Introduction to Sodium Metabisulfite (Na₂S₂O₅)
Sodium metabisulfite, with the chemical formula Na2S2O5, is a chemical compound that belongs to the family of sulfites. It is commonly used in various industrial and culinary applications due to its versatile properties. Here’s an introduction to sodium metabisulfite:
Chemical Structure:
Sodium metabisulfite is composed of two sodium (Na) ions, two sulfur (S) atoms, and five oxygen (O) atoms, making it a sodium salt of metabisulfite anion (S2O5^2-). Its chemical formula is Na2S2O5.
Physical Properties:
Sodium metabisulfite typically appears as a white crystalline powder or small crystals.
It is readily soluble in water, which makes it convenient for various applications.
Uses and Applications:
Sodium metabisulfite is employed in a variety of industries and processes:
Food and Beverage Industry: It is used as a food preservative and antioxidant to extend the shelf life of certain products. It can help prevent browning in fruits and vegetables and inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms.
Winemaking: Sodium metabisulfite is a common additive in winemaking. It is used to sterilize equipment, prevent oxidation, and control fermentation. It also plays a role in preserving the flavor and aroma of wine.
Photography: In the past, it was used in photographic development and printing processes. Its ability to release sulfur dioxide gas makes it useful for reducing silver halides in film and paper development.
Water Treatment: Sodium metabisulfite is used to remove chlorine and chloramine from drinking water. It is an effective dechlorinating agent.
Chemical Industry: It is employed as a reducing agent in various chemical reactions.
Textile Industry: In dyeing and printing processes, it is used to remove excess dye and to bleach textile materials.
Sanitization and Cleaning: It can be used as a disinfectant and sterilizing agent for equipment and surfaces in various industries.
Health and Safety Considerations:
Sodium metabisulfite can cause respiratory and skin irritation in its solid form or if the fumes are inhaled. Proper safety precautions should be taken when handling this chemical.
Allergies and Sensitivities:
Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to sodium metabisulfite, experiencing symptoms like skin rashes, hives, or respiratory issues upon exposure.
Regulatory Status:
The use of sodium metabisulfite in food and beverage products is regulated by health authorities, and maximum allowable concentrations are specified to ensure safety for consumers.
Sodium metabisulfite is a versatile compound with numerous practical applications, particularly in the preservation and treatment of various products. However, it should be handled with care, and its use in food and other consumer products is subject to regulatory oversight to ensure safety.
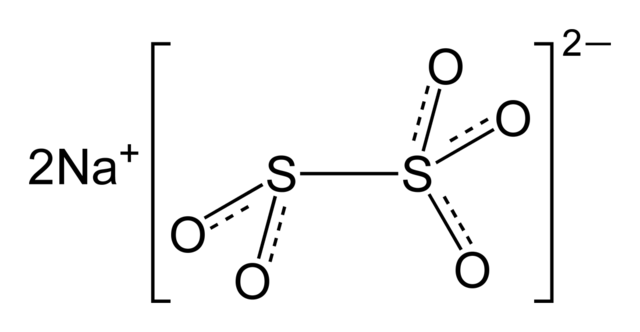
Chemical Structure of Sodium Metabisulfite (Na₂S₂O₅)
The chemical structure of sodium metabisulfite (Na₂S₂O₅) can be represented as:
O O
/
S
/
Na–O O–S
|
O
In this structure, the two sulfur atoms are connected by an oxygen atom in the middle. Each sulfur atom is bonded to an oxygen atom on one side, and the other sulfur atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms on the other side. The sodium atom is bonded to one of the oxygen atoms connected to the sulfur atom.
Properties and Uses of Sodium Metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5) is a chemical compound with a wide range of properties and uses in various industries. Here are some of its key properties and common applications:
Properties:
Chemical Structure: Sodium metabisulfite is composed of two sodium (Na) ions, two sulfur (S) atoms, and five oxygen (O) atoms, forming a sodium salt of the metabisulfite anion (S2O5^2-).
Physical Form: It typically exists as a white crystalline powder or small crystals, which are readily soluble in water.
Reduction Agent: Sodium metabisulfite is a potent reducing agent, meaning it has the ability to donate electrons in chemical reactions. This property makes it useful in various applications where reduction reactions are required.
Release of Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): When sodium metabisulfite is exposed to moisture or an acidic environment, it releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas. This property is valuable in several applications, particularly as a preservative and antioxidant.
Common Uses:
Food and Beverage Industry: Sodium metabisulfite is widely used in the food and beverage industry for various purposes:
Preservative: It acts as a preservative, helping to extend the shelf life of products such as dried fruits, wine, beer, and some processed foods.
Antioxidant: Sodium metabisulfite prevents the oxidation of food products, helping to maintain their color, flavor, and nutritional quality.
Browning Inhibitor: It can be used to prevent browning in fresh-cut fruits and vegetables.
Winemaking: Sodium metabisulfite is a critical additive in winemaking:
Sanitization: It is used to sterilize equipment and prevent contamination by undesirable microorganisms.
Oxidation Control: It helps control oxidation during fermentation and storage, preserving the aroma and flavor of the wine.
Water Treatment: Sodium metabisulfite is employed in water treatment processes:
Dechlorination: It is used to remove chlorine and chloramine from drinking water, making it safe for consumption.
Photography: While less common today due to digital technology, sodium metabisulfite was used in photographic development and printing processes to reduce silver halides.
Textile Industry: It is used in the textile industry for bleaching and dyeing processes to remove excess dye.
Chemical Industry: Sodium metabisulfite is a versatile reducing agent used in various chemical reactions and processes.
Sanitization and Cleaning: It can be used as a disinfectant and sterilizing agent for equipment and surfaces in various industries.
Leather Industry: It is used in the tanning process to remove excess dye and chemicals.
Analytical Chemistry: Sodium metabisulfite is used as a reducing agent in certain chemical tests and analyses.
Art Conservation: It can be used in the preservation and restoration of art and cultural artifacts.
It’s important to note that while sodium metabisulfite has numerous valuable applications, it should be handled with care, and its use in food and other consumer products is subject to regulatory standards and maximum allowable concentrations to ensure the safety of consumers. Additionally, individuals with sensitivities or allergies to sulfites should be cautious when products containing sodium metabisulfite are involved.
Safety Considerations and Health Effects of Sodium Metabisulfite
Sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5) is a chemical compound that has several industrial and culinary uses. However, it is important to be aware of safety considerations and potential health effects when handling or consuming products containing sodium metabisulfite. Here are some key safety considerations and potential health effects associated with this compound:
Safety Considerations:
Irritant: Sodium metabisulfite in its solid form can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. When handling the compound, it is advisable to wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves and safety goggles, and to work in a well-ventilated area.
Allergies and Sensitivities: Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to sodium metabisulfite. Exposure to the compound can lead to allergic reactions, which may include skin rashes, hives, itching, and respiratory issues. People with known sulfite allergies should avoid products containing sodium metabisulfite.
Inhalation Hazards: When sodium metabisulfite is exposed to moisture or acidic conditions, it can release sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas. Inhaling sulfur dioxide fumes can irritate the respiratory system and cause coughing, difficulty breathing, and other respiratory symptoms. Adequate ventilation is essential when using this compound.
Corrosive to Metals: Sodium metabisulfite can be corrosive to some metals. When stored or used with metal equipment or containers, it can lead to corrosion and damage.
Storage and Handling: Proper storage is crucial to prevent contamination and exposure. Store sodium metabisulfite in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials, and keep it tightly sealed in its original container.
Health Effects:
Ingestion: Ingesting sodium metabisulfite can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. In severe cases, it may lead to more significant health issues.
Skin Contact: Direct contact with the skin may result in irritation, redness, itching, or dermatitis, especially in individuals with sensitivities or allergies to sulfites.
Eye Contact: Contact with the eyes can cause irritation, redness, and tearing. Rinse the eyes with plenty of water if exposed and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
Inhalation: Inhaling sulfur dioxide gas, released when sodium metabisulfite is exposed to moisture or acidic conditions, can irritate the respiratory system. Symptoms may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Seek fresh air if exposed and seek medical attention if symptoms are severe.
It’s important to follow safety guidelines and handle sodium metabisulfite with care to minimize the risk of adverse effects. In the food and beverage industry, the use of sodium metabisulfite is regulated to ensure that concentrations are within safe limits for consumers. Individuals with known allergies or sensitivities to sulfites should read product labels carefully and avoid products that contain sodium metabisulfite. If you experience any adverse reactions or health concerns related to exposure, it’s advisable to seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chemistry is a vast and complex scientific field that studies the composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter. It plays a crucial role in our everyday lives, from the production of medicines and materials to the understanding of natural phenomena and the development of sustainable technologies. By studying chemistry, we can better understand the world around us and make informed decisions to improve our quality of life and protect the environment. Additionally, chemistry is an ever-evolving discipline that continues to uncover new discoveries and advancements, offering endless opportunities for future research and innovation.

Abigail Gutmann Doyle is a renowned Organic chemistry professor in Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the development of new chemical transformations in organic chemistry. She has won awards such as: Bayer Early Excellence in Science Award, Phi Lambda Upsilon National Fresenius Award, Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers, BMS Unrestricted Grant in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.