Introduction
Introduction:
A union refers to an organized group of workers who come together to collectively represent and advocate for their common interests and rights in the workplace. The main purpose of a union is to negotiate with employers on behalf of its members regarding wages, benefits, working conditions, and other employment-related matters. Unions can exist in various industries and sectors, including manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, education, and more. This collective representation aims to achieve better treatment, fair treatment, and improved working conditions for workers.
Unions typically have a democratic structure, where members elect leaders to represent them and make decisions on their behalf. These leaders, known as union representatives or shop stewards, play a crucial role in communicating with management, addressing grievances, and ensuring that the rights of workers are protected. By joining a union, workers gain the power of collective bargaining, enabling them to negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions than they would likely achieve individually.
In addition to negotiating with employers, unions also engage in activities such as organizing strikes, conducting awareness campaigns, and advocating for labor laws that protect workers’ rights. By mobilizing their members and utilizing collective action, unions can effectively influence workplace policies and advocate for broader social and economic issues that benefit the working class.
While unions have been instrumental in improving the conditions of workers over the years, they have also faced criticism and challenges. Some argue that unions can lead to increased costs for employers, reduced flexibility, and hinder economic growth. Others believe that unions can be corrupt or fail to adequately represent the interests of all workers. Nevertheless, unions continue to play a significant role in protecting workers’ rights, promoting fair labor practices, and striving for better working conditions for employees across different industries and sectors.
Definition of Union
Union has multiple definitions, depending on the context.
1. In the context of a labor union, it refers to an organized association of workers, typically from the same industry or profession, formed to address common concerns and negotiate with employers on behalf of its members. The primary goals of a labor union are to protect the rights and interests of workers, improving their working conditions, wages, and benefits.
2. In the context of a political union, it refers to a formal agreement or alliance between two or more states or nations, usually for the purpose of mutual benefit and cooperation. The European Union (EU) is one prominent example, where member countries collaborate on economic, political, and social issues while maintaining their own sovereignty.
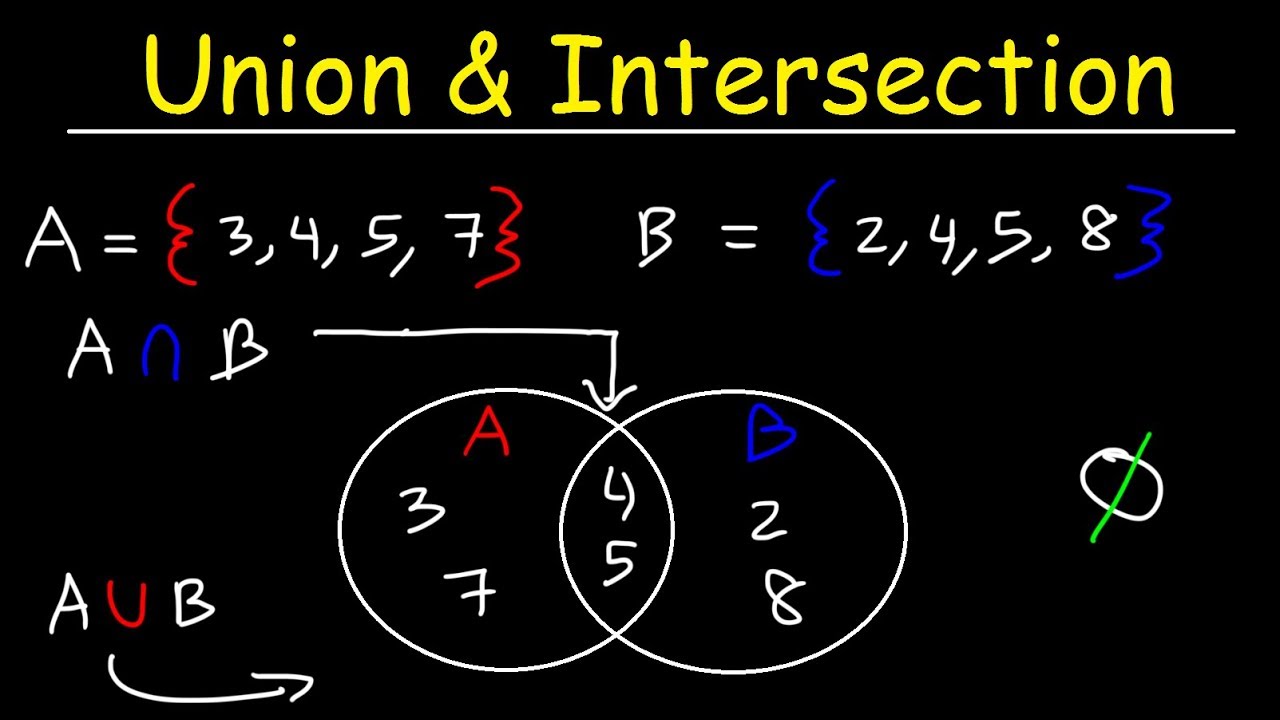
3. In the context of sets, a union refers to the combination or merger of two or more sets to create a new set that contains all the elements from the original sets, without any repetition. The union of sets A and B, denoted as A ∪ B, includes all the elements found in either A or B or both.
4. In the context of marriage, a union refers to the legal and formal bond between two individuals, typically recognized by law, customs, or religious practices. Marriage often implies a committed partnership between a man and a woman or between two people of the same gender, involving certain rights, obligations, and responsibilities.
Examples of Union in Mathematics
In mathematics, the union operation is used to combine two or more sets to create a new set that contains all the elements from the original sets.
1. Set Union: Let’s consider two sets, A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {3, 4, 5}. Their union, denoted as A ∪ B, is the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, which contains all the elements present in both sets.
2. Interval Union: Suppose we have two intervals, I1 = [1, 5] and I2 = (3, 8]. The union of these intervals, denoted as I1 ∪ I2, is the interval [1, 8], including all the numbers from 1 to 8, but excluding the endpoints 3 and 8.
3. Union of Events: In probability theory, the union of two events refers to the occurrence of either one or both events. For instance, if event A represents rolling an even number on a fair die (A = {2, 4, 6}) and event B represents rolling a number less than 4 (B = {1, 2, 3}), then their union, denoted as A ∪ B, is the event {1, 2, 3, 4, 6}, indicating the possibility of rolling any number less than 4 or an even number.
4. Union of Topological Spaces: In topology, the union of two topological spaces is a space that combines the elements and structure of both spaces. For example, if we have two topological spaces, X and Y, their union X ∪ Y is a new space that contains all the elements and open sets from X and Y.
These are just a few examples of how the union operation is used in mathematics to combine sets, intervals, events, and topological spaces. The union is a fundamental concept that allows for the creation of new sets with more elements based on the elements present in the original sets.
Properties of Union
The term “Union” can refer to two different contexts: mathematical union and labor union. Here are the properties associated with each:
1. Mathematical Union:
– Closure: The union of two sets A and B, denoted as A ∪ B, results in a set that contains all the elements from both sets. In other words, if x is an element of A or B (or both), then x is an element of A ∪ B.
– Associativity: The union operation is associative, which means that the order in which the unions are performed does not matter. For example, (A ∪ B) ∪ C = A ∪ (B ∪ C).
– Commutativity: The union operation is commutative, which means that the order of the sets being joined does not matter. For example, A ∪ B = B ∪ A.
– Idempotence: If a set A is unioned with itself, the result will be the same set. In other words, A ∪ A = A.
– Absorption: If a set A is unioned with the empty set (∅), the result will be A. In other words, A ∪ ∅ = A.
2. Labor Union:
– Representation: A labor union represents a collective group of workers who come together to negotiate better wages, working conditions, benefits, and other rights with their employers.
– Membership: Workers join a labor union voluntarily and become members. They pay membership dues to support the union’s activities and benefit from the collective bargaining power that the union provides.
– Collective Bargaining: Labor unions engage in collective bargaining to negotiate employment terms, such as wages, hours, health insurance, retirement plans, work rules, and more, on behalf of their members.
– Advocacy: Unions advocate for workers’ rights and interests, both within the workplace and in legislative and political arenas. They may focus on issues such as worker safety, fair treatment, job security, and equitable employment opportunities.
– Legal Recognition: Labor unions seek legal recognition from employers to represent their members. This recognition allows the union to negotiate labor contracts and represent workers’ interests in disputes or grievances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a union is an important and effective means of collective bargaining and representation for workers. It helps to ensure that workers have a voice in the decision-making processes of their employers and protects their rights and interests. Unions can negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions, leading to improved job security and overall well-being for workers. Additionally, unions play a crucial role in advocating for fair labor practices and promoting social equality in the workplace. Overall, unions contribute to a more balanced and equitable relationship between workers and employers, creating a more sustainable and harmonious work environment.
Topics related to Union
Intersection of Sets, Union of Sets and Venn Diagrams – YouTube
Intersection of Sets, Union of Sets and Venn Diagrams – YouTube
Sets: Union, Intersection, Complement – YouTube
Sets: Union, Intersection, Complement – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
What is a Union? (Set Theory) – YouTube
What is a Union? (Set Theory) – YouTube
Union and Intersection in Venn Diagrams? | Don't Memorise – YouTube
Union and Intersection in Venn Diagrams? | Don't Memorise – YouTube
How to find AUB?#maths #mathematics #MATHSFUN#union#sets #shorts – YouTube
How to find AUB?#maths #mathematics #MATHSFUN#union#sets #shorts – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (A intersection B, A' union B') – YouTube
Venn Diagrams (A intersection B, A' union B') – YouTube
Venn Diagrams Operations on Sets union intersection and differences of Sets NCERT Maths Solution – YouTube
Venn Diagrams Operations on Sets union intersection and differences of Sets NCERT Maths Solution – YouTube
Some Set Theory Symbols 📚 #Shorts #math #maths #mathematics #education #learn #learning – YouTube
Some Set Theory Symbols 📚 #Shorts #math #maths #mathematics #education #learn #learning – YouTube
Venn Diagrams | Union , Intersection , Difference Of sets | Set Theory | Sets #shorts #youtubeshorts – YouTube
Venn Diagrams | Union , Intersection , Difference Of sets | Set Theory | Sets #shorts #youtubeshorts – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.