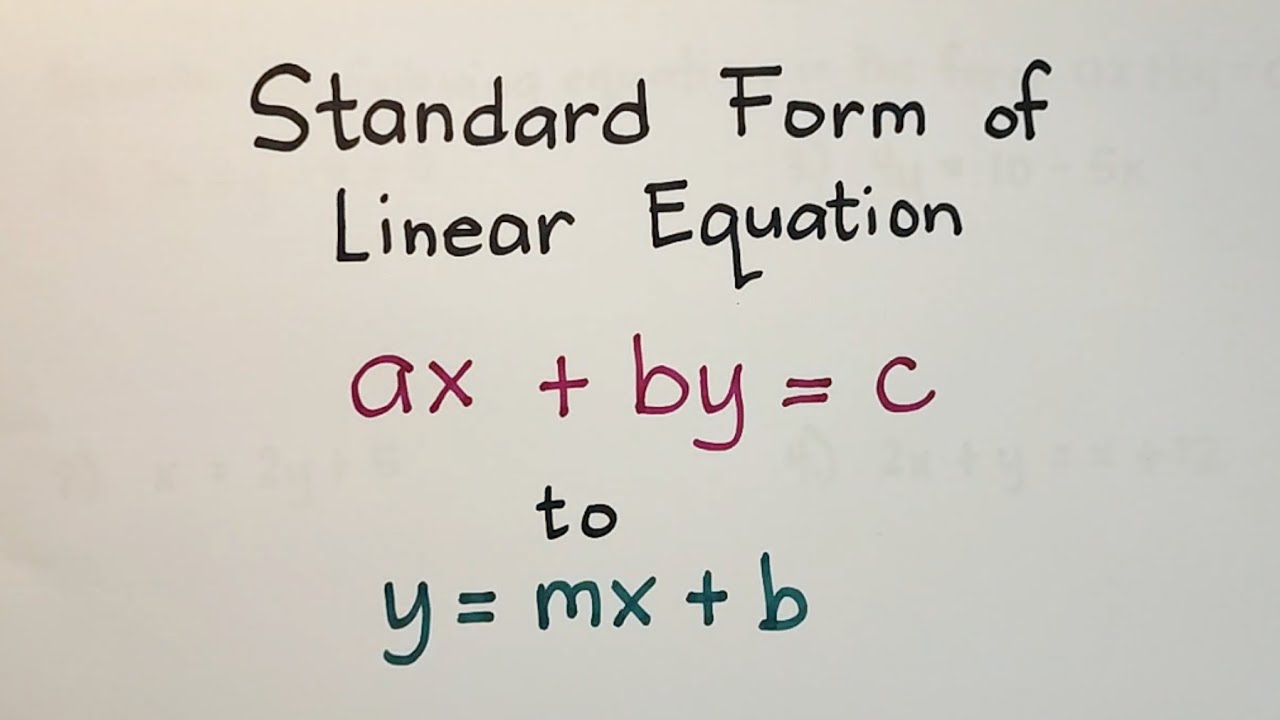Definition of slope-intercept form
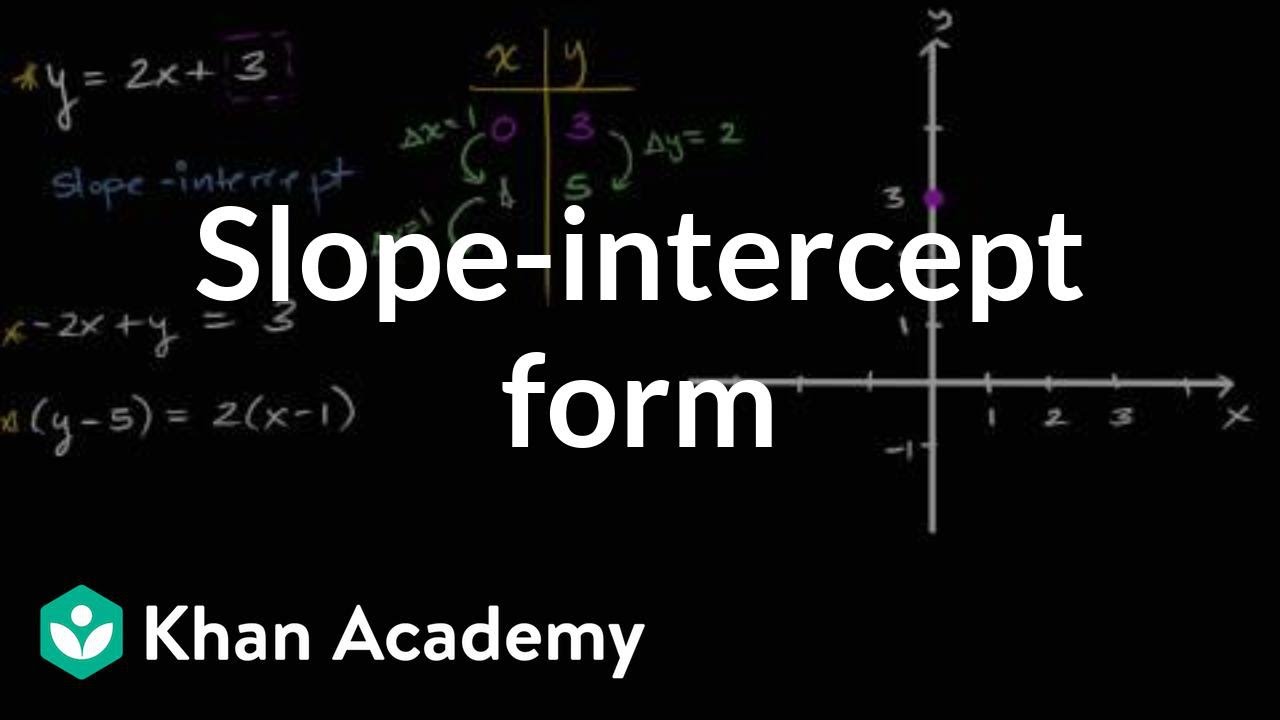
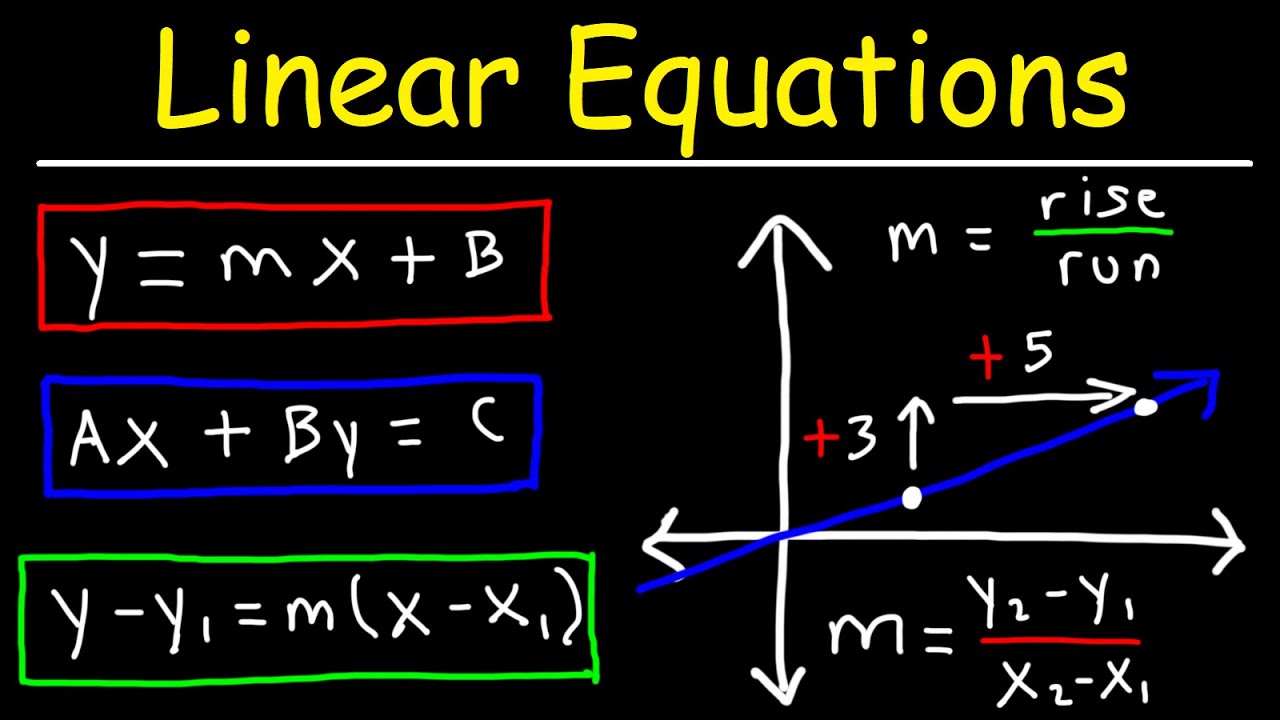
Slope-intercept form is a way to represent a linear equation in the form y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept.
The slope, m, indicates the rate of change of the line, or how steep the line is. A positive slope indicates a line that is increasing from left to right, while a negative slope indicates a line that is decreasing.
The y-intercept, b, represents the point where the line crosses the y-axis. It gives the value of y when x is equal to 0.
By using the slope-intercept form, it becomes easier to graph a linear equation and determine important characteristics of the line, such as the slope and y-intercept. It also allows for simple manipulation of the equation to solve for unknown values or to find the equation of a line given certain conditions.
Equation form and components of slope-intercept form
The slope-intercept form of an equation is a commonly used form to represent a linear equation in the format y = mx + b, where:
– y represents the dependent variable or the output value
– x represents the independent variable or the input value
– m represents the slope of the line, which determines the steepness or the angle of the line
– b represents the y-intercept, which is the point where the line intersects the y-axis
In this form, the slope (m) is multiplied by the input variable (x), and the product is added to the y-intercept (b) to determine the value of the output variable (y).
For example, if we have the equation y = 3x + 2, the slope (m) is 3, and the y-intercept (b) is 2. This means that for every unit increase in x, y will increase by 3 units. The y-intercept tells us that the line intersects the y-axis at the point (0, 2).
The slope-intercept form can be useful for graphing linear equations, as it explicitly shows the slope and the y-intercept, making it easier to identify key characteristics of the line.
Applications of slope-intercept form in mathematics
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation in mathematics is expressed as y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept. This form is particularly useful in various applications within mathematics. Here are some examples:
1. Graphing linear equations: The slope-intercept form allows us to easily graph linear equations on a coordinate plane. By identifying the slope and y-intercept, we can plot two points and draw a straight line connecting them.
2. Finding the slope: The slope-intercept form allows us to directly identify the slope of a line. The value of m indicates the rate of change of y with respect to x, providing information on how the line is inclined.
3. Finding the y-intercept: The slope-intercept form also helps us determine the y-intercept, which is the point on the y-axis where the line intersects. The value of b represents the y-coordinate when x is equal to 0.
4. Writing linear equations: The slope-intercept form is commonly used to express linear equations in a simplified and concise manner. Given the slope and y-intercept, we can easily write the equation that represents a specific line.
5. Solving systems of linear equations: In systems of linear equations, where there are multiple lines intersecting, the slope-intercept form facilitates finding the solution. By equating the y-values of the lines’ equations, we can determine the point of intersection.
6. Calculating parallel and perpendicular lines: The slope-intercept form is useful for identifying parallel and perpendicular lines. If two lines have the same slope (m), they are parallel, while lines with slopes that are negative reciprocals of each other are perpendicular.
Overall, the slope-intercept form offers a simple and versatile way to analyze and represent linear relationships in mathematics.
Converting equations to slope-intercept form
The slope-intercept form of an equation is represented as y = mx + b, where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept.
To convert an equation to slope-intercept form, follow these steps:
1. Simplify the equation if necessary.
2. Solve the equation for y.
3. Rewrite the equation in the form y = mx + b.
For example, let’s convert the equation 3x – 2y = 8 to slope-intercept form.
1. Simplify the equation:
-2y = -3x + 8
2. Solve the equation for y:
Divide both sides of the equation by -2 to isolate y:
y = (3/2)x – 4
3. Rewrite the equation in slope-intercept form:
y = (3/2)x – 4
Now the equation is in slope-intercept form, where the slope is 3/2 and the y-intercept is -4.
Solving problems using slope-intercept form
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is given by:
y = mx + b
Where:
– m is the slope of the line
– b is the y-intercept (the point where the line crosses the y-axis)
To solve problems using the slope-intercept form, you need to know either the slope and y-intercept or two points on the line.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to solve problems using slope-intercept form:
1. Identify the given information: Determine what information is given in the problem. This can include the slope, y-intercept, or two points on the line.
2. Write the equation: If you know the slope (m) and y-intercept (b), simply substitute these values into the slope-intercept form equation (y = mx + b) to write the equation of the line.
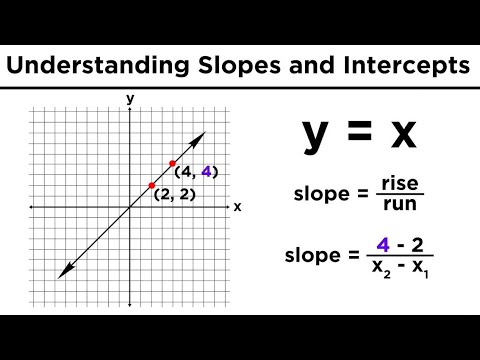
3. Find the slope: If you are given two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) on the line, you can use the formula for slope:
m = (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1)
4. Substitute values: If you are given the slope (m) and one point (x1, y1), you can substitute these values into the slope-intercept form equation to find the y-intercept (b).
5. Solve for the desired variable: Once you have the equation of the line, you can solve for the desired variable. This might involve rearranging the equation or plugging in specific values.
6. Check your solution: After finding the solution, double-check that it satisfies the original problem condition. Plug the solution back into the original equation or test it with other given information to ensure that it works.
By following these steps, you can effectively solve problems using the slope-intercept form of a linear equation.
Topics related to Slope-intercept form
Slope Intercept Form Y=mx+b | Algebra – YouTube
Slope Intercept Form Y=mx+b | Algebra – YouTube
Slope-intercept form | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
Slope-intercept form | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
Graphing Lines in Algebra: Understanding Slopes and Y-Intercepts – YouTube
Graphing Lines in Algebra: Understanding Slopes and Y-Intercepts – YouTube
Basic Linear Functions – Math Antics – YouTube
Basic Linear Functions – Math Antics – YouTube
Algebra Basics: Slope And Distance – Math Antics – YouTube
Algebra Basics: Slope And Distance – Math Antics – YouTube
Linear Equations – Algebra – YouTube
Linear Equations – Algebra – YouTube
Slope Intercept Form (Math Rap) – YouTube
Slope Intercept Form (Math Rap) – YouTube
Slope intercept form explained – YouTube
Slope intercept form explained – YouTube
How to write an equation from standard form to slope intercept form – YouTube
How to write an equation from standard form to slope intercept form – YouTube
Standard Form and Slope Intercept Form of Linear Equation in Two Variables – Grade 8 Math – YouTube
Standard Form and Slope Intercept Form of Linear Equation in Two Variables – Grade 8 Math – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.