Definition of a right triangle
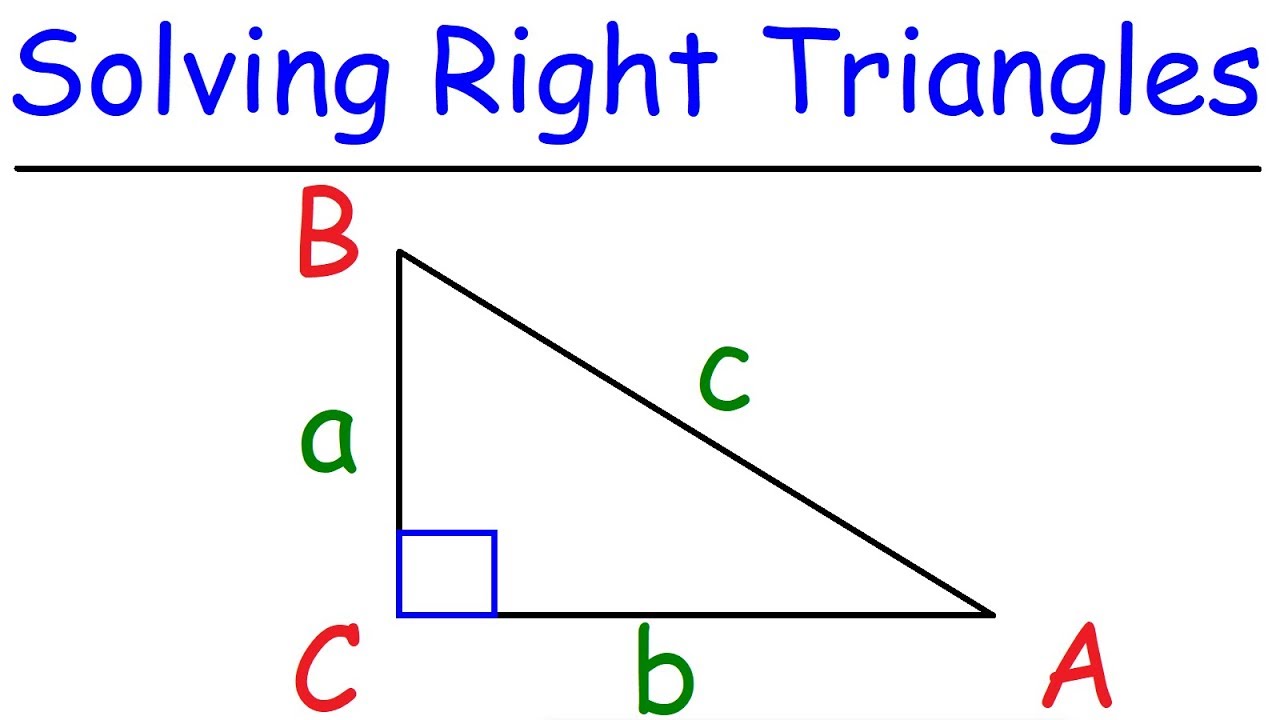
A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees, which is referred to as a right angle. The other two angles in a right triangle are acute angles, meaning they are less than 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is the longest side and is called the hypotenuse. The other two sides are called the legs of the right triangle. The relationship between the three sides of a right triangle is defined by the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs.
Properties of a right triangle
A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring 90 degrees, also known as a right angle. Here are some properties specific to right triangles:
1. Right Angle: A right triangle has one angle measuring 90 degrees. This angle is formed by the intersection of the two shorter sides, known as the legs, in the triangle.
2. Hypotenuse: The longest side of a right triangle is called the hypotenuse. It is opposite to the right angle and is always the side opposite the 90-degree angle.
3. Pythagorean Theorem: The Pythagorean theorem describes the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. It states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Mathematically, it is represented as c^2 = a^2 + b^2, where c represents the hypotenuse and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
4. Special Ratios: Right triangles have special ratio relationships between their sides. For example, the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse is known as the sine of the angle. Similarly, the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse is known as the cosine of the angle. These ratios are the foundation of trigonometry.
5. Similarity: Right triangles that have the same angles are considered similar. This means that their corresponding sides are proportional, and their corresponding angles are congruent.
6. Height and Base: A right triangle can be divided into two smaller triangles by drawing an altitude, also known as a height, from the right angle to the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse can then be considered as the base of the triangle, and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the vertex opposite the base.
These are some of the main properties of right triangles. They have unique characteristics that make them useful in various mathematical and real-world applications.
Pythagorean Theorem and right triangles
A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring 90 degrees, which is also called a right angle. The other two angles of a right triangle are acute angles, which means they are less than 90 degrees.
The Pythagorean Theorem is a relationship between the sides of a right triangle. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
The hypotenuse is defined as the side opposite the right angle in a right triangle. It is the longest side of the triangle.
The other two sides of a right triangle are called the legs. One leg is the side adjacent to the angle you are considering, and the other leg is the side opposite to that angle.
By using the Pythagorean Theorem, we can calculate the length of one side of a right triangle if we know the lengths of the other two sides. Conversely, if we know the length of the hypotenuse and one leg of a right triangle, we can calculate the length of the other leg using the Pythagorean Theorem.
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in geometry and has various applications in real-life situations, such as calculating distances, determining the heights of objects, and solving problems involving right triangles.
Special types of right triangles
Right triangles are a type of triangle that have one angle measuring 90 degrees, commonly referred to as a right angle. They are known for having some special characteristics and types, including:
1. Pythagorean triples: These are right triangles with integer side lengths that satisfy the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Some examples of Pythagorean triples include (3, 4, 5), (5, 12, 13), and (8, 15, 17).
2. Isosceles right triangle: This is a right triangle where two sides are of equal length, forming two congruent acute angles. Since one angle is already fixed at 90 degrees, the other two angles in an isosceles right triangle are each 45 degrees. The side lengths can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem.
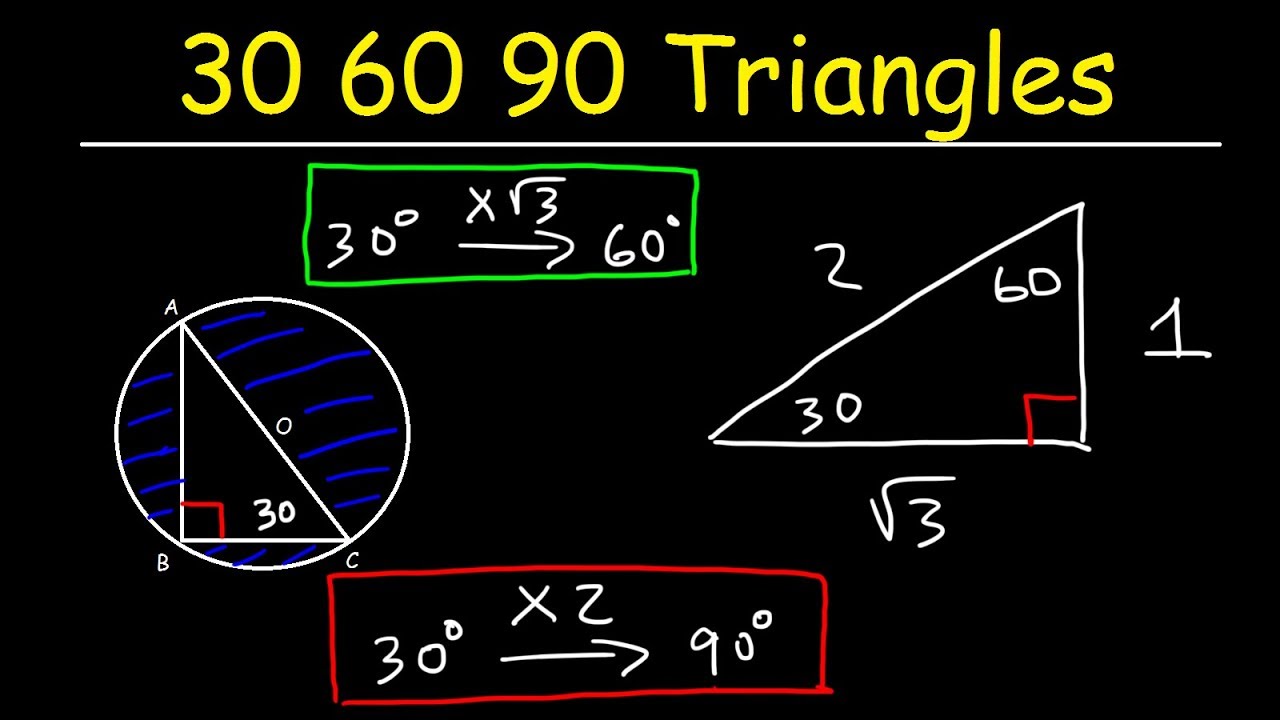
3. 30-60-90 triangle: This is a right triangle with angles measuring 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees. The lengths of the sides in this triangle have a specific relationship: the hypotenuse is twice the length of the shorter leg, and the longer leg is equal to the shorter leg times the square root of 3. For example, if the shorter leg is 5 units, the longer leg will be 5√3 units, and the hypotenuse will be 10 units.
4. 45-45-90 triangle: This is a right triangle with two angles measuring 45 degrees and one angle measuring 90 degrees. The two legs of this triangle are of equal length, and the hypotenuse is equal to the length of the legs times the square root of 2. For example, if the legs are both 3 units, the hypotenuse will be 3√2 units.
These special types of right triangles are often used in geometry and trigonometry to simplify calculations and solve problems involving right triangles.
Applications of right triangles in mathematics and real life
Right triangles have numerous applications in mathematics and real-life situations. Some of the key uses include:
1. Pythagorean Theorem: The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental concept in right triangles. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This theorem is widely used in various fields of math and science.
2. Trigonometry: Right triangles are used in trigonometry to study the relationships between the angles and sides of a triangle. The three primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, and tangent) are defined based on the sides of a right triangle.
3. Angle measurement: Right triangles are crucial for measuring angles using trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. These functions relate the lengths of the sides of a right triangle to the angles.
4. Navigation: In navigation, right triangles are used to determine distances on land or sea. By using angles and measurements from the right triangle formed between two points of reference, navigators can calculate distances and bearings.
5. Surveying: Surveying involves measuring distances, elevations, and angles. Right triangles are commonly used to calculate elevations and distances between points. Surveying instruments like theodolites and total stations rely on right triangles to determine angles and distances accurately.
6. Architecture and engineering: Right triangles find applications in architecture and engineering, where they are used to calculate the dimensions, angles, and stability of structures. For example, architects and engineers use right triangles to determine the slopes and angles of roofs and staircases.
7. Electronics and signal processing: Right triangles play a vital role in the analysis and design of electronic circuits and signal processing systems. They are used to calculate phase differences, angles of waveform distortion, and frequency responses.
8. Physics: Right triangles are heavily utilized in physics to analyze forces, motions, and components of vectors. They are used to break down forces or vectors into their components along different axes.
Overall, right triangles are a fundamental concept in mathematics and have countless practical applications in various fields, including science, engineering, navigation, and design.
Topics related to Right triangle
Trigonometry – How To Solve Right Triangles – YouTube
Trigonometry – How To Solve Right Triangles – YouTube
Trigonometry: Solving Right Triangles… How? (NancyPi) – YouTube
Trigonometry: Solving Right Triangles… How? (NancyPi) – YouTube
How to find Right angle triangle Side :- Pythagoras theorem – YouTube
How to find Right angle triangle Side :- Pythagoras theorem – YouTube
Elegant way to find the Perimeter of a right triangle | (step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
Elegant way to find the Perimeter of a right triangle | (step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
Special Right Triangles – 30 60 90 – Geometry & Trigonometry | SAT Math – YouTube
Special Right Triangles – 30 60 90 – Geometry & Trigonometry | SAT Math – YouTube
What is the area of the Circle? | (Step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
What is the area of the Circle? | (Step-by-step explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
Can you find area of the Blue semicircle in the square? | (Geometry skills explained) | #math #maths – YouTube
Can you find area of the Blue semicircle in the square? | (Geometry skills explained) | #math #maths – YouTube
Let's think outside the box | Find Area of the Trapezoid | Trapezium | (Trapezoid) | #math #maths – YouTube
Let's think outside the box | Find Area of the Trapezoid | Trapezium | (Trapezoid) | #math #maths – YouTube
Let's Think outside the Box! | Find the chord length AB | (Simple explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
Let's Think outside the Box! | Find the chord length AB | (Simple explanation) | #math #maths – YouTube
ADRE 2.0, Assam Police, Pollution Board 2023 (Grade III and IV) | Maths Class By Abhijit Sir – YouTube
ADRE 2.0, Assam Police, Pollution Board 2023 (Grade III and IV) | Maths Class By Abhijit Sir – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.