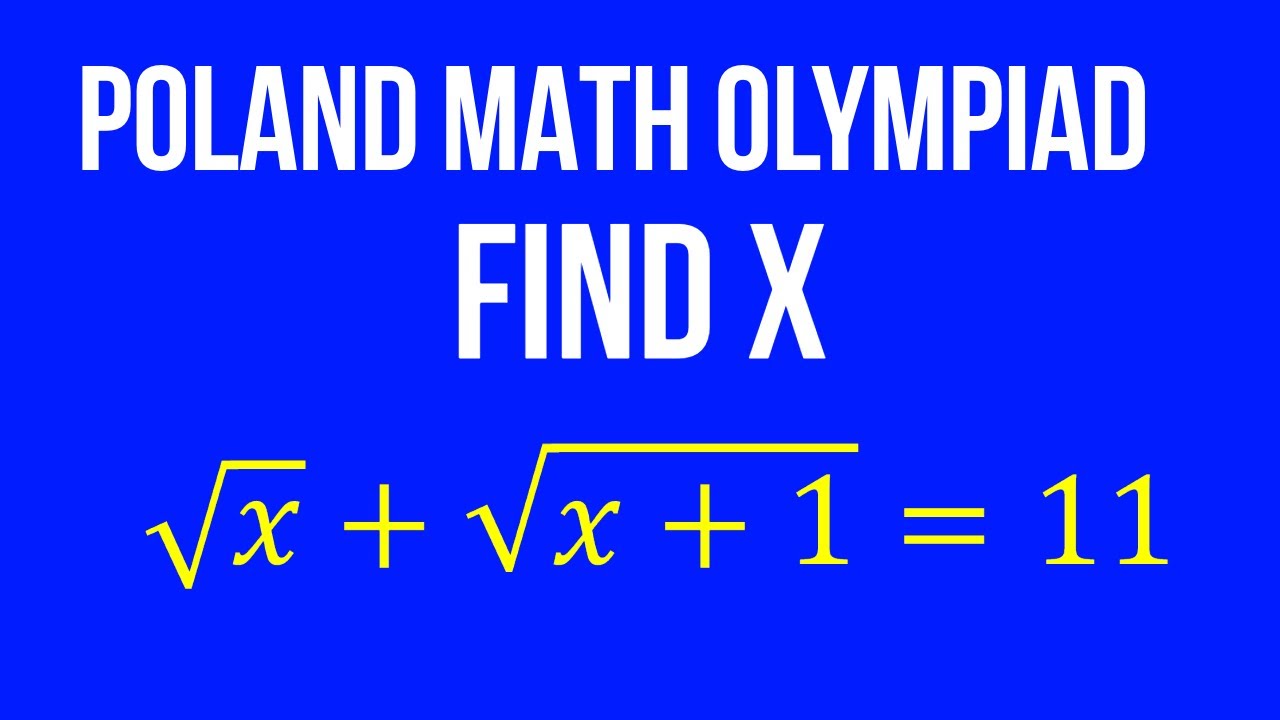Definition of Equilateral in Mathematics
In mathematics, an equilateral shape or figure refers to a shape or figure that has all sides of equal length.
For example, an equilateral triangle is a triangle that has all three sides of equal length, meaning each side is the same length as the other two sides. Similarly, an equilateral polygon is a polygon with all sides of equal length.
Equilateral shapes have some unique properties. For instance, in an equilateral triangle, all three angles are equal to 60 degrees. In an equilateral polygon, all interior angles are also equal. Equilateral shapes are symmetric and have a high degree of regularity.
Characteristics of Equilateral Figures
Equilateral figures are defined by the following characteristics:
1. All sides are congruent: In an equilateral figure, all sides are of equal length. This means that if you measure any two sides of the figure, they will be the same length.
2. All angles are congruent: In an equilateral figure, all angles are equal. Specifically, each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees.
3. Symmetry: Equilateral figures exhibit symmetry. This means that if you draw a line through the center of the figure, dividing it into two halves, each half will be a mirror image of the other.
4. Regularity: Equilateral figures are regular polygons, meaning they have equal sides and equal angles. Examples of equilateral figures include equilateral triangles, equilateral quadrilaterals (squares), equilateral pentagons, and so on.
5. High degree of symmetry: Equilateral figures have rotational symmetry. This means that if you rotate the figure around its center by a certain angle, it will appear exactly the same as the original figure.
6. Constrained geometric properties: Due to their regularity, equilateral figures have certain geometric properties. For example, in an equilateral triangle, the altitudes, medians, and angle bisectors are all the same segment.
Overall, equilateral figures are characterized by their equal sides, equal angles, symmetry, and regularity. These properties make them useful in various mathematical and geometric contexts.
Properties of Equilateral Triangles
The properties of an equilateral triangle include:
1. All three sides are of equal length: In an equilateral triangle, all three sides have the same length. This property distinguishes it from other types of triangles.
2. All three angles are of equal measure: Each angle in an equilateral triangle is 60 degrees. This property also makes it distinct from other types of triangles.
3. The sum of the angles is always 180 degrees: Since all three angles of an equilateral triangle are equal, their sum will always be 180 degrees. This property holds true for all triangles.
4. The altitude, median, and angle bisector all coincide: In an equilateral triangle, the line segments drawn from any vertex to the opposite side (including the altitude, median, and angle bisector) will all coincide with each other. This means that the centroid, circumcenter, and incenter are all the same point.
5. It has rotational symmetry of order 3: An equilateral triangle can be rotated 120 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise around its centroid, and it will look the same. This rotational symmetry gives it a total of three possible positions.
6. It has reflectional symmetry: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry. Each line is formed by folding the triangle so that one side overlaps the other. These lines divide the triangle into three congruent parts.
7. It has the least perimeter for a given area: Among all triangles with a given area, the equilateral triangle has the smallest perimeter. This property is derived from the fact that an equilateral triangle maximizes the area for a given perimeter.
8. It can be used to tessellate a plane: By repeating equilateral triangles congruently and without gaps or overlaps, you can fill the entire plane. This property is useful in various mathematical and artistic applications.
Examples of Equilateral Figures
Examples of equilateral figures include:
1. Equilateral Triangle: All three sides and angles of an equilateral triangle are equal.
2. Equilateral Pentagon: A polygon with five equal sides and five equal angles.
3. Equilateral Hexagon: A polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles.
4. Equilateral Octagon: A polygon with eight equal sides and eight equal angles.
5. Equilateral Pyramid: A three-dimensional figure with an equilateral triangle as its base and all triangular faces are equilateral.
6. Equilateral Prism: A three-dimensional figure with an equilateral polygon as its base and all lateral faces are rectangles.
7. Equilateral Cone: A three-dimensional figure with a circular base and the apex connected to the center of the base, forming equilateral triangles.
8. Equilateral Cylinder: A three-dimensional figure with circular bases and all lateral faces are rectangles of equal height.
These are just a few examples of equilateral figures, and there are many more variations and combinations possible.
Applications of Equilateral Shapes in Mathematics
shapes are widely used in various areas of mathematics due to their unique properties and symmetry. Some applications of equilateral shapes in mathematics include:
1. Geometry: Equilateral triangles are fundamental in the study of geometry. Their sides and angles are equal, which allows for the derivation and proof of various geometrical theorems. Equilateral polygons, such as equilateral hexagons or equilateral parallelograms, are also used in geometry to study properties of regular polygons and tessellations.
2. Trigonometry: Equilateral triangles are particularly useful in trigonometry. The angles of an equilateral triangle are all 60 degrees, which makes it easy to calculate trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent. Equilateral triangles can also be used to prove trigonometric identities and solve various trigonometric equations.
3. Calculus and Analytic Geometry: Equilateral shapes, such as equilateral circles or equilateral cylinders, are used in calculus and analytic geometry to study curves and surfaces. Equilateral circles are used in the definition of trigonometric functions and are fundamental in calculus, while equilateral cylinders help determine the volume and surface area of various geometric figures.
4. Number Theory: Equilateral shapes are utilized in number theory to study properties of numbers. For instance, equilateral triangles are used to investigate triangular numbers, which are a sequence of numbers that can be represented by equilateral triangles with dots. These patterns in equilateral triangles can reveal properties of divisibility and factors of numbers.
5. Graph Theory: In graph theory, equilateral shapes can be used to represent nodes or vertices in a graph. Equilateral polygons, such as an equilateral pentagon or equilateral hexagon, can be used to construct regular graphs with equal distances between nodes. This can help analyze connectivity, cycles, and other properties of graphs.
6. Combinatorics: Equilateral shapes are used in combinatorics to study arrangements and combinations. For example, equilateral grids or arrangements of equilateral triangles can be used to count the number of possible ways to arrange objects or analyze patterns and symmetries in the arrangements.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of equilateral shapes in mathematics. Equilateral shapes provide a foundation for understanding various mathematical concepts and play a crucial role in many mathematical fields.
Topics related to Equilateral
Math Antics – Triangles – YouTube
Math Antics – Triangles – YouTube
GCSE Maths – Types of Triangle #100 – YouTube
GCSE Maths – Types of Triangle #100 – YouTube
60 degree angle with compass | Construction of equilateral triangle – YouTube
60 degree angle with compass | Construction of equilateral triangle – YouTube
Area of an Equilateral Triangle | SAT Math Shorts 01 | SAT Math with JP Sir – YouTube
Area of an Equilateral Triangle | SAT Math Shorts 01 | SAT Math with JP Sir – YouTube
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangle Theorem – YouTube
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangle Theorem – YouTube
What is the area of the Circle? | (Step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
What is the area of the Circle? | (Step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
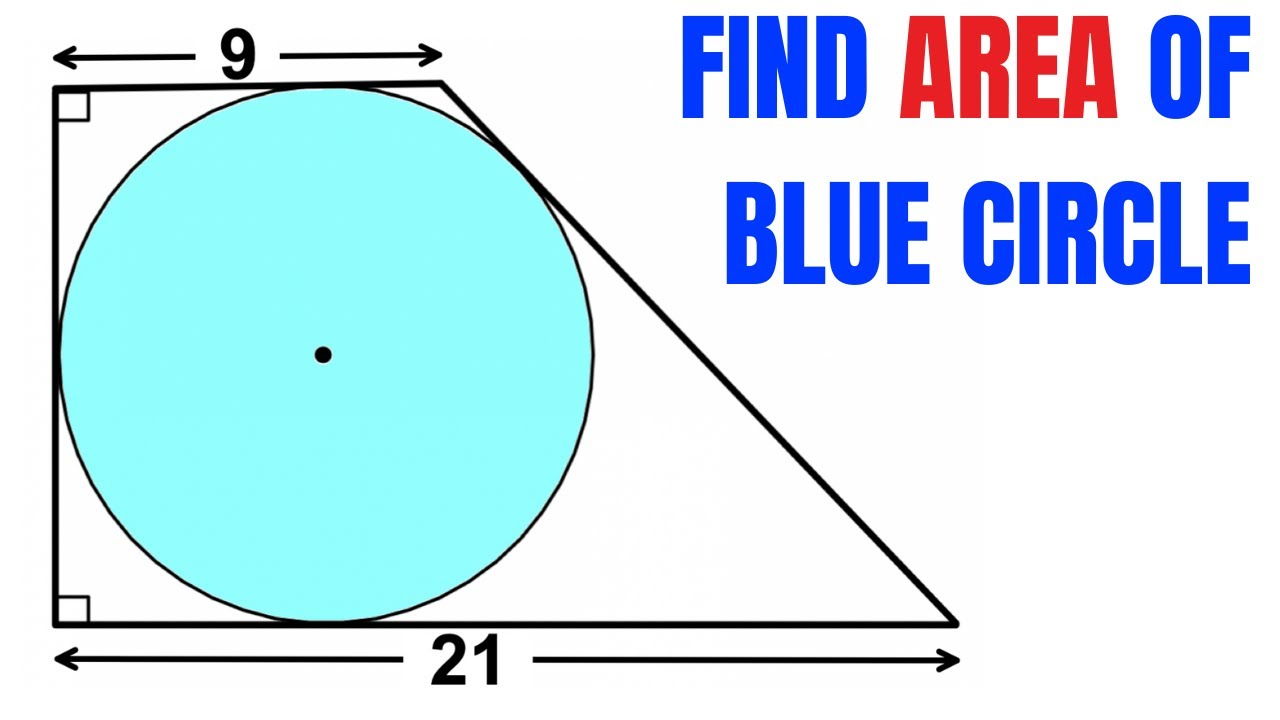
Pitot Theorem Proof | Find area of the blue shaded circle | Tangential Quadrilateral | Trapezoid – YouTube
Pitot Theorem Proof | Find area of the blue shaded circle | Tangential Quadrilateral | Trapezoid – YouTube
Poland math olympiad problem I I SAT I MCAT I SSC I IXth I Xth I KVYP I NTSE I GRE I JEE MAIN – YouTube
Poland math olympiad problem I I SAT I MCAT I SSC I IXth I Xth I KVYP I NTSE I GRE I JEE MAIN – YouTube
Find Area of Triangle ABC | Maths Olympiad | Important Geometry Skills Explained | 2 Methods – YouTube
Find Area of Triangle ABC | Maths Olympiad | Important Geometry Skills Explained | 2 Methods – YouTube
WORKING OF AEROPLANE (HINGLISH) – YouTube
WORKING OF AEROPLANE (HINGLISH) – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.