Introduction to Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass
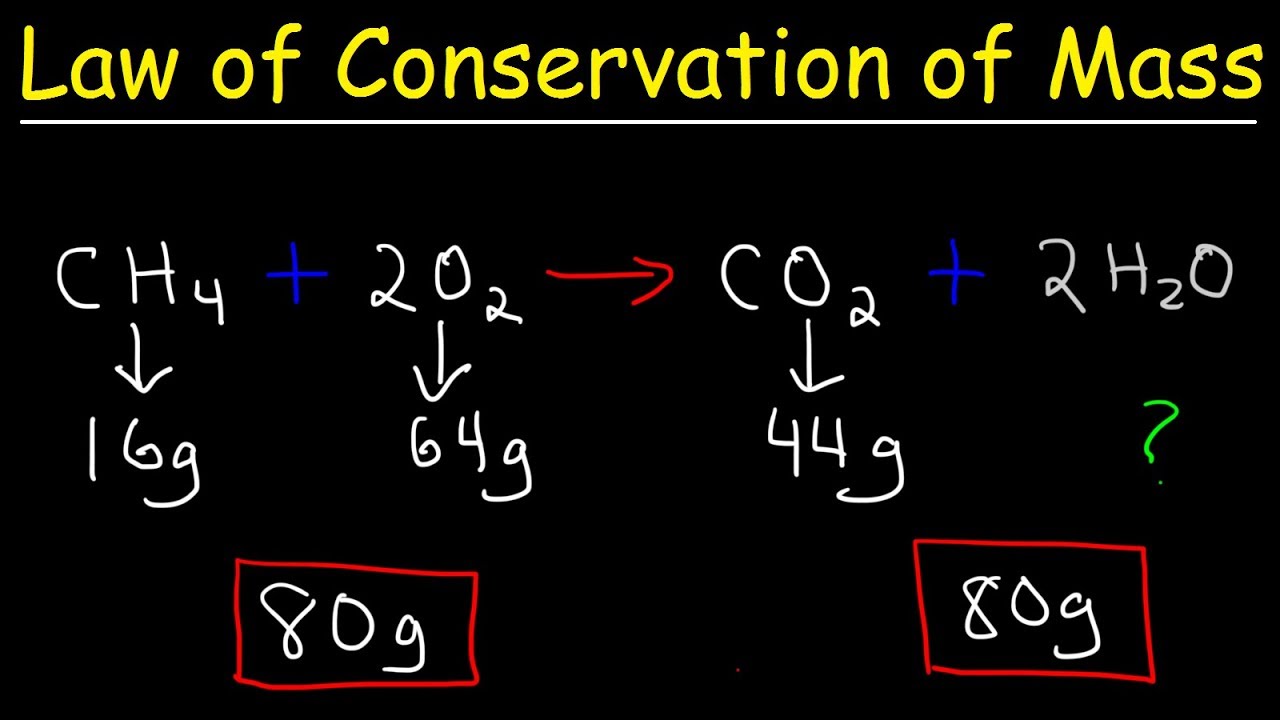
The Law of Conservation of Mass, also known as Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass, is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. It was formulated by French chemist Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century.
Lavoisier conducted numerous experiments to understand the nature of chemical reactions and the changes that occur during these processes. Through his observations, he concluded that in a closed system, the total mass of the substances before a reaction is equal to the total mass of the substances after the reaction.
In simpler terms, this law implies that matter cannot simply disappear or emerge out of nowhere during a chemical reaction. The atoms of the reactants rearrange themselves to form new substances, but the total number and types of atoms remains the same. This concept is now known as the law of conservation of atoms or the law of conservation of matter.
Lavoisier’s discovery of this law laid the foundation for the development of the modern field of chemistry. It revolutionized the understanding of chemical reactions and paved the way for the formulation of other fundamental principles such as the law of definite proportions and the law of multiple proportions.
This law is of immense practical importance in the field of chemistry. It is used to calculate the quantities of reactants and products in a reaction, to balance chemical equations, and to analyze the efficiency of chemical processes. Without the law of conservation of mass, it would be impossible to accurately study and understand the changes that occur in chemical reactions.
Explanation of Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass
Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass, also known as the Law of Conservation of Matter, states that in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. This means that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
Antoine Lavoisier, a French chemist, proposed this law in the late 18th century after conducting various experiments on chemical reactions. He observed that no matter how substances were transformed or combined, the total mass remained constant.
This law contradicted the prevailing belief at the time, known as the phlogiston theory, which suggested that substances lost weight when they burned. Lavoisier’s experiments proved that the apparent weight loss was due to the escape of gases produced during the reactions.
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry and is still widely applied today. It is often used in stoichiometric calculations to determine the amount of reactants required or the amount of products formed in a given reaction.
Overall, Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass highlights the fundamental concept that matter is conserved in chemical reactions, reinforcing the idea that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms rather than the creation or destruction of matter.
Historical Overview of Lavoisier’s Contribution to Physics
Antoine Lavoisier was a French chemist who made significant contributions to the fields of chemistry and physics during the late 18th century. One of his most notable contributions was the formulation of the Law of Conservation of Mass, which laid the foundation for modern physical theories.
During Lavoisier’s time, the prevailing belief in chemistry was the idea of phlogiston, a hypothetical substance thought to be released during combustion. However, Lavoisier challenged this theory by conducting meticulous experiments and observing the mass changes that occurred during chemical reactions.
Lavoisier’s experiments involved measuring the weights of reactants and products in a closed system. He noticed that regardless of the chemical reaction taking place, the total mass of the substances involved always remained constant. This led him to formulate the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but rather it is conserved.
Lavoisier’s law fundamentally changed the way scientists understood chemical reactions. It eliminated the need for the phlogiston theory and provided a solid foundation for future studies in the field of chemistry. His work paved the way for the development of the concept of elements and compounds, as well as the understanding of stoichiometry.
Furthermore, Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass not only influenced the field of chemistry but also had significant implications for physics. It became a fundamental principle in the study of energy and the development of the concept of energy conservation.
Overall, Lavoisier’s contribution to physics through the formulation of the Law of Conservation of Mass revolutionized the understanding of chemical reactions and had a profound impact on the fields of chemistry and physics. His work laid the foundation for the development of modern chemical and physical theories, making him one of the most influential scientists of his time.
Applications of Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass
Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but only changes its form. This fundamental principle of chemistry has numerous applications in various fields:
1. Chemical reactions: Lavoisier’s law is the foundation of chemical reactions. It allows scientists to balance chemical equations, ensuring that the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products. This is crucial for calculating the amount of substances needed for a reaction or the amount of product obtained.
2. Stoichiometry: Lavoisier’s law is central to stoichiometry, which deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. By considering the conservation of mass, stoichiometry enables scientists to calculate the amount of reactants required or the amount of products formed in a reaction.
3. Synthesis and decomposition: Lavoisier’s law helps in understanding the synthesis (combination) and decomposition (breakdown) of compounds. It allows chemists to predict the mass of products formed when certain substances react or the mass of reactants needed to obtain a desired amount of product.
4. Environmental chemistry: Lavoisier’s law is relevant in studying various environmental processes involving matter, such as the combustion of fuels, atmospheric reactions, and the transformation of pollutants. It provides a basis for understanding the mass changes occurring during these processes and enables scientists to develop strategies to minimize environmental impacts.
5. Industrial processes: Lavoisier’s law guides manufacturing and industrial processes that involve chemical reactions. By understanding the conservation of mass, engineers and chemists can design efficient and cost-effective processes, ensuring that the input materials are utilized optimally and waste generation is minimized.
6. Forensic science: Lavoisier’s law serves as a fundamental principle in forensic investigations. It aids forensic scientists in determining the quantities and identities of substances involved in a crime scene. By analyzing the mass changes during reactions or the conservation of mass in various samples, they can draw conclusions and provide evidence in criminal cases.
7. Biological processes: Lavoisier’s law is applicable in studying various biological processes, such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and digestion. It allows scientists to determine the mass changes occurring during these processes and understand how matter is transformed within living organisms.
In summary, Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass has wide-ranging applications in chemistry, environmental science, industry, forensics, and biology. It provides a fundamental framework for understanding and predicting mass changes in chemical reactions and processes.
Importance and Significance of Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass in Physics
Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass is of great importance and significance in physics. This law states that in a closed system, mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
One of the key implications of this law is that it supports the idea that matter is conserved. This means that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction will always be equal to the total mass of the products. Therefore, the law provides a fundamental understanding of the conservation of matter.
The law has several important implications. Firstly, it allows scientists to accurately measure the amount of substances involved in a chemical reaction. By carefully measuring the mass of substances before and after a reaction occurs, one can determine the stoichiometry (the ratio of reactants and products) of the reaction. This is crucial in understanding the quantitative aspects of chemical reactions.
Moreover, Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass is closely linked to other fundamental principles in physics. It connects to the law of energy conservation, as both mass and energy are conserved in a closed system. This concept is key in thermodynamics and other areas of physics.
Additionally, the law has practical applications. It is utilized in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and engineering. Understanding the conservation of mass is essential for ensuring the efficiency and safety of chemical reactions and industrial processes.
Overall, Lavoisier’s Law of Conservation of Mass plays a fundamental role in our understanding of the physical world. It provides the basis for measuring and quantifying chemical reactions and has significant implications for various scientific fields.
Topics related to Lavoisierʼs Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Conservation of Mass | Don't Memorise – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass | Don't Memorise – YouTube
The Law of Conservation of Mass – MeitY OLabs – YouTube
The Law of Conservation of Mass – MeitY OLabs – YouTube
What Is The Law of Conservation of Mass | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
What Is The Law of Conservation of Mass | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass Example – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass Example – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass – Fundamental Chemical Laws, Chemistry – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass – Fundamental Chemical Laws, Chemistry – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass experiment | Law of conservation of matter | Chemistry – YouTube
Law of Conservation of Mass experiment | Law of conservation of matter | Chemistry – YouTube
The Law of Conservation of Matter – YouTube
The Law of Conservation of Matter – YouTube
Conservation of Mass Experiment – YouTube
Conservation of Mass Experiment – YouTube
Best Conservation of Mass Experiment EVER!(maybe) – YouTube
Best Conservation of Mass Experiment EVER!(maybe) – YouTube
Example of #Momentum, law of conservation of #Momentum #short #shorts By Special Study Pro – YouTube
Example of #Momentum, law of conservation of #Momentum #short #shorts By Special Study Pro – YouTube

Konstantin Sergeevich Novoselov is a Russian-British physicist born on August 23, 1974. Novoselov is best known for his groundbreaking work in the field of condensed matter physics and, in particular, for his co-discovery of graphene. Novoselov awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Konstantin Novoselov has continued his research in physics and materials science, contributing to the exploration of graphene’s properties and potential applications.