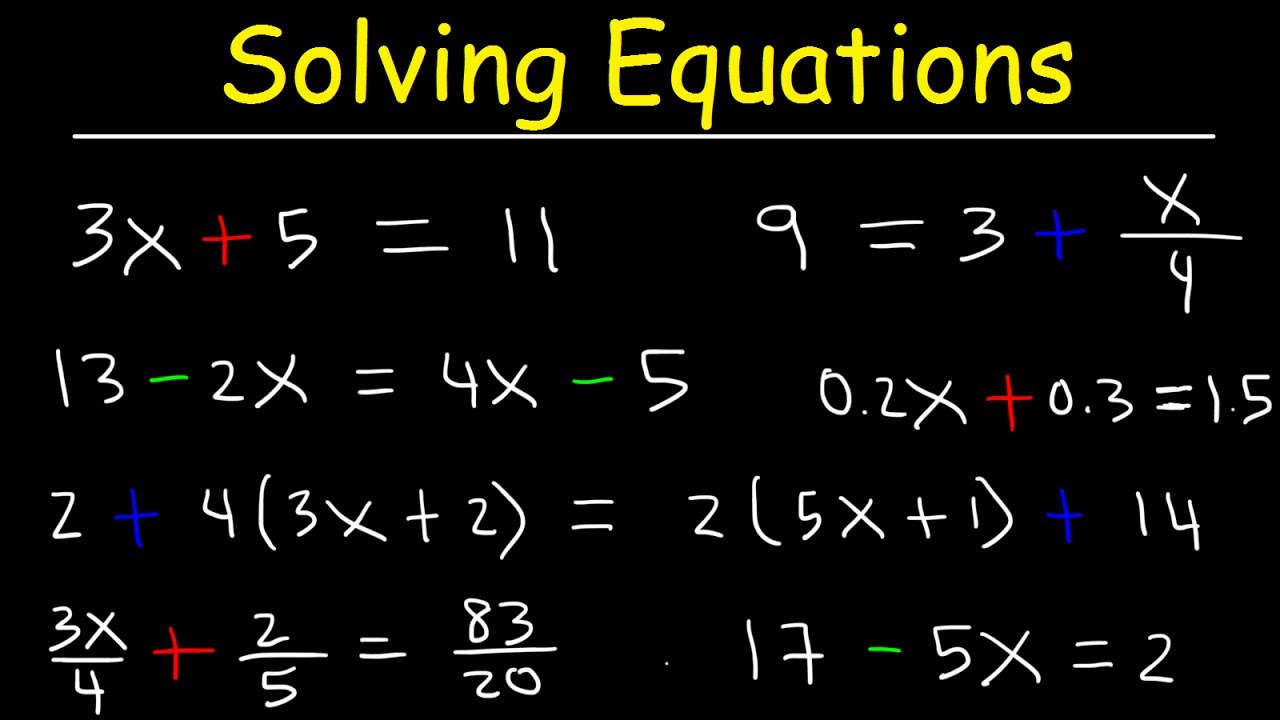
Introduction to algebraic equations
Algebraic equations are mathematical expressions that involve one or more variables, as well as mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These equations are used to solve problems and find the values of the variables that make the equation true.
In an algebraic equation, variables are represented by letters, such as x or y. The goal is to find the value of the variable that satisfies the equation. This is done by manipulating the equation using algebraic operations to isolate the variable on one side of the equation.
For example, consider the equation 2x + 3 = 9. Here, x is the variable and the equation states that twice the value of x added to 3 is equal to 9. To find the value of x, we need to rearrange the equation to isolate x. We can do this by subtracting 3 from both sides of the equation, giving us 2x = 6. Then, dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we find that x = 3. Therefore, the value of x that satisfies the equation is 3.
Algebraic equations are used in various fields such as physics, engineering, economics, and finance. They provide a way to represent relationships between variables and solve problems by finding unknown quantities. The study of algebraic equations is fundamental in mathematics and serves as a foundation for higher-level math concepts.
Definition of algebraic equations
An algebraic equation is a mathematical expression that relates two or more variables with constants using mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It is usually written in the form of an equality, where both sides of the equation have the same value.
For example, the equation “2x + 3 = 7” is an algebraic equation. It states that when you multiply the variable x by 2, add 3 to the result, the sum will be equal to 7. Solving this equation involves finding the value of x that makes the equation true.
Algebraic equations are used in a wide range of mathematical and scientific applications to model relationships between variables and calculate unknown values. They form the basis of algebraic manipulation and solving equations is an essential skill in mathematics.
Types of algebraic equations
There are several types of algebraic equations:
1. Linear equations: These equations involve variables raised to the first power (no exponents). They can usually be solved by isolating the variable on one side of the equation.
Example: 2x + 3 = 7
2. Quadratic equations: These equations involve variables raised to the second power. They can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants. Quadratic equations usually have two solutions.
Example: x^2 – 4x + 4 = 0
3. Cubic equations: These equations involve variables raised to the third power. They can be written in the form ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d = 0, where a, b, c, and d are constants. Cubic equations can have one or three real solutions.
Example: x^3 – 6x^2 + 11x – 6 = 0
4. Exponential equations: These equations involve variables in the exponent. They can often be solved using logarithms.
Example: 2^x = 8
5. Logarithmic equations: These equations involve logarithms of variables. They can usually be solved by applying inverse operations to eliminate the logarithms.
Example: log(x) + log(x + 1) = 2
6. Radical equations: These equations involve variables under a radical (square root, cube root, etc.). They can often be solved by raising both sides of the equation to an appropriate power.
Example: √(x + 2) = 4
These are just a few examples of the many types of algebraic equations that exist. Each type may require different methods and techniques to solve.
Solving algebraic equations
An algebraic equation is a mathematical statement that equates two expressions using an equal sign “=”.
To solve an algebraic equation, the goal is typically to find the value of the variable that satisfies the equation. This involves performing various operations to isolate the variable on one side of the equation.
Here are the general steps to solve an algebraic equation:
1. Simplify both sides of the equation by combining like terms and performing any necessary operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) to reduce the equation to its simplest form.
2. If there are any parentheses or brackets, apply the appropriate operations to remove them.
3. Identify the like terms on either side of the equation and combine them.
4. Use inverse operations to isolate the variable on one side of the equation. For example, if the variable is being added or subtracted, undo this operation using its inverse (subtract or add). If the variable is being multiplied or divided, undo this operation using its inverse (divide or multiply).
5. Continue applying inverse operations until the variable is isolated on one side and all other terms are on the other side.
6. Simplify the equation if necessary by combining like terms again.
7. Determine the value of the variable by solving for it. If the variable is isolated on one side of the equation, the value on the other side represents the solution.
It’s important to note that whatever operations are performed on one side of the equation must also be performed on the other side in order to maintain the equality of the equation.
Example of an algebraic equation:
Solve for x: 3x + 5 = 17
1. Start by subtracting 5 from both sides of the equation:
3x + 5 – 5 = 17 – 5
3x = 12
2. Divide both sides of the equation by 3 to isolate x:
3x/3 = 12/3
x = 4
Therefore, the solution to the equation 3x + 5 = 17 is x = 4.
Applications of algebraic equations
There are numerous real-world applications of algebraic equations. Some common examples include:
1. Finance and Economics: Algebraic equations are used to model and solve problems related to investments, loans, interest rates, and economic forecasting. For instance, equations such as compound interest formulas are used to calculate future values of investments.
2. Physics and Engineering: Algebraic equations play a crucial role in physics and engineering to describe relationships between quantities, such as Newton’s equations of motion or Ohm’s law in electrical engineering. These equations can help solve problems related to motion, forces, energy, and electrical circuits.
3. Medicine and Biology: Algebraic equations are used in the fields of medicine and biology to model and understand various processes. For example, equations are used to describe the growth of populations, the spread of diseases, pharmacokinetics (how drugs are absorbed and distributed in the body), or the dynamics of biochemical reactions.
4. Geometry and Architecture: Algebraic equations are used in geometry to express and solve geometric problems, such as finding the equations of lines or circles. Architects may also utilize algebraic equations when designing structures, calculating dimensions, or solving problems related to angles and areas.
5. Computer Science and Programming: Algebraic equations are used in computer science to solve problems, design algorithms, and optimize code. They are heavily utilized in computer graphics, robotics, artificial intelligence, and cryptography.
6. Statistics and Data Analysis: Algebraic equations are used to model relationships between variables in statistics and data analysis. Equations such as linear regression models or logistic regression models are used to fit data and make predictions.
Overall, algebraic equations serve as powerful tools in various fields, providing a systematic way to model, solve, and understand complex problems.
Topics related to Algebraic equation
GCSE Maths – How to Solve Algebraic Equations (Part 1 of 3) #43 – YouTube
GCSE Maths – How to Solve Algebraic Equations (Part 1 of 3) #43 – YouTube
Algebra – How To Solve Equations Quickly! – YouTube
Algebra – How To Solve Equations Quickly! – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Algebra Basics: What Is Algebra? – Math Antics – YouTube
Algebra Basics: What Is Algebra? – Math Antics – YouTube
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS | GRADE 6 – YouTube
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS | GRADE 6 – YouTube
Algebraic Expressions (Basics) – YouTube
Algebraic Expressions (Basics) – YouTube
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions With Parentheses & Variables – Combining Like Terms – Algebra – YouTube
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions With Parentheses & Variables – Combining Like Terms – Algebra – YouTube
Algebra ( बीजगणित ) // Important Questions with tricky solution – YouTube
Algebra ( बीजगणित ) // Important Questions with tricky solution – YouTube
France – Math Olympiad Question | An Algebraic Expression | You should be able to solve this! – YouTube
France – Math Olympiad Question | An Algebraic Expression | You should be able to solve this! – YouTube
20 important algebra formula | बीजगणित सूत्र | bijganit ke sutra | algebra ka formula | bijganit | – YouTube
20 important algebra formula | बीजगणित सूत्र | bijganit ke sutra | algebra ka formula | bijganit | – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.