Introduction
Chemistry is the scientific study of matter and the changes it undergoes. It is a branch of science that focuses on the composition, properties, and reactions of substances. In other words, chemistry explores the building blocks of everything around us – from the air we breathe, the water we drink, to the food we eat.
Chemistry is a fundamental science that plays a crucial role in various fields such as medicine, environmental science, materials science, and the development of new technologies. It helps us understand the behavior of elements, compounds, and mixtures, and allows us to manipulate matter to create new substances and solve practical problems.
Chemists use various tools, techniques, and theories to investigate chemical phenomena. They deal with atoms, which are the basic units of matter, and molecules, which are groups of atoms bonded together. Chemical reactions, which involve the rearrangement of atoms in molecules, are studied to understand and predict the behavior of substances.
In order to comprehend chemistry, it is necessary to have a strong foundation in topics such as atomic structure, periodic table, chemical bonding, stoichiometry, and thermodynamics. Throughout the study of chemistry, concepts such as acids and bases, kinetics, equilibrium, and organic chemistry are progressively explored.
Overall, chemistry is a fascinating subject that provides a deep understanding of the world around us at the atomic and molecular level. It allows us to uncover the mysteries of matter and contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge and applied technologies.
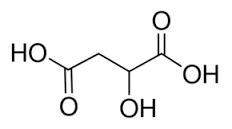
Chemical Structure of Malic Acid (C₄H₆O₅)
Malic acid, with the chemical formula C₄H₆O₅, has a molecular structure consisting of four carbon atoms (C₄), six hydrogen atoms (H₆), and five oxygen atoms (O₅). It is a dicarboxylic acid, meaning it contains two carboxylic acid functional groups (-COOH).
The structure of malic acid can be depicted as follows:
HOOC-CH₂-CH(OH)-COOH
In this structure, the carboxylic acid functional groups are attached to the two adjacent carbon atoms. The carbon atom between them is connected to two hydrogen atoms and a hydroxyl group (-OH).
Properties of Malic Acid
Malic acid, chemical formula C4H6O5, is a dicarboxylic acid that occurs naturally in various fruits, particularly in apples. It is a white crystalline solid with a sour taste. Here are some important properties of malic acid in chemistry:
1. Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of malic acid is approximately 134.09 g/mol.
2. Structure: Malic acid exists as a chiral molecule with two stereoisomers: L-malic acid and D-malic acid. The L-form is the more common and biologically active isomer.
3. Solubility: Malic acid is highly soluble in water, with a solubility of about 550 g/L at 20°C. It also exhibits moderate solubility in polar organic solvents such as ethanol.
4. Acidity: Malic acid is a dibasic acid, meaning it has two carboxylic acid groups. Its pKa values for the first and second protonation steps are approximately 3.4 and 5.1, respectively. These values indicate that malic acid is a moderately strong acid.
5. Hydrophilicity: Due to its polar nature, malic acid is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere.
6. Stability: Malic acid is relatively stable under normal conditions, but it can undergo thermal decomposition at high temperatures, releasing carbon dioxide and producing maleic anhydride.
7. Chemical Reactions: Malic acid can undergo various chemical reactions, including esterification, dehydration, and decarboxylation. It can be converted to its anhydride (maleic anhydride) by heating.
8. Food Additive: Malic acid is commonly used as a food additive, especially in the food and beverage industry, owing to its sour taste. It is recognized as a safe and natural ingredient.
9. Biological Roles: Malic acid plays crucial roles in various metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) in cellular respiration. It is involved in the generation of energy by facilitating the conversion of glucose to ATP.
These are some key properties of malic acid in chemistry. It is important to note that malic acid has numerous applications beyond its chemical properties, including its use as a flavoring agent, pH adjuster, and antioxidant.
Uses of Malic Acid
Malic acid (C4H6O5) is a dicarboxylic acid commonly found in plant tissues, particularly in fruits. It has several uses in chemistry, including:
1. Food and beverage industry: Malic acid is widely used as a flavoring agent in the food and beverage industry. It gives a tart or sour taste and is commonly found in sour candies, soft drinks, and fruit-flavored products.
2. pH adjustment: Malic acid can be used as a pH adjustment agent in various chemical processes. It is used to decrease the pH of solutions or to control the acidity of certain reactions.
3. Metal cleaning and balancing: Malic acid can be used as a chelating agent for certain metals. It helps in cleaning metal surfaces by removing mineral deposits and scales. It is also used in metal plating processes to help balance pH levels.
4. Chemical synthesis: Malic acid can be used in various chemical reactions for the synthesis of other organic compounds. It can undergo esterification reactions with alcohols, oxidation reactions, and condensation reactions to form other useful compounds.
5. Pharmaceutical applications: Malic acid is used as an excipient in the pharmaceutical industry. It is often used as a pH adjuster or acidity regulator in oral medications and topical formulations.
6. Cosmetics: Malic acid is used in cosmetic products for its exfoliating properties. It can help remove dead skin cells and promote skin rejuvenation. It is commonly found in facial peels, masks, and skincare products.
7. Biotechnology: Malic acid is used in certain biotechnological processes as a substrate or nutrient source for microorganisms. It can be utilized by certain bacteria and fungi for the production of other organic compounds or as a source of energy.
Overall, malic acid has various applications in chemistry, particularly in the food and beverage industry, pH adjustment, metal cleaning, chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and biotechnology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chemistry is a fundamental branch of science that involves the study of matter, its properties, composition, and behavior. It plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives, including medicine, agriculture, industry, and environmental protection. Through meticulous research and experimentation, chemists have made significant contributions to the development of new technologies, materials, and drugs, ultimately improving the quality of life for humanity. Furthermore, chemistry provides a solid foundation for understanding the world around us and enables us to make informed decisions based on scientific evidence. With ongoing advancements in the field, chemistry continues to push boundaries and unlock new possibilities for solving complex problems and addressing global challenges.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.