Definition of Domain
Domain can have several meanings, depending on the context. Here are two common definitions:
1. In the context of the internet, a domain refers to the unique name that identifies a website. It consists of two parts: the domain name (e.g., example.com) and the domain extension (e.g., .com, .org, .net). It is used to locate and access websites on the internet.
2. In mathematics, the domain refers to the set of input values for which a function or equation is defined. It represents the range of permissible inputs that can be plugged into a mathematical expression or function without resulting in an error. The domain can be specified as a set of numbers, a range, or specific conditions that the input must satisfy.
Importance of Domain in Mathematics
In mathematics, the domain refers to the set of values for which a function or equation is defined. It is important because it determines the input values that can be used with a function to obtain meaningful and valid results.
Understanding the domain of a function is crucial for various reasons:
1. Validity of operations: Knowing the domain of a function helps in determining which operations can be performed on it. For example, square root functions are only defined for non-negative numbers, so the domain of such a function would exclude negative numbers.
2. Range of values: The domain helps establish the range of values for which the function will produce output. It allows us to identify the potential outputs or solutions to a problem.
3. Avoiding division by zero: Many functions involve division, and division by zero is undefined. Therefore, knowing the domain helps avoid situations where dividing by zero may occur.
4. Identifying exclusions: The domain can help identify any values that need to be excluded to prevent certain mathematical anomalies. For instance, in a rational function, any inputs that would result in a denominator of zero must be excluded from the domain.
5. Mathematical modeling: When using mathematics to model real-world phenomena, determining the appropriate domain helps ensure that the model accurately represents the problem at hand. Different situations may have different restrictions on the domain, and understanding these restrictions is essential for accurate modeling.
In summary, the domain is of utmost importance in mathematics as it helps define the valid inputs for a function, determines the range of possible outputs, avoids mathematical anomalies, and ensures the accuracy of mathematical modeling.
Examples of Domain
Examples of Domain:
1. www.amazon.com – the domain for the online shopping platform Amazon.
2. www.nytimes.com – the domain for The New York Times, a leading newspaper in the United States.
3. www.apple.com – the domain for Apple Inc., a multinational technology company.
4. www.microsoft.com – the domain for Microsoft Corporation, a software and technology company.
5. www.spotify.com – the domain for Spotify, a popular music streaming platform.
Examples of Domain:
1. .com – a top-level domain commonly used by commercial websites.
2. .org – a top-level domain commonly used by non-profit organizations.
3. .edu – a top-level domain reserved for educational institutions such as universities and colleges.
4. .gov – a top-level domain used by government agencies and departments.
5. .net – a top-level domain originally intended for network-related websites, now used by a variety of entities.
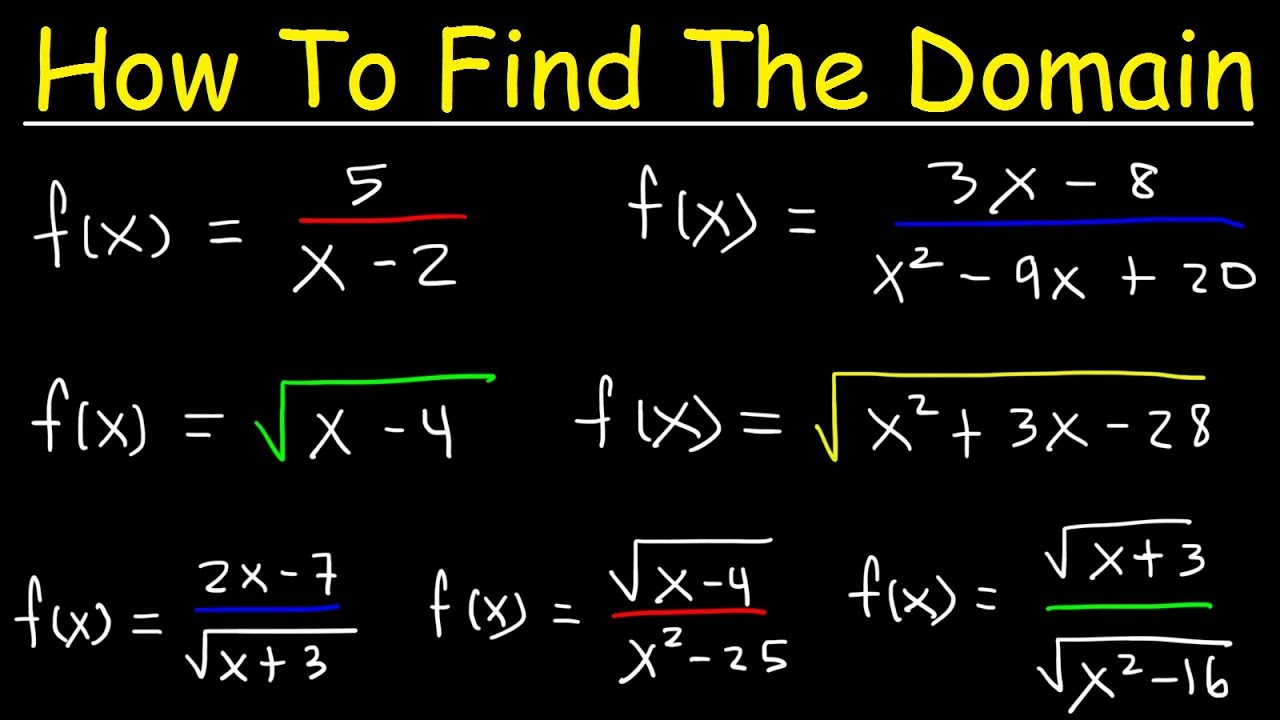
Finding the Domain of a Function
The domain of a function refers to all the possible values of the input (independent variable) for which the function is defined. In other words, it is the set of all values that can be plugged into the function to yield a valid output.
To find the domain of a function, you need to consider any restrictions or limitations on the input values. Here are some common cases to consider:
1. Rational functions: Look out for denominators, since they cannot be zero. Exclude any values that would make the denominator zero from the domain.
2. Square roots: The radicand (the expression inside the square root) must be positive or zero. Exclude any values that would make the radicand negative.
3. Exponents: If the function has an exponent, such as x^2, then any real number can be plugged in. There are no restrictions on the domain.
4. Logarithmic functions: The argument of the logarithm must be positive. Exclude any values that would make the argument negative or zero.
5. Trigonometric functions: These functions have a periodic nature, so they are defined for all real numbers. There are no restrictions on the domain.
Additionally, there may be other specific restrictions depending on the problem or context of the function. It is important to evaluate and analyze the function to determine any specific limitations on the domain.
Once you have determined any restrictions or limitations, you can describe the domain in interval notation, set-builder notation, or with inequalities, depending on the specific situation.
Applications of Domain in Mathematics
In mathematics, the concept of domain is used in various applications. Some common applications of domain include:
1. In functions: The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values for which the function is defined. It helps to determine the range of values for which the function can be evaluated.
2. In calculus: In calculus, the domain is important for determining the limits, continuity, and differentiability of a function. It helps in studying the behavior of functions at specific points or intervals.
3. In solving equations: When solving equations, the domain provides the restrictions on the values of variables that satisfy the equation. It helps in finding valid solutions and excluding invalid ones.
4. In trigonometry: The domain of trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent is limited to specific ranges of angles. Knowledge of their domain helps in understanding their periodic behavior and properties.
5. In linear programming: Domain constraints play a crucial role in linear programming problems. The domain of variables determines the feasible region, i.e., the set of possible values that satisfy the given constraints.
6. In probability theory: The domain of a random variable specifies the possible values it can take. It helps in defining the probability distribution and determining the likelihood of different outcomes.
7. In set theory: The domain of a function is often related to the set of elements in the Cartesian product of two sets. It helps in studying the relationships between sets and functions.
In summary, the domain is a fundamental concept in mathematics that has applications in various branches, including algebra, calculus, trigonometry, probability theory, and set theory.
Topics related to Domain
How To Find The Domain of a Function – Radicals, Fractions & Square Roots – Interval Notation – YouTube
How To Find The Domain of a Function – Radicals, Fractions & Square Roots – Interval Notation – YouTube
What is the domain of a function? | Functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
What is the domain of a function? | Functions | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
The Map of Mathematics – YouTube
The Map of Mathematics – YouTube
Mathematics : What Is a Domain in Math? – YouTube
Mathematics : What Is a Domain in Math? – YouTube
Maths-Domain and Range-Understanding Simple and Easy (O-Level) – YouTube
Maths-Domain and Range-Understanding Simple and Easy (O-Level) – YouTube
What's The "Domain" Of This MATH Function? – YouTube
What's The "Domain" Of This MATH Function? – YouTube
How to find domain and range of function graphs – YouTube
How to find domain and range of function graphs – YouTube
Concept of Domain,Range and Co-domain🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥#shorts #domain #codomain – YouTube
Concept of Domain,Range and Co-domain🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥#shorts #domain #codomain – YouTube
Domain and Range of sqrt(9-x^2) | asH maths – YouTube
Domain and Range of sqrt(9-x^2) | asH maths – YouTube
How to find the domain of a function – YouTube
How to find the domain of a function – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.