Introduction to Cyanuric Acid
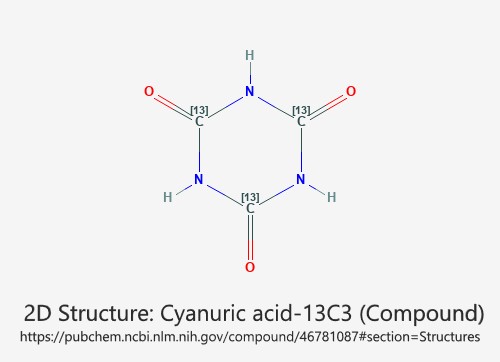
Cyanuric acid is a chemical compound with the formula (C3H3N3O3). It is a white, crystalline solid that has a variety of uses in chemistry. The compound is classified as a triazine derivative, as it contains a six-membered ring consisting of three nitrogen atoms and three carbon atoms.
One of the primary uses of cyanuric acid is as a stabilizer for chlorine compounds, particularly in swimming pools. It helps extend the lifespan of chlorine by protecting it from the degrading effects of sunlight. This stabilizing effect is crucial in maintaining the effectiveness of chlorine as a disinfectant.
Cyanuric acid is also used as a precursor for the synthesis of various other chemicals. It can be reacted with amines and alcohols to form alkylated or acylated derivatives. These derivatives find applications in the production of herbicides, flame retardants, and polymer additives.
Additionally, cyanuric acid can act as a ligand in coordination chemistry. It can form complexes with metal ions, such as copper or zinc, through the nitrogen atoms in its ring structure. These complexes have been studied for their potential applications in catalysis and materials science.
In recent years, cyanuric acid has gained attention due to its environmental impact. When chlorine reacts with cyanuric acid, a byproduct known as chloroamine can form. Chloroamine is a disinfection byproduct that has been linked to potential health concerns.
Overall, cyanuric acid is a versatile compound that finds uses in various fields of chemistry. While its role as a stabilizer for chlorine compounds is crucial, ongoing research aims to better understand its impact on human health and explore its potential applications in other areas of chemistry.
Chemical Formula and Structure of Cyanuric Acid
Properties of Cyanuric Acid
Cyanuric acid, also known as 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol, is a white crystalline solid with the molecular formula C3H3N3O3. It is a derivative of melamine and is commonly used as a stabilizer for chlorine in swimming pools. Here are some properties of cyanuric acid in chemistry:
1. Chemical structure: Cyanuric acid has a triazine ring structure with three hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to the carbon atoms of the ring. The chemical structure makes it a weak acid and a triprotic acid that can donate three hydrogen ions (protons).
2. Solubility: Cyanuric acid is sparingly soluble in water. At room temperature, approximately 0.25 grams of cyanuric acid can dissolve in 100 mL of water, giving a solubility of about 2.5 g/L. However, its solubility increases with increasing temperature.
3. Acidity: Cyanuric acid is a weak acid due to the presence of hydroxyl groups. It can dissociate its three protons successively in water, forming three corresponding series of cyanurate ions.
4. Stabilizer for chlorinated compounds: One of the main uses of cyanuric acid is as a stabilizer for chlorine-based disinfectants, such as trichloroisocyanuric acid and sodium dichloroisocyanurate. It helps in preventing the degradation of chlorine molecules by sunlight (UV radiation), extending the effectiveness of the disinfectants in maintaining pool water hygiene.
5. Melting and decomposition point: Cyanuric acid has a melting point of approximately 320 °C. At higher temperatures, above 360 °C, it decomposes into various products, including carbon dioxide, ammonia, and cyanuric acid anhydride.
6. Stability: Cyanuric acid is relatively stable and does not readily decompose under normal storage conditions. However, it can decompose at high temperatures, such as during combustion or thermal decomposition processes.
7. Biodegradability: Cyanuric acid is considered to be biodegradable under aerobic conditions. It can be broken down by microorganisms present in the environment, leading to carbon dioxide, water, and other byproducts.
8. Toxicity: Cyanuric acid is considered to have low acute toxicity. However, it is recommended to handle this chemical with care and follow proper safety protocols to prevent exposure.
These are some of the properties of cyanuric acid in chemistry. It is important to note that the specific properties of cyanuric acid can vary depending on factors such as purity, temperature, and pH conditions.
Uses and Applications of Cyanuric Acid
Cyanuric acid is a chemical compound with the formula C3H3N3O3. It has several uses and applications in chemistry, including:
1. Stabilizer in swimming pools: One of the primary uses of cyanuric acid is as a stabilizer in swimming pools. It helps to protect chlorine from the degrading effects of sunlight, thereby increasing its effectiveness and prolonging its lifespan. Cyanuric acid forms a complex with chlorine, which releases chlorine slowly as needed, reducing the need for frequent chlorine additions.
2. Industrial chemical reagent: Cyanuric acid is used as a reagent in various industrial chemical reactions. It can be used as a precursor for the synthesis of other chemicals, such as herbicides, disinfectants, and flame retardants. Its ability to form stable complexes with metal ions makes it useful in many chemical processes.
3. Adhesive production: Cyanuric acid is used in the manufacture of adhesives and resins. It acts as a cross-linking agent, helping to improve the adhesive strength and durability of the final product. It is commonly used in the production of melamine-formaldehyde resins, which are widely used in wood laminates, countertops, and other construction materials.
4. Analytical chemistry: Cyanuric acid is used in several analytical techniques in chemistry. It can be used as a standard in titration and calibration experiments. Additionally, its ability to form complexes with metal ions makes it useful in the determination of certain metals, such as iron, zinc, and copper, in various solutions.
5. Water treatment: Cyanuric acid is also used in water treatment processes. It can be added to water systems to control the growth of bacteria and algae. The complex formed between cyanuric acid and chlorine helps to prevent the degradation of chlorine by UV light, allowing it to remain effective for longer periods.
In summary, cyanuric acid finds applications as a stabilizer in swimming pools, industrial reagent, adhesive production, analytical chemistry, and water treatment. Its unique properties make it a versatile compound with various uses in different areas of chemistry.
Safety and Environmental Considerations of Cyanuric Acid
Safety Considerations of Cyanuric Acid:
1. Cyanuric acid is considered to be a corrosive substance and can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes. It is important to wear appropriate protective clothing, such as gloves and goggles, when handling this compound.
2. Inhalation of cyanuric acid dust or vapors can irritate the respiratory system and cause respiratory distress. It is advisable to handle this substance in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
3. Cyanuric acid may react violently with certain chemicals, such as strong oxidizers or reducing agents. It is important to avoid mixing it with incompatible substances to prevent hazardous reactions.
4. Ingestion of cyanuric acid can be toxic and may cause gastrointestinal irritation, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It should be stored in a secure location away from food and beverages.
5. Proper storage and handling practices should be followed to prevent accidental spills or leaks. Spilled material should be carefully contained and disposed of according to local regulations.
Environmental Considerations of Cyanuric Acid:
1. Cyanuric acid is persistent in the environment and does not readily degrade. It can accumulate in soil, water bodies, and aquatic organisms, leading to potential environmental pollution.
2. It is important to prevent the release of cyanuric acid into the environment through proper containment and disposal practices.
3. Cyanuric acid can have adverse effects on aquatic organisms if released into water bodies. It is toxic to fish, aquatic invertebrates, and algae, leading to potential disruptions in the aquatic ecosystem.
4. When considering the use of cyanuric acid, it is important to assess any potential risks to the environment and implement appropriate measures to minimize those risks.
5. Recycling or reusing cyanuric acid waste can reduce its environmental impact. However, it is important to ensure that any recycling or reusing processes are carried out safely and in compliance with regulations to prevent further environmental contamination.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.