Introduction to Glycolic Acid
Glycolic acid is a type of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that is commonly used in chemistry. It is a colorless, odorless, and water-soluble substance that has a chemical formula of C2H4O3. The most common source of glycolic acid is sugar cane, although it can also be derived from other natural sources such as fruits and milk.
Glycolic acid is known for its ability to exfoliate the skin and promote skin cell turnover, making it a popular ingredient in skincare products. It works by loosening the bonds between dead skin cells on the surface of the skin, allowing them to be easily sloughed off and revealing fresher, brighter skin underneath. This exfoliating action can help improve the appearance of acne, fine lines, wrinkles, and uneven skin tone.
In addition to its skincare benefits, glycolic acid also has various other applications in chemistry. It is commonly used as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of various compounds. It can be converted into different esters, ethers, and amides, which are then used in the production of polymers, solvents, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals.
Glycolic acid is also used as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions. Its strong acidity allows it to effectively catalyze reactions such as esterification, transesterification, and hydrolysis. It can also be used to remove metal oxide layers from surfaces, as it can complex with metal ions and dissolve metal oxides.
Overall, glycolic acid plays a significant role in both skincare and chemistry. Its ability to exfoliate and promote skin cell turnover makes it a valuable ingredient in skincare products, while its chemical properties make it useful in various chemical reactions and processes.
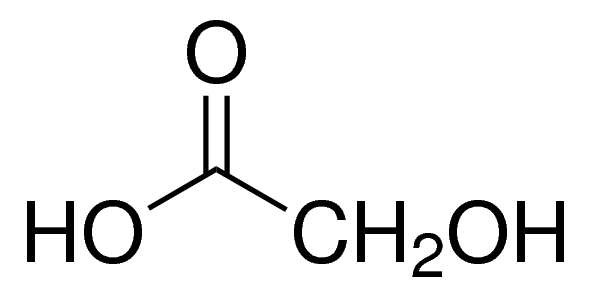
Chemical Structure of Glycolic Acid (C₂H₄O₃)
The chemical structure of glycolic acid (C2H4O3) can be represented using structural formula as follows:
H
|
H-C-OH
|
H
In this structure, the carbon (C) atoms are represented by the vertices, and the hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms are represented by the lines and labels. The subscript numbers indicate the number of each atom in the formula. In glycolic acid’s structure, two carbon atoms are bonded together with a single bond (represented by the line), and each carbon is bonded to one hydroxyl group (OH) and one hydrogen atom (H).
Properties and Characteristics of Glycolic Acid
Glycolic acid is a type of alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) that is commonly used in skincare products and chemical peels. It has several important properties and characteristics in chemistry, including:
1. Chemical formula: Glycolic acid has a chemical formula of C2H4O3, indicating that it consists of two carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms, and three oxygen atoms.
2. Molecular weight: The molecular weight of glycolic acid is approximately 76.05 g/mol.
3. Physical state: Glycolic acid is a colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic liquid at room temperature.
4. Solubility: Glycolic acid is highly soluble in water, alcohol, and acetone, making it easy to incorporate into various formulations.
5. Acidic nature: Glycolic acid is a strong acid, with a pKa value of approximately 3.83. This means that it readily donates a proton (H+) when dissolved in water, making it an effective exfoliating agent.
6. Hydrophilic properties: Due to its hydrophilic (water-loving) nature, glycolic acid has the ability to attract water molecules from its surroundings, enhancing its moisturizing and hydrating effects on the skin.
7. Reactivity: Glycolic acid is reactive and can undergo various chemical reactions, including esterification, amidation, and oxidation.
8. Skin penetration: One of the key characteristics of glycolic acid is its small molecular size, which allows it to easily penetrate the skin’s outermost layer, known as the stratum corneum. This allows it to effectively exfoliate and promote cell turnover.
9. pH levels: Glycolic acid has a low pH level, typically around 3-4, which helps to enhance its exfoliating and skin-renewing properties.
10. Safety precautions: While glycolic acid is generally considered safe for topical use, it can cause skin irritation, especially at higher concentrations. It is important to use it in appropriate concentrations and follow proper usage guidelines to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Overall, glycolic acid is a versatile and widely used compound with various properties and characteristics that make it effective in skincare formulations and chemical peels.
Applications and Uses of Glycolic Acid
Glycolic acid, also known as hydroxyacetic acid, is a versatile chemical compound with numerous applications and uses in the field of chemistry. Some of its important applications are:
1. Skin care: Glycolic acid is commonly used in skincare products, such as chemical peels, facial cleansers, and anti-aging creams. It acts as an exfoliant, helping to remove dead skin cells and improve the overall texture and appearance of the skin.
2. pH adjustment: Glycolic acid is a useful tool for adjusting the pH of various solutions. It is a strong acid, so it can be added in controlled quantities to lower the pH of alkaline solutions.
3. Chemical synthesis: Glycolic acid is used in the synthesis of various organic compounds. It can act as a reactant, catalyst, or a solvent in different chemical reactions. For example, it can be used in the production of polymers, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetic ingredients.
4. Rust removal: Glycolic acid can be used as a rust remover due to its ability to dissolve iron oxide (rust). It can effectively remove rust from metal surfaces by forming water-soluble complexes with iron ions.
5. Paint stripping: Glycolic acid can be utilized in the paint stripping process. Its strong acidic nature helps to break down the chemical bonds present in paint, making it easier to remove.
6. Oil and grease removal: Glycolic acid is effective in removing oil and grease stains from surfaces. It breaks down the bonds between the oil molecules, allowing them to be easily wiped away.
7. pH indicator: Glycolic acid can be used as a pH indicator due to its ability to change color with changes in pH. It can be used to identify the endpoint of a titration or to monitor pH changes in various chemical reactions.
8. Leather tanning: Glycolic acid is used in leather tanning processes to remove hair and epidermis from animal hides. It helps to break down the proteins present in these tissues, facilitating their removal.
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications and uses of glycolic acid in chemistry. Its versatile nature and chemical properties make it a valuable compound in various industries and research fields.
Safety and Precautions when Handling Glycolic Acid
When handling glycolic acid in chemistry, there are several safety precautions that should be followed to ensure personal safety and reduce the risk of accidents or injuries. Here are some guidelines to consider:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles or safety glasses, and lab coat or protective clothing. This is crucial to protect your skin, eyes, and clothes from potential contact with glycolic acid.
2. Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Ensure that you are working in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood. Glycolic acid may release irritating vapors, and proper ventilation helps to minimize the inhalation of these vapors.
3. Understanding the Properties and Hazards: Familiarize yourself with the properties of glycolic acid, such as its corrosive nature and the potential for skin and eye irritation. This knowledge will help you take necessary precautions and respond appropriately in case of accidental exposure.
4. Storage and Handling: Store glycolic acid in a well-sealed container, preferably in a designated chemical storage area away from incompatible materials. Always handle the acid with care and avoid any spills or splashes.
5. Emergency Preparedness: Familiarize yourself with the location and proper use of safety equipment, such as eyewash stations, safety showers, and fire extinguishers. It is also wise to have an emergency response plan in place.
6. Dilution and Mixing: If diluting or mixing glycolic acid with other substances, always follow proper procedures and guidelines. It is essential to add glycolic acid to water slowly, while stirring, to minimize heat generation and potential splattering.
7. Cleanliness and Waste Disposal: Keep your workspace clean and free from any spills or clutter. Dispose of waste or unused glycolic acid in proper chemical waste containers according to local regulations and guidelines.
8. First Aid Training: Ensure that you are familiar with the appropriate first aid measures in case of accidental exposure or injury. Learn how to treat skin and eye contact, inhalation, or ingestion of glycolic acid and seek medical assistance if needed.
Remember to always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and any specific guidance provided by your institution or organization when working with glycolic acid or any other chemical.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.