Introduction
Introduction:
Linolenic acid is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid that belongs to the omega-3 fatty acid family. It is also known as α-linolenic acid (ALA) and is considered essential because the human body cannot synthesize it on its own and must obtain it through dietary sources.
Linolenic acid plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and is a precursor for the synthesis of other important omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are known for their numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, supporting brain health, and promoting heart health.
Sources of Linolenic acid include various plant-based foods such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and soybeans. It can also be found in certain vegetable oils like flaxseed oil, canola oil, and soybean oil.
In addition to its role in fatty acid synthesis, Linolenic acid has been researched for its potential therapeutic effects. It has been suggested that consuming adequate amounts of Linolenic acid may help reduce the risk of various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer. However, more research is needed to fully understand and verify these potential health benefits.
Overall, Linolenic acid is an essential nutrient that is important for overall health and well-being. Including dietary sources of this fatty acid in your diet can contribute to a balanced and nutritious eating plan that supports optimal health.
Definition of Linolenic Acid
Linolenic acid is an essential omega-3 fatty acid that is found primarily in plant-based oils and foods. It is a polyunsaturated fat that contains three double bonds in its carbon chain.
Linolenic acid is important for maintaining overall health and is considered essential because the human body cannot produce it on its own. It is a precursor to other omega-3 fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are critical for brain function and reducing inflammation in the body.
Sources of linolenic acid include flaxseed oil, chia seeds, walnuts, and soybean oil. Consuming an adequate amount of linolenic acid as part of a balanced diet can help promote heart health, support mental function, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and arthritis.
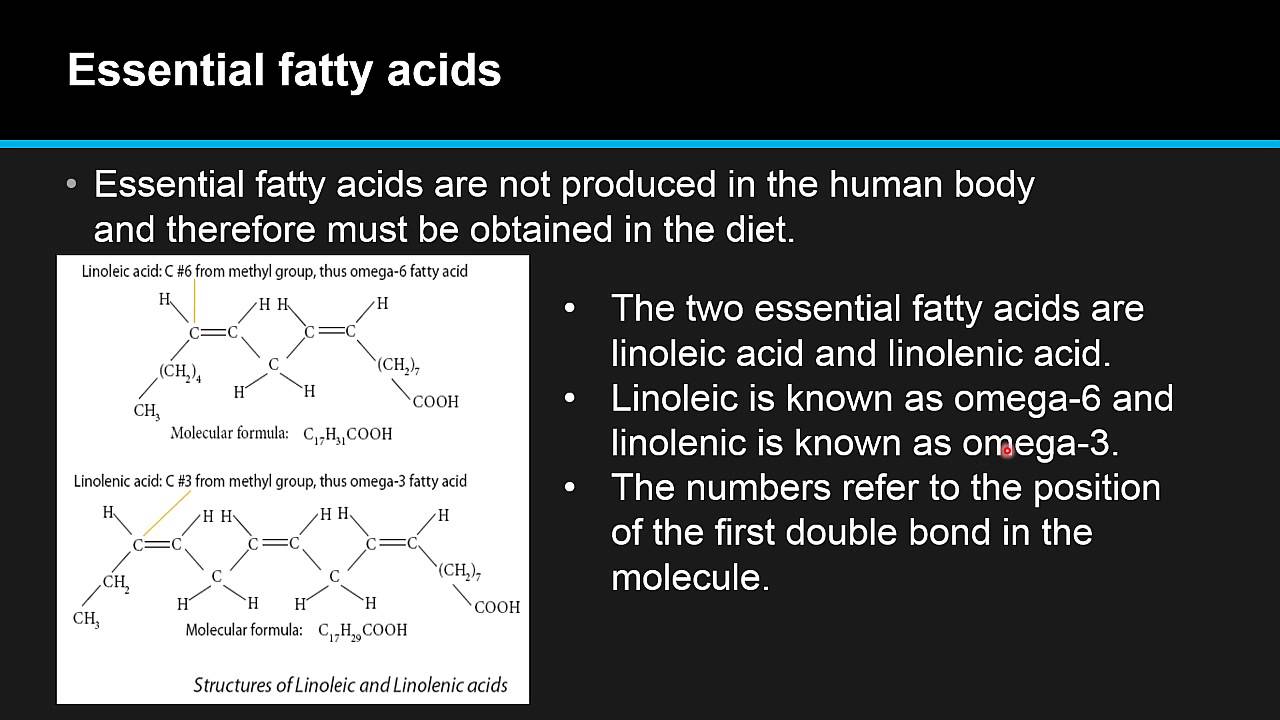
Chemical Structure of Linolenic Acid
The chemical structure of linolenic acid is a fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms. It has three double bonds, located at the 9th, 12th, and 15th carbon atoms. The molecular formula of linolenic acid is C18H30O2.
The structure of linolenic acid can be represented as follows:
H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
H – C = C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C – OH
| | | | |
H H H H H
The double bonds in linolenic acid are in the cis configuration, meaning that hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the double bond.
Linolenic acid is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid found in plant oils, such as flaxseed oil and soybean oil. It is widely known for its health benefits, including its role in reducing inflammation and improving cardiovascular health.
Functions and Importance of Linolenic Acid
Linolenic acid is an essential omega-3 fatty acid that plays numerous roles in the human body. It is important for overall health and well-being. Here are some functions and the importance of linolenic acid:
1. Heart Health: Linolenic acid helps reduce the risk of heart disease by improving lipid profiles, reducing inflammation, and decreasing blood pressure.
2. Brain Health: Linolenic acid is a crucial component of cell membranes in the brain, supporting proper brain function and development. It is also associated with a lower risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Inflammation and Immunity: Linolenic acid serves as a precursor to other omega-3 fatty acids like eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which have anti-inflammatory properties. These fatty acids help regulate the immune response and reduce chronic inflammation.
4. Eye Health: The retina contains a high concentration of DHA, which is synthesized from linolenic acid. Consuming sufficient linolenic acid is essential for maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
5. Skin Health: Linolenic acid helps maintain the integrity of the skin barrier, preventing moisture loss and improving overall skin health. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate symptoms of dermatological conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
6. Hormonal Balance: Linolenic acid is involved in the production of hormones and can influence menstrual health and alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
7. Weight Management: Linolenic acid may help in weight management by reducing appetite and promoting the feeling of fullness. It also supports metabolic processes and fat oxidation.
Including dietary sources of linolenic acid in the form of flaxseed oil, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, and leafy green vegetables is crucial for meeting the body’s omega-3 fatty acid needs. However, it is important to maintain a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids to ensure optimal health.
Dietary Sources and Health Benefits of Linolenic Acid
Linolenic acid is an essential omega-3 fatty acid that cannot be produced by the human body and must be obtained through dietary sources. It provides various health benefits and plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being.
Dietary Sources of Linolenic Acid:
1. Flaxseeds and Flaxseed Oil: Flaxseeds are one of the richest sources of linolenic acid. They can be consumed whole or in the form of oil.
2. Chia Seeds: Chia seeds are another excellent source of linolenic acid and can be added to various dishes.
3. Hemp Seeds and Hemp Oil: Hemp seeds and oil are also rich sources of linolenic acid.
4. Walnuts: Walnuts are a plant-based source of linolenic acid and make a healthy snack.
5. Soybeans and Soybean Oil: Soybeans and soybean oil contain linolenic acid and are commonly used in cooking and food processing.
6. Canola Oil: Canola oil is derived from the rapeseed plant and contains a good amount of linolenic acid.
Health Benefits of Linolenic Acid:
1. Heart Health: Linolenic acid has been shown to have a positive impact on heart health. It helps lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and improve cholesterol levels. It may also help prevent the formation of blood clots and arterial plaques.
2. Brain Function: Omega-3 fatty acids, including linolenic acid, are essential for normal brain development and function. They can improve cognitive functions, such as memory and concentration, and may help reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
3. Inflammation and Autoimmune Conditions: Linolenic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body. This can be beneficial for individuals with autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
4. Skin Health: Consuming adequate amounts of linolenic acid promotes healthy skin by reducing inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the skin barrier. It can also help alleviate symptoms of various skin conditions, including eczema and psoriasis.
5. Eye Health: Linolenic acid is beneficial for maintaining good eye health. It helps protect against age-related macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome.
6. Weight Management: Linolenic acid may aid in weight management by increasing satiety, reducing appetite, and boosting metabolism.
It is important to note that linolenic acid can be converted into other important omega-3 fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in the body. However, this conversion is limited, and direct sources of EPA and DHA, such as fatty fish and fish oil supplements, are also recommended for optimal health benefits.
Topics related to Linolenic acid
Unsaturated Fatty Acids Part 1: Nomenclature and Structure – YouTube
Unsaturated Fatty Acids Part 1: Nomenclature and Structure – YouTube
B.4.4 Compare the structures of the two essential fatty acids. – YouTube
B.4.4 Compare the structures of the two essential fatty acids. – YouTube
Fats – biochemistry – YouTube
Fats – biochemistry – YouTube
Lipids – Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids – YouTube
Lipids – Fatty Acids, Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Terpenes, Waxes, Eicosanoids – YouTube
Alpha-linolenic Acid – YouTube
Alpha-linolenic Acid – YouTube
Omega 3 fatty acids || Notation and configuration – YouTube
Omega 3 fatty acids || Notation and configuration – YouTube
4. Fatty Acids: Short Hand Technique to Represent Fatty Acids – YouTube
4. Fatty Acids: Short Hand Technique to Represent Fatty Acids – YouTube
Seed oils and fat cells: linoleic acid makes fat cells insulin resistant. – YouTube
Seed oils and fat cells: linoleic acid makes fat cells insulin resistant. – YouTube
List of acids/acids formula and names/acid formula writing /अम्ल के रासायनिक सूत्र – YouTube
List of acids/acids formula and names/acid formula writing /अम्ल के रासायनिक सूत्र – YouTube
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) Reduces Acne And Makes Skin GLOW! #shorts – YouTube
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) Reduces Acne And Makes Skin GLOW! #shorts – YouTube

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.