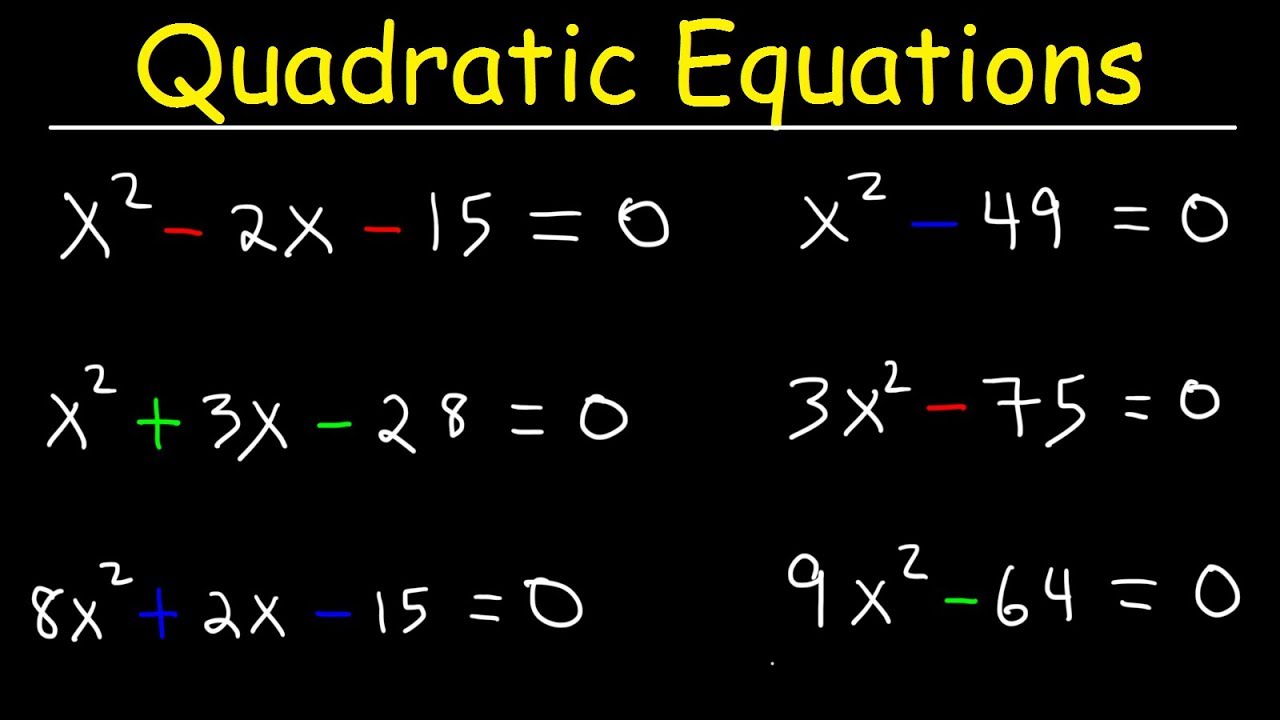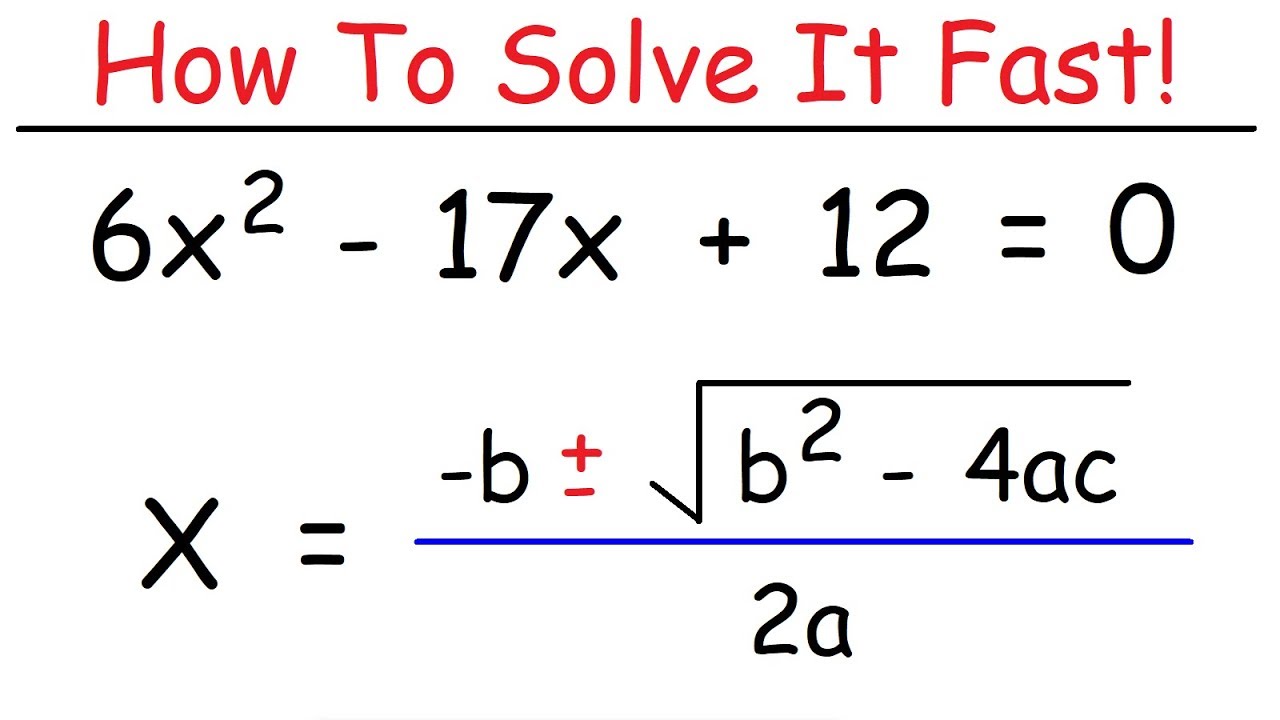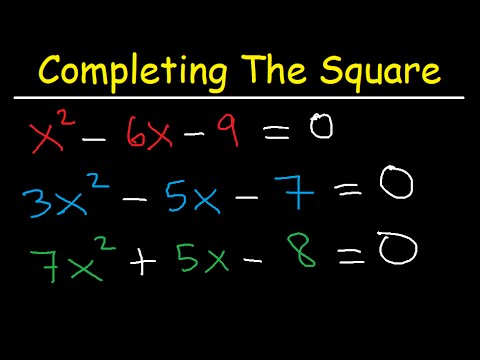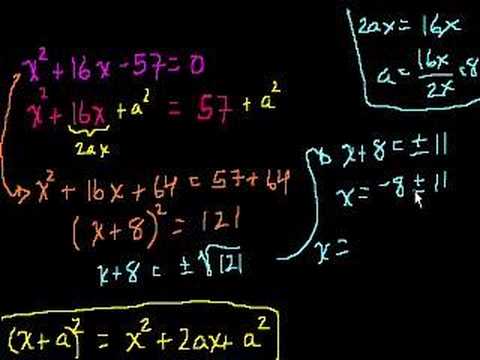Definition of quadratic equation
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of degree 2, which means it contains at least one term raised to the power of 2 and no terms with higher powers. It can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants with a not equal to 0, and x is the unknown variable. The solutions to a quadratic equation are the values of x that make the equation true. These solutions can be found using methods such as factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula.
Standard form of a quadratic equation
The standard form of a quadratic equation is where the equation is written in the form:
ax^2 + bx + c = 0,
where a, b, and c are coefficients, and x is the variable.
This form represents a quadratic equation, which is a polynomial equation of degree two, and it can be solved using various methods such as factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula.
Solving quadratic equations
To solve a quadratic equation, you can use several methods: factoring, completing the square, or applying the quadratic formula.
First, let’s consider a quadratic equation in the standard form: ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants.
Method 1: Factoring
1. Rewrite the equation in the standard form: 0 = ax^2 + bx + c.
2. Factor the quadratic equation, if possible, into two binomials. This involves finding two numbers that multiply to give c (the constant term) and add up to give b (the coefficient of x).
3. Set each factor equal to zero and solve for x to find the values of x that satisfy the equation.
Method 2: Completing the Square
1. Rewrite the equation in the standard form: 0 = ax^2 + bx + c.
2. If necessary, divide the entire equation by a to make the coefficient of x^2 equal to 1.
3. Arrange the equation so that the constant term is on the right side.
4. Take half of the coefficient of x (b/2) and square it. Add this value to both sides of the equation to complete the square on the left side.
5. Factor the left side of the equation, if possible, into a perfect square trinomial.
6. Take the square root of both sides of the equation and solve for x to find the values of x that satisfy the equation.
Method 3: Quadratic Formula
1. For the equation in standard form: 0 = ax^2 + bx + c, use the quadratic formula: x = (-b ± sqrt(b^2 – 4ac)) / (2a).
2. Plug in the values of a, b, and c into the quadratic formula and simplify.
3. The quadratic formula often yields two solutions for x, as indicated by the ± symbol. Solve for both values of x to find the solutions to the equation.
Remember, not every quadratic equation has real solutions. In some cases, the solutions may be complex numbers.
Applications of quadratic equations
Quadratic equations have various applications in different fields such as physics, engineering, finance, and computer science. Some common applications of quadratic equations are:
1. Projectile motion: Quadratic equations are used to model the trajectory of objects in projectile motion, such as a ball thrown into the air or a rocket launched into space.
2. Optimal solutions: Quadratic equations are utilized to find the optimum solutions in optimization problems, such as determining the maximum or minimum values of a function.
3. Engineering design: Quadratic equations are employed in engineering to analyze and design structures that undergo bending, such as bridges or beams.
4. Electrical circuits: Quadratic equations play a role in analyzing and solving electrical circuits, particularly in analyzing resonant frequencies or the roots of characteristic equations.
5. Financial modeling: Quadratic equations are utilized to analyze and model financial situations, such as calculating the future value of investments or solving for interest rates.
6. Computer graphics: Quadratic equations are used to create visually appealing computer graphics, particularly in animating curves or rendering three-dimensional shapes.
7. Growth and decay models: Quadratic equations are used to model exponential growth and decay in various fields, such as population growth, radioactive decay, or the spread of diseases.
8. Motion of free-falling objects: Quadratic equations are employed to model the motion of objects falling freely under the influence of gravity.
These are just a few examples of how quadratic equations are applied in real-world scenarios. The versatility of quadratic equations makes them an essential tool in various disciplines and problem-solving contexts.
Summary and conclusion
In summary, a quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree where the highest power of the variable is 2. It can be written in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants.
The general method to solve a quadratic equation is to use the quadratic formula, x = (-b ± √(b^2 – 4ac))/(2a). This formula gives the values of x where the equation is satisfied.
There are three possible scenarios for the solutions of a quadratic equation:
1. Two distinct real solutions when the discriminant (b^2 – 4ac) is positive.
2. One real solution when the discriminant is zero.
3. Two complex solutions when the discriminant is negative.
Quadratic equations have many applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, finance, and computer science. They are used to model and solve problems involving parabolas, projectile motion, object trajectories, optimization, and more.
In conclusion, quadratic equations are an important concept in mathematics with various practical applications. The quadratic formula provides a systematic way to solve such equations and find their solutions. Understanding and solving quadratic equations can be useful in solving real-world problems and advancing in many fields.
Topics related to Quadratic equation
How To Solve Quadratic Equations By Factoring – Quick & Simple! | Algebra Online Course – YouTube
How To Solve Quadratic Equations By Factoring – Quick & Simple! | Algebra Online Course – YouTube
How To Solve Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula – YouTube
How To Solve Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Math Made Easy by StudyPug! F3.0.0 – YouTube
Quadratic Equations – Basics | Don't Memorise – YouTube
Quadratic Equations – Basics | Don't Memorise – YouTube
GCSE Maths – Solving Quadratics Using the Quadratic Formula #51 – YouTube
GCSE Maths – Solving Quadratics Using the Quadratic Formula #51 – YouTube
The Maths Prof: Solve Quadratic Equations using Quadratic Formula – YouTube
The Maths Prof: Solve Quadratic Equations using Quadratic Formula – YouTube
Completing The Square Method and Solving Quadratic Equations – Algebra 2 – YouTube
Completing The Square Method and Solving Quadratic Equations – Algebra 2 – YouTube
Introduction to the quadratic equation | Quadratic equations | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
Introduction to the quadratic equation | Quadratic equations | Algebra I | Khan Academy – YouTube
How to Solve Quadratic Equations using Three Methods – When Leading Coefficient is Not One – YouTube
How to Solve Quadratic Equations using Three Methods – When Leading Coefficient is Not One – YouTube
Completing the square – YouTube
Completing the square – YouTube

Peter Scholze is a distinguished German mathematician born on December 11, 1987. Widely recognized for his profound contributions to arithmetic algebraic geometry, Scholze gained international acclaim for his work on perfectoid spaces. This innovative work has significantly impacted the field of mathematics, particularly in the study of arithmetic geometry. He is a leading figure in the mathematical community.