Introduction
Introduction:
The factor theorem is a fundamental theorem in algebra that helps in finding factors of a polynomial function. It provides a useful tool for factoring polynomials, which is essential in solving polynomial equations and understanding the behavior of polynomial functions.
Factor Theorem:
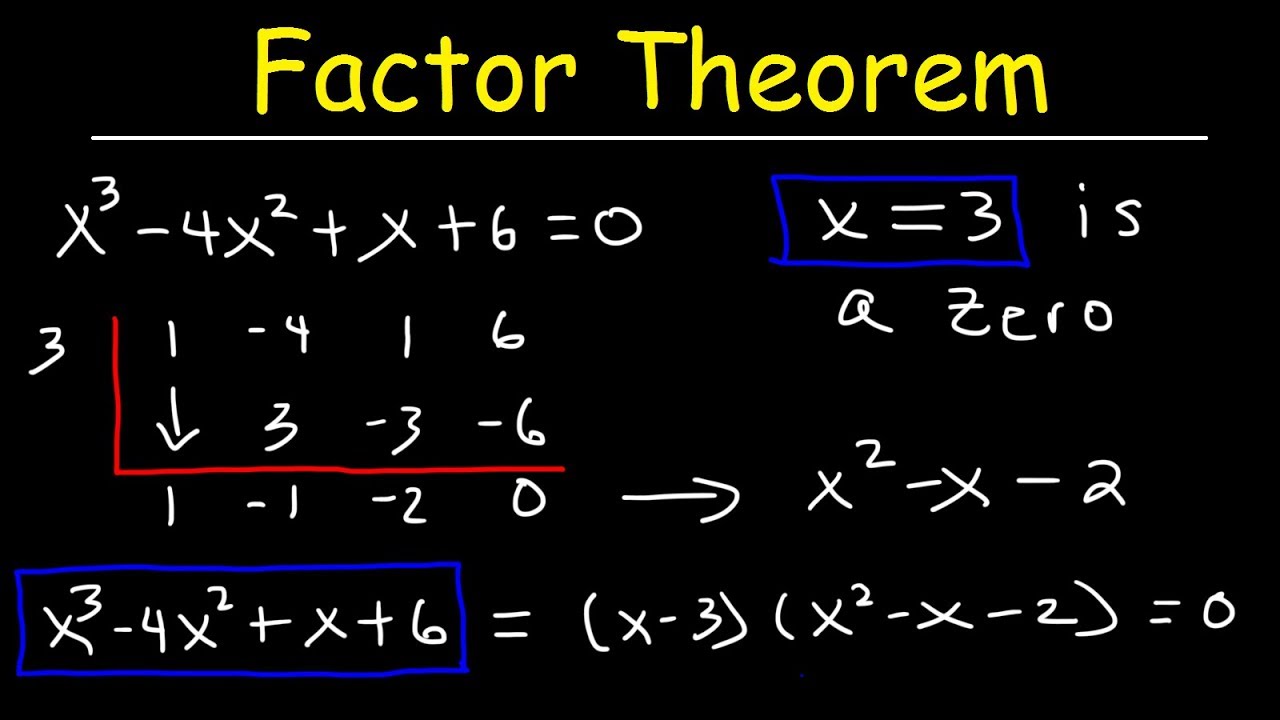
The factor theorem relates to the relationship between a polynomial function and its roots or zeros. It states that if a polynomial function has a root or zero, then the polynomial can be divided by the linear factor (x – a), where ‘a’ is the root of the polynomial.
In other words, the factor theorem states that if the polynomial function P(x) has a root at x = a, then (x – a) is a factor of P(x). This means that dividing the polynomial function by (x – a) will yield a quotient with a degree one less than the original polynomial.
For example, if P(x) = x^3 – 3x^2 – 4x + 12 has a root at x = 2, then (x – 2) is a factor of P(x). Dividing P(x) by (x – 2) results in a quotient of x^2 – x – 6.
The factor theorem is closely related to the concept of synthetic division, which is a method for dividing polynomials. Synthetic division allows us to quickly determine whether a given number is a zero of a polynomial and to find the remaining factors.
Understanding the factor theorem and applying it in factoring polynomials is essential in algebra and helps in solving polynomial equations, graphing polynomial functions, and analyzing their behavior.
In summary, the factor theorem is a powerful tool in algebra that helps in finding factors of polynomial functions. It states that if a polynomial function has a root, then the linear factor (x – a) is a factor of the polynomial. The factor theorem is crucial in factoring polynomials, solving equations, and understanding the behavior of polynomial functions.
Definition of Factor Theorem
The Factor Theorem is a fundamental concept in algebra that relates to polynomial functions. It states that if a polynomial function f(x) has a factor (x – a), where ‘a’ is any real number or constant, then when you divide f(x) by (x – a), the remainder will be zero.
In other words, the Factor Theorem tells us that if a polynomial function has a specific value ‘a’ as a root or a solution, then (x – a) can be factored out of the polynomial expression evenly, resulting in a remainder of zero when divided.
The Factor Theorem is often used in conjunction with the Remainder Theorem to find roots or solutions of polynomial equations. By determining the factors of a polynomial, we can factorize it or find its roots to solve equations or simplify polynomial expressions.
Application of Factor Theorem
The Factor Theorem is a useful tool in algebra that helps us factor polynomials and find their roots. It states that if a polynomial f(x) has a factor (x – c), then c is a root of the polynomial.
One application of the Factor Theorem is in finding the roots of a polynomial equation. By factoring the polynomial using the Factor Theorem, we can easily determine its roots. For example, if we have a polynomial f(x) = 2x^2 – 5x – 3, we can use the Factor Theorem to find its roots. By factoring out (x – 3), we get f(x) = (x – 3)(2x + 1). Setting each factor equal to zero, we find that x = 3 and x = -1/2 are the roots of the polynomial.
Another application of the Factor Theorem is in polynomial long division. If we have a polynomial f(x) and we want to divide it by a quadratic polynomial (x – c)^2, we can use the Factor Theorem to simplify the division. By dividing f(x) by (x – c), we can determine any remainder or find the quotient. This is particularly useful when we want to find partial fractions or simplify complex fractions.
In summary, the Factor Theorem is applied in various situations where we need to factor polynomials or find their roots. It allows us to break down complex expressions, simplify calculations, and solve polynomial equations more easily.
Examples and Illustrations
The factor theorem states that if a polynomial function f(x) has a factor (x – a), where ‘a’ is a constant, then the polynomial function will have a zero at x = a. In simple terms, if we can factorize a polynomial and find a ‘root’ or ‘solution’, then we know that (x – root) is a factor of the polynomial.
Let’s take an example to illustrate the factor theorem:
Example 1:
Consider the polynomial f(x) = x^3 – 6x^2 + 11x – 6. We want to determine if (x – 2) is a factor of f(x).
To check if (x – 2) is a factor, we substitute x = 2 into the polynomial and check if the result is zero.
f(2) = (2)^3 – 6(2)^2 + 11(2) – 6
= 8 – 24 + 22 – 6
= 0
Since f(2) = 0, we can conclude that (x – 2) is a factor of f(x) by the factor theorem. This means that the polynomial can be factorized as (x – 2)(x^2 – 4x + 3).
Example 2:
Consider the polynomial g(x) = 2x^4 – 5x^3 + 2x^2 + 3x – 1. We want to determine if (x + 1) is a factor of g(x).
To check if (x + 1) is a factor, we substitute x = -1 into the polynomial and check if the result is zero.
g(-1) = 2(-1)^4 – 5(-1)^3 + 2(-1)^2 + 3(-1) – 1
= 2 – 5 + 2 – 3 – 1
= -5
Since g(-1) = -5 ≠ 0, we can conclude that (x + 1) is not a factor of g(x) by the factor theorem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Factor Theorem is a useful tool in algebraic calculations. It helps to determine whether a given polynomial has a specific factor by factoring it out and solving for the potential factor. By applying the Factor Theorem, we can efficiently find roots and factors of polynomial equations. This theorem is an essential concept in polynomial manipulation and solving equations, making it a valuable tool in mathematics.
Topics related to Factor theorem
A-Level Maths: B6-11 [Polynomials: Introducing the Factor Theorem] – YouTube
A-Level Maths: B6-11 [Polynomials: Introducing the Factor Theorem] – YouTube
Factor Theorem Grade 12: Introduction – YouTube
Factor Theorem Grade 12: Introduction – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
The Factor Theorem | ExamSolutions – YouTube
The Factor Theorem | ExamSolutions – YouTube
Factor Theorem and Synthetic Division of Polynomial Functions – YouTube
Factor Theorem and Synthetic Division of Polynomial Functions – YouTube
FACTOR THEOREM || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q1 – YouTube
FACTOR THEOREM || GRADE 10 MATHEMATICS Q1 – YouTube
The Factor Theorem | Algebra | GCSE Further Maths | A-Level Maths Series – YouTube
The Factor Theorem | Algebra | GCSE Further Maths | A-Level Maths Series – YouTube
Maxim Kontsevich – 2/4 Birational Invariants from Gromov-Witten Theory – YouTube
Maxim Kontsevich – 2/4 Birational Invariants from Gromov-Witten Theory – YouTube
Can you find area of the Blue semicircle in the square? | (Geometry skills explained) | #math #maths – YouTube
Can you find area of the Blue semicircle in the square? | (Geometry skills explained) | #math #maths – YouTube
जानिए आखिर कैसा है गणित का आखिरी Theorem | Last theorem of mathematics | Fermat's last theorem – YouTube
जानिए आखिर कैसा है गणित का आखिरी Theorem | Last theorem of mathematics | Fermat's last theorem – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.