Definition of Permutation
Permutation refers to the arrangement or ordering of a set of objects in a particular sequence. It is a way to change the order of elements within a set. In mathematics, permutations are often represented by the symbol “P” and are used to calculate the number of possible ways to arrange objects. For example, if you have a set of three objects A, B, and C, there are six possible permutations: ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, and CBA. Permutations are widely studied in various branches of mathematics, including combinatorics and statistics.
Permutation Formula
The formula for calculating permutations is given by:
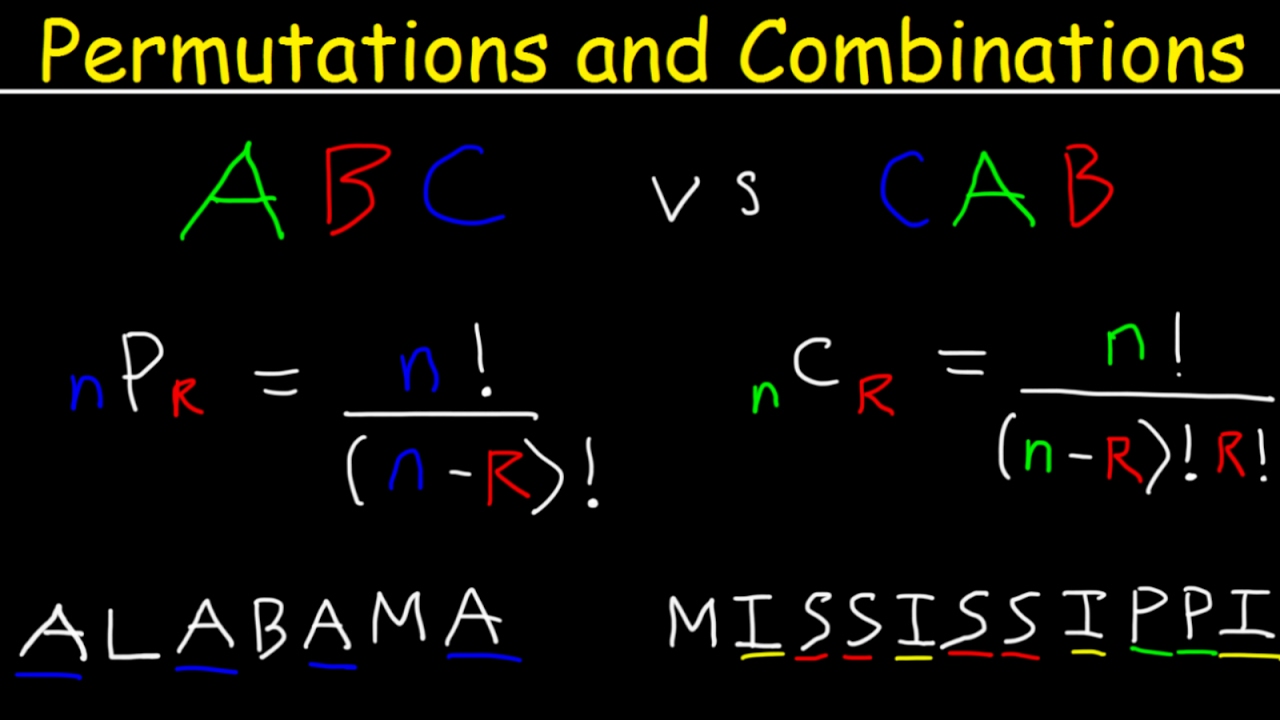
nPr = n! / (n – r)!
Here, n represents the total number of items or elements, and r represents the number of items or elements chosen at a time.
The exclamation mark (!) denotes the factorial of a number, which means multiplying the number by all positive integers less than it down to 1.
For example, if you have 5 items and want to choose 3 at a time, the permutation formula would be:
5P3 = 5! / (5 – 3)! = 5! / 2! = (5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1) / (2 x 1) = 60
So, there are 60 different permutations possible when choosing 3 items out of 5.
Permutation vs Combination
Permutation and combination are both concepts in mathematics that deal with counting and arranging objects. However, there is a difference between the two.
Permutation refers to the arrangement or ordering of objects. It focuses on the order in which objects are placed or selected. For example, if you have a set of three letters {A, B, C}, the permutations of these letters would include arrangements such as ABC, BCA, CAB, etc. Each permutation is a distinct ordering of the objects.
In permutation, the number of possible arrangements depends on the number of objects and the order in which they are arranged. The formula to calculate the number of permutations is given by nP r = n! / (n-r)!, where n represents the total number of objects and r represents the number of objects to be arranged.
Permutation is often used when the order of objects is important, such as in arranging people in a line or arranging letters to form words.
On the other hand, combination refers to the selection of objects without considering the order or arrangement. It focuses on the subsets that can be formed from a larger set of objects. For example, if you have a set of three letters {A, B, C}, the combinations of these letters could include subsets such as {A, B}, {A, C}, {B, C}, etc.
In combination, the number of possible combinations is determined by the number of objects and the number of objects in each subset. The formula to calculate the number of combinations is given by nC r = n! / (r! * (n-r)!), where n represents the total number of objects and r represents the number of objects in each subset.
Combination is often used when the order of objects is not important, such as selecting a group of people from a larger group or choosing items from a menu.
In summary, permutation deals with arranging objects in a particular order, while combination deals with selecting objects without considering the order.
Applications of Permutation in Mathematics
Permutations have various applications in mathematics, particularly in combinatorics and probability. Here are some examples:
1. Counting: Permutations can be used to count the number of different arrangements or orders of objects. For instance, you can determine the number of ways to arrange a set of letters or numbers without repetition.
2. Probability: Permutations provide a way to calculate the probability of specific outcomes. For instance, when dealing with a deck of cards, you can use permutations to determine the probability of drawing a particular hand.
3. Cryptography: Permutations are crucial in cryptography, where they are used in techniques like permutation ciphers to ensure secure communication.
4. Group theory: In abstract algebra, permutation groups are studied extensively. These groups consist of permutations of a finite set and help analyze symmetry properties of mathematical structures.
5. Graph theory: Permutations can be used to analyze permutations of vertices in a graph. This approach helps in understanding the properties of graphs and solving various graph-related problems.
6. Design theory: Permutations play a vital role in design theory, particularly in the construction of combinatorial designs, such as Latin squares and orthogonal arrays.
7. Game theory: Permutations can be utilized in analyzing strategic decision-making and outcomes in game theory scenarios, such as permutations of players’ strategies in games like poker or chess.
8. Combinatorial optimization: Permutations are helpful in solving optimization problems, such as the traveling salesman problem, where finding the best ordering of cities requires considering all possible permutations.
These are just a few examples of how permutations are applied in mathematics. In general, permutations provide a powerful tool for analyzing and solving problems related to ordering, arrangement, and counting in various mathematical domains.
Examples of Permutation Problems
1. In how many ways can the letters of the word “BANANA” be rearranged?
2. A committee of 4 people needs to be formed from a group of 10 individuals. How many different committees can be formed?
3. There are 6 books on a shelf, and each book can be placed in any order. How many different arrangements are possible?
4. In how many ways can the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 be arranged to form a 5-digit number, where repetition is not allowed?
5. A password consists of 4 letters and 2 numbers. How many different passwords are possible if each letter can only be used once, and each number can only be used once?
Topics related to Permutation
Permutation formula | Probability and combinatorics | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
Permutation formula | Probability and combinatorics | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy – YouTube
Permutations and Combinations Tutorial – YouTube
Permutations and Combinations Tutorial – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac2 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0ac2 – YouTube
Permutation | Grade 10 | Math Corner – YouTube
Permutation | Grade 10 | Math Corner – YouTube
[Discrete Mathematics] Permutation Practice – YouTube
[Discrete Mathematics] Permutation Practice – YouTube
PERMUTATION AND COMBINATION (P AND C) SHORTCUT//TRICKS FOR NDA/JEE/AIRFOCRE GROUP X/ CLASS 11 NCERT – YouTube
PERMUTATION AND COMBINATION (P AND C) SHORTCUT//TRICKS FOR NDA/JEE/AIRFOCRE GROUP X/ CLASS 11 NCERT – YouTube
Permutation and Combination – YouTube
Permutation and Combination – YouTube
even and odd permutations. – YouTube
even and odd permutations. – YouTube
Permutation and Combination #mathsscam #shorts #youtubeshorts #trending – YouTube
Permutation and Combination #mathsscam #shorts #youtubeshorts #trending – YouTube
PERMUTATION| @LoveMATHTV – YouTube
PERMUTATION| @LoveMATHTV – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.