Definition of synthetic division
Synthetic division is a method of dividing a polynomial by a linear factor using a simplified algorithm. It is often used to quickly find the quotient and remainder when dividing a polynomial by a linear expression of the form (x – c), where “c” is a constant.
The process involves systematically dividing each term of the polynomial by the constant term of the linear expression and then performing a sequence of simple additions and multiplications to arrive at the quotient and remainder.
Synthetic division is a straightforward and efficient method that allows for the division of polynomials without the need for long division. It is commonly taught and used in algebra and is particularly helpful for solving equations and finding roots of polynomials.
Steps involved in synthetic division
Synthetic division is a method used to divide a polynomial by a linear factor. Here are the steps involved:
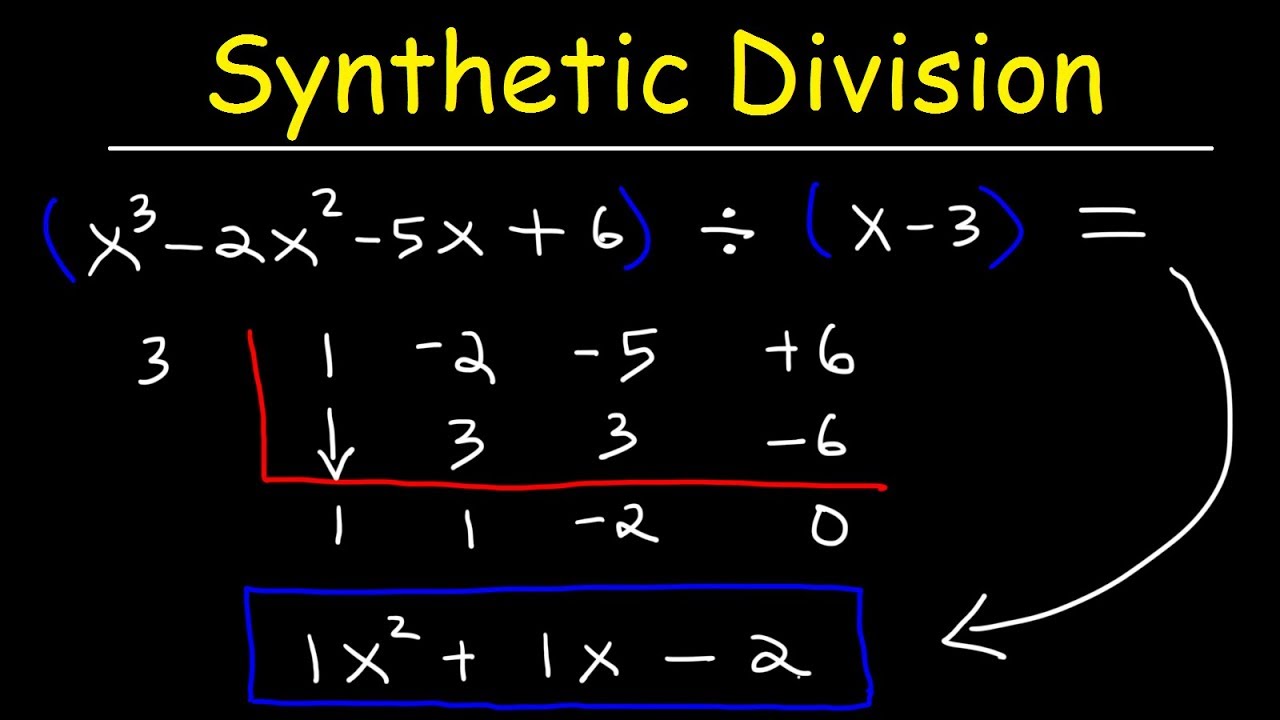
1. Write the polynomial in descending order of powers. For example, if you have a polynomial of degree 3, write it as ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d.
2. Identify the divisor, which should be a linear factor of the form x – r, where r is a constant. For example, if the divisor is x – 2, the value of r would be 2.
3. Set up the synthetic division table. Write the coefficients of the polynomial in the first row, excluding the coefficient of the highest power term.
4. In the second row, write the constant r, which is the opposite sign of the constant term in the divisor.
5. Bring down the first coefficient from the first row to the second row below the line.
6. Multiply r by the number in the second row, and write the result below the next coefficient in the first row. Repeat this process for all coefficients.
7. Add the numbers in the second row to the numbers in the first row, and write the results below the line. Repeat this process for all coefficients.
8. The numbers in the last row (excluding the remainder) represent the coefficients of the quotient polynomial.
9. Write the quotient polynomial using the coefficients obtained in the previous step.
10. The remainder is the last number in the second row.
These steps allow you to divide a polynomial by a linear factor using synthetic division.
Applications of synthetic division
Synthetic division is a method used in algebra to divide a polynomial by a binomial of the form (x – a). It is a convenient and efficient way to perform polynomial long division, especially when the divisor has the form (x – a).
Here are some common applications of synthetic division:
1. Finding the roots of a polynomial: Synthetic division can be used to determine whether a polynomial has a specific value (“a”) as a root. If the remainder obtained through synthetic division is zero, then “a” is a root of the polynomial.
2. Factoring polynomials: Synthetic division can be used to factorize polynomials. By repeatedly dividing a polynomial by its factors, you can break it down into simpler factors.
3. Solving equations: Synthetic division is often used to solve polynomial equations. By dividing the polynomial equation by a potential solution, you can eliminate that root and obtain a simpler equation.
4. Dividing polynomials: Synthetic division allows you to divide a polynomial by a binomial quickly and efficiently, without having to go through the traditional long division process.
5. Finding coefficients: Synthetic division can be used to find the coefficients of a polynomial, given the roots. By dividing the polynomial by (x – a), where “a” is a known root, you can find the remaining factors and coefficients.
Overall, synthetic division is a useful tool in various algebraic calculations involving polynomials. It simplifies the process of polynomial division, factorization, equation solving, and coefficient determination.
Advantages of using synthetic division
Synthetic division is a method used to divide polynomials, specifically polynomials of the form P(x)/D(x), where P(x) is the dividend and D(x) is the divisor. Here are some advantages of using synthetic division:
1. Simplicity: Synthetic division provides a simpler and more efficient method for division compared to long division. It involves fewer steps and calculations, making it easier to perform and understand.
2. Speed: Synthetic division is faster than long division since it requires fewer calculations. This can be especially beneficial when dividing large polynomials, saving time and effort.
3. Error reduction: Synthetic division reduces the chances of making errors because it is a more straightforward process. It eliminates the need for multiple subtractions and brings more clarity to the division process, enabling a higher level of accuracy in calculations.
4. Suitable for linear divisors: Synthetic division is particularly useful when dividing by a linear divisor of the form (x – a). It provides a convenient way to find the quotient and remainder without the need for complex polynomial division.
5. Finding factors: Synthetic division can help determine whether a given number is a factor of a polynomial. By using synthetic division to divide the polynomial by the number, one can easily determine if it evenly divides or not. If the remainder is zero, the number is a factor.
6. Better understanding of the polynomial: Synthetic division allows for a better understanding of the polynomial’s properties. It reveals information about the presence of factors, roots, and zeros, which can be used to simplify or analyze the polynomial further.
Overall, synthetic division offers a simpler, faster, and more error-free method for polynomial division, making it a valuable tool in various mathematical and engineering applications.
Limitations and alternate methods
Synthetic division is a useful method for dividing a polynomial by a linear factor. However, there are limitations to this method as well as alternate methods that can be used.
1. Linear Factors Only: Synthetic division can only be used when dividing a polynomial by a linear factor of the form (x – a). It cannot be used for dividing by quadratic or higher-order factors.
2. Leading Coefficient: Synthetic division assumes that the leading coefficient of the polynomial is 1. If the leading coefficient is not 1, the polynomial must be divided by the leading coefficient first before using synthetic division.
3. No Remainders: Synthetic division can only be used when the division is exact, meaning there is no remainder. If there is a remainder, the long division method must be used instead.
Alternate Methods:
1. Long Division: Long division is a more general method for dividing polynomials where there are no restrictions on the type of factor being divided by. It can be used for dividing by linear, quadratic, or higher-order factors. It may be more time-consuming than synthetic division but is a reliable method for all types of divisions.
2. Factoring: If possible, factoring the polynomial before dividing can simplify the process. By factoring out common factors or using other factoring techniques such as the quadratic formula, the polynomial can be broken down into simpler terms that are easier to divide.
3. Polynomial Division App: There are several online or mobile apps available that can perform polynomial divisions, including long division and synthetic division. These apps can be convenient alternatives to manual calculations and ensure accurate results.
Topics related to Synthetic division
Synthetic Division of Polynomials – YouTube
Synthetic Division of Polynomials – YouTube
Synthetic Division – YouTube
Synthetic Division – YouTube
Synthetic division example (NEVER use polynomial long division again!) #shorts – YouTube
Synthetic division example (NEVER use polynomial long division again!) #shorts – YouTube
Synthetic Division | Dividing Polynomials – YouTube
Synthetic Division | Dividing Polynomials – YouTube
Synthetic Division – YouTube
Synthetic Division – YouTube
Math – Dividing Polynomials – Synthetic Division – #shorts – YouTube
Math – Dividing Polynomials – Synthetic Division – #shorts – YouTube
how to use synthetic division to divide polynomials #shorts – YouTube
how to use synthetic division to divide polynomials #shorts – YouTube
Synthetic Division (SING TO LEARN) – YouTube
Synthetic Division (SING TO LEARN) – YouTube
Shortest Trick to Divide Polynomials II Synthetic Division II Division of Polynomials #viral #shorts – YouTube
Shortest Trick to Divide Polynomials II Synthetic Division II Division of Polynomials #viral #shorts – YouTube
Another Example of Synthetic Division Expanded – YouTube
Another Example of Synthetic Division Expanded – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.