Introduction
Introduction:
Diameter is a fundamental concept in mathematics and geometry that refers to the measurement of a straight line passing through the center of a circle or a sphere, connecting two points on its circumference. It is the longest distance that can be drawn within the circular shape.
Diameter in Geometry:
In geometry, the diameter of a circle is of particular significance. It is defined as the distance between any two points on the circle that passes through its center. The diameter is always twice the length of the radius (the distance from the center to any point on the circle). Therefore, by knowing the diameter, one can easily calculate the radius and vice versa, using the equation: diameter = 2 * radius.
Properties of Diameter:
The diameter has several important properties that make it useful in various mathematical applications. Some of these properties are:
1. The diameter bisects the circle: The diameter divides the circle into two equal halves or semicircles. This means that any straight line passing through the center of the circle will always bisect it into two equal parts.
2. Maximum distance: The diameter is the longest possible distance that can be drawn within the circle. No other line segment inside the circle can have a greater length.
3. Passes through the center: Unlike the radius, which starts from the center and ends at a point on the circumference, the diameter passes through the center of the circle or sphere.
Applications of Diameter:
The concept of diameter finds application in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and physics. Some common applications are:
1. Circles in geometry: The diameter is used to calculate the area and circumference of a circle, as well as other properties such as chord lengths and arc lengths.
2. Mechanical engineering: In mechanical systems, the diameter is often used to determine the size and dimensions of pipes, rods, and bearings.
3. Astronomy: The diameter of celestial objects, such as planets, stars, and galaxies, provides critical information about their size and structure.
In conclusion, the diameter is a fundamental concept in mathematics and geometry that plays a crucial role in various fields. It is the longest distance that can be drawn within a circle or sphere, passing through its center. By understanding its properties and applications, we can gain a deeper understanding of the geometrical and physical properties of objects.
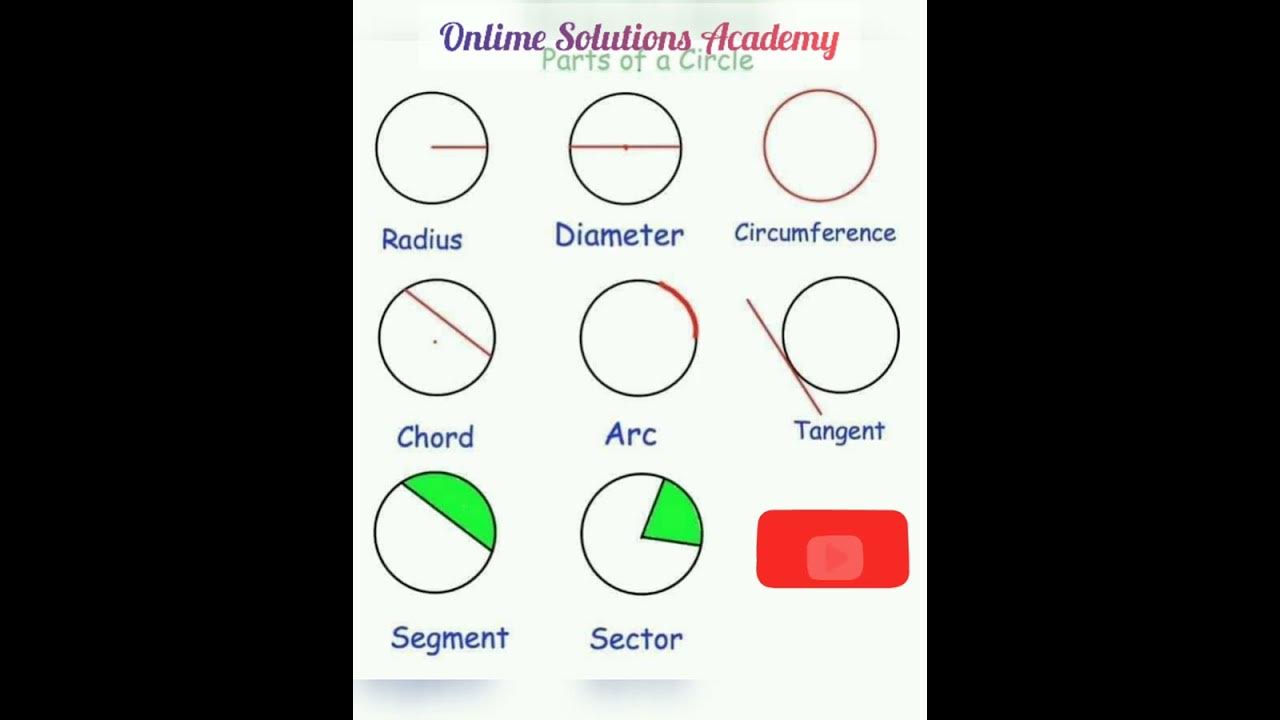
Definition of Diameter
The diameter is a straight line segment that passes through the center of a geometric figure, typically a circle, and has endpoints on the boundary or surface. It is the longest distance between any two points on a circle, passing through the center. In other words, the diameter is twice as long as the radius of a circle.
Calculation of Diameter
The diameter of a geometric shape is usually calculated using the formula:
Diameter = (2 * Radius)
Where the radius is the distance from the center of the shape to any point on its circumference.
For example, if the radius of a circle is given as 5 units, the diameter would be:
Diameter = (2 * 5) = 10 units.
Application of Diameter
The concept of diameter has various applications in different fields. Here are some examples:
1. Geometry: In geometry, the diameter is used to calculate the size, shape, and position of different geometric figures. For instance, in a circle, the diameter is a line segment that passes through the center and connects two points on the circumference. It is essential in determining the radius, area, circumference, and other properties of a circle.
2. Engineering: In engineering, the diameter is crucial for designing and manufacturing components and structures. It is used in determining the appropriate size for pipes, tubes, wires, and other cylindrical objects. For example, in plumbing systems, the diameter of pipes is determined to ensure efficient flow of fluids.
3. Astronomy: In astronomy, the concept of diameter is used to measure the size of celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, and planets. It helps astronomers understand the scale and structures of these objects and analyze their properties.
4. Medicine: In the field of medicine, the diameter is often used to measure the size of blood vessels, tumors, and other anatomical structures. For example, the diameter of a blood vessel can indicate its health, and measuring the size of a tumor can help diagnose and monitor its growth.
5. Networking: In computer networks, the term “diameter” refers to the maximum distance between any two nodes in a network. It is a crucial metric to determine the efficiency, scalability, and overall performance of a network. Network administrators use this information to optimize network routing, bandwidth allocation, and congestion control.
6. Biology: In biology, the diameter is used to measure the size of cells, bacteria, and other microscopic organisms. It helps biologists understand their structure, function, and relationships to other organisms. Measuring the diameter can also be used to determine the growth rate or response to different stimuli.
Overall, the concept of diameter finds applications in various fields, from mathematics and engineering to astronomy and medicine. Its use provides valuable information about size, structure, and relationships in different contexts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diameter is a measurement that refers to the distance across a circle, passing through the center. It is twice the length of the radius and can be calculated using the formula d = 2r, where d represents the diameter and r represents the radius. The diameter plays a crucial role in various mathematical and geometrical calculations, such as finding the circumference, area, and volume of a circle. Additionally, it is important in other fields like engineering and physics for determining the size and dimensions of objects. Overall, understanding and considering the diameter is essential for accurately describing and analyzing circular shapes and objects.
Topics related to Diameter
Finding the Diameter of a Circle Given the Radius | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
Finding the Diameter of a Circle Given the Radius | Math with Mr. J – YouTube
How to Calculate the Diameter of a Circle – YouTube
How to Calculate the Diameter of a Circle – YouTube
The future of testing, here today – YouTube
The future of testing, here today – YouTube
Circles: radius, diameter, circumference and Pi | Geometry | Khan Academy – YouTube
Circles: radius, diameter, circumference and Pi | Geometry | Khan Academy – YouTube
Circle | Parts of a Circle | Radius | Diameter | Chord | Sector | segment #circle #radius #maths – YouTube
Circle | Parts of a Circle | Radius | Diameter | Chord | Sector | segment #circle #radius #maths – YouTube
How to Find the Area of a Sector | Maths GCSE – YouTube
How to Find the Area of a Sector | Maths GCSE – YouTube
Parts of a circle / Radius / Diameter / Chord / Circumference / Sector / Arc / Segment – YouTube
Parts of a circle / Radius / Diameter / Chord / Circumference / Sector / Arc / Segment – YouTube
Math Hacks: Circles – Parts of a Circle – YouTube
Math Hacks: Circles – Parts of a Circle – YouTube
Diameter and radius of a circle ll Basic concepts ll Mathematics – YouTube
Diameter and radius of a circle ll Basic concepts ll Mathematics – YouTube
Maths shorts #shorts# circle formula #area #radius #diameter #circumference #arc #no. of revolutions – YouTube
Maths shorts #shorts# circle formula #area #radius #diameter #circumference #arc #no. of revolutions – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.