Defining Intersection in Mathematics
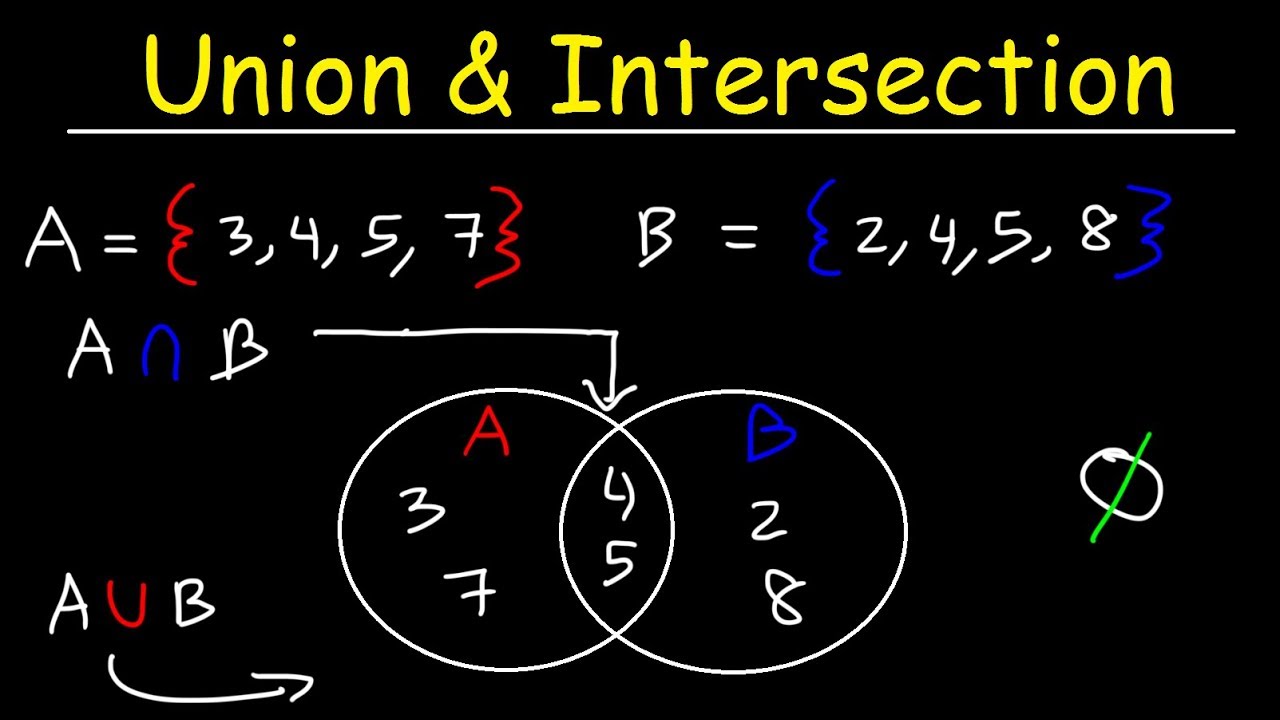
In mathematics, the intersection refers to the common elements or values shared between two or more sets. It is denoted by the symbol ∩ (an upside-down U). In other words, the intersection of sets A and B represents the set containing all the elements that are present in both A and B. If there is no common element between the sets, the intersection would be an empty set denoted by ∅. For example, if A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5}, their intersection would be {3, 4}, as these are the elements present in both sets.
Set Theory and Intersection
Set theory is a branch of mathematical logic that deals with the study of sets, which are collections of distinct objects. One of the fundamental operations in set theory is the intersection.
The intersection of two sets, denoted by the symbol ∩, is the set that contains all the elements that are common to both sets. In other words, it is the set of elements that are present in both sets simultaneously.
For example, consider two sets: A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5}. The intersection of these two sets would be the set {3, 4}, as these are the elements that are common to both A and B.
The intersection operation can be extended to more than two sets as well. For instance, if we have three sets A, B, and C, then the intersection of these three sets would be the set of elements that are present in all three sets.
It is important to note that if the intersection of two sets is empty, i.e., there are no elements that are common to both sets, then the two sets are said to be disjoint.
The intersection operation plays a significant role in various areas of mathematics, including set theory, logic, and calculus. It allows mathematicians to analyze and manipulate sets, identify common elements, and establish relationships between different sets.
Intersection of Lines and Planes
The intersection of lines and planes refers to the point or set of points where a line and a plane meet.
In general, a line can intersect a plane in three different ways:
1. No intersection: The line and the plane do not intersect at all. This means that the line lies completely outside the plane or is parallel to it.
2. Single point: The line intersects the plane at a single point. This occurs when the line crosses the plane at a specific location.
3. Infinite intersection: The line lies entirely on the plane. This happens when the line is contained within the plane and extends infinitely in both directions.
The specific intersection of a line and a plane can be determined using various methods, such as comparing the equations of the line and the plane in three-dimensional coordinate systems. This allows us to find the coordinates or equations of the intersection point(s) or determine if there is an intersection at all.
Intersection of Curves
The intersection of curves refers to the points where two or more curves meet or cross each other on a graph. These points represent the common solutions or values that satisfy the equations represented by the curves. The number of intersections can vary depending on the nature of the curves and their equations. In algebraic terms, finding the intersection involves solving the equations simultaneously to determine the values of variables that satisfy all the equations at once. The intersection can provide important information about relationships, solutions, or common properties between the curves.
Intersection in Probability and Statistics
The term “intersection” is used in both probability and statistics, but with slightly different meanings.
In probability, the intersection refers to the event where two or more events occur simultaneously. It is denoted by the symbol “∩”. For example, if we have events A and B, the intersection of A and B (A ∩ B) represents the event where both A and B occur together.
In statistics, the intersection refers to the common elements or observations that are present in two or more sets or groups. It is used to find the overlapping or shared characteristics between different groups or variables. It is similar to the concept of intersection in set theory. For example, if we have two datasets representing the heights of men and women, their intersection would represent the common heights that occur in both groups.
In both probability and statistics, the intersection is used to analyze the relationship between different events or groups and to determine the likelihood of specific outcomes or characteristics occurring together.
Topics related to Intersection
Intersection of Sets, Union of Sets and Venn Diagrams – YouTube
Intersection of Sets, Union of Sets and Venn Diagrams – YouTube
OPERATIONS ON SETS – Union, Intersection, Difference, and Complement of a Set | Ms Rosette – YouTube
OPERATIONS ON SETS – Union, Intersection, Difference, and Complement of a Set | Ms Rosette – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Sets: Union, Intersection, Complement – YouTube
Sets: Union, Intersection, Complement – YouTube
Union and Intersection of Sets | Set Operations | Grade 7 Math @MathTeacherGon – YouTube
Union and Intersection of Sets | Set Operations | Grade 7 Math @MathTeacherGon – YouTube
Intersection and union of sets | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
Intersection and union of sets | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (ABC, intersections, unions and brackets) – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (ABC, intersections, unions and brackets) – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (A intersection B, A' union B') – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (A intersection B, A' union B') – YouTube
A intersection B | Sets | same values | class 9 &10 | – YouTube
A intersection B | Sets | same values | class 9 &10 | – YouTube
Intersection of 2 Sets and Venn Diagram || Math || Sets || #shorts – YouTube
Intersection of 2 Sets and Venn Diagram || Math || Sets || #shorts – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.